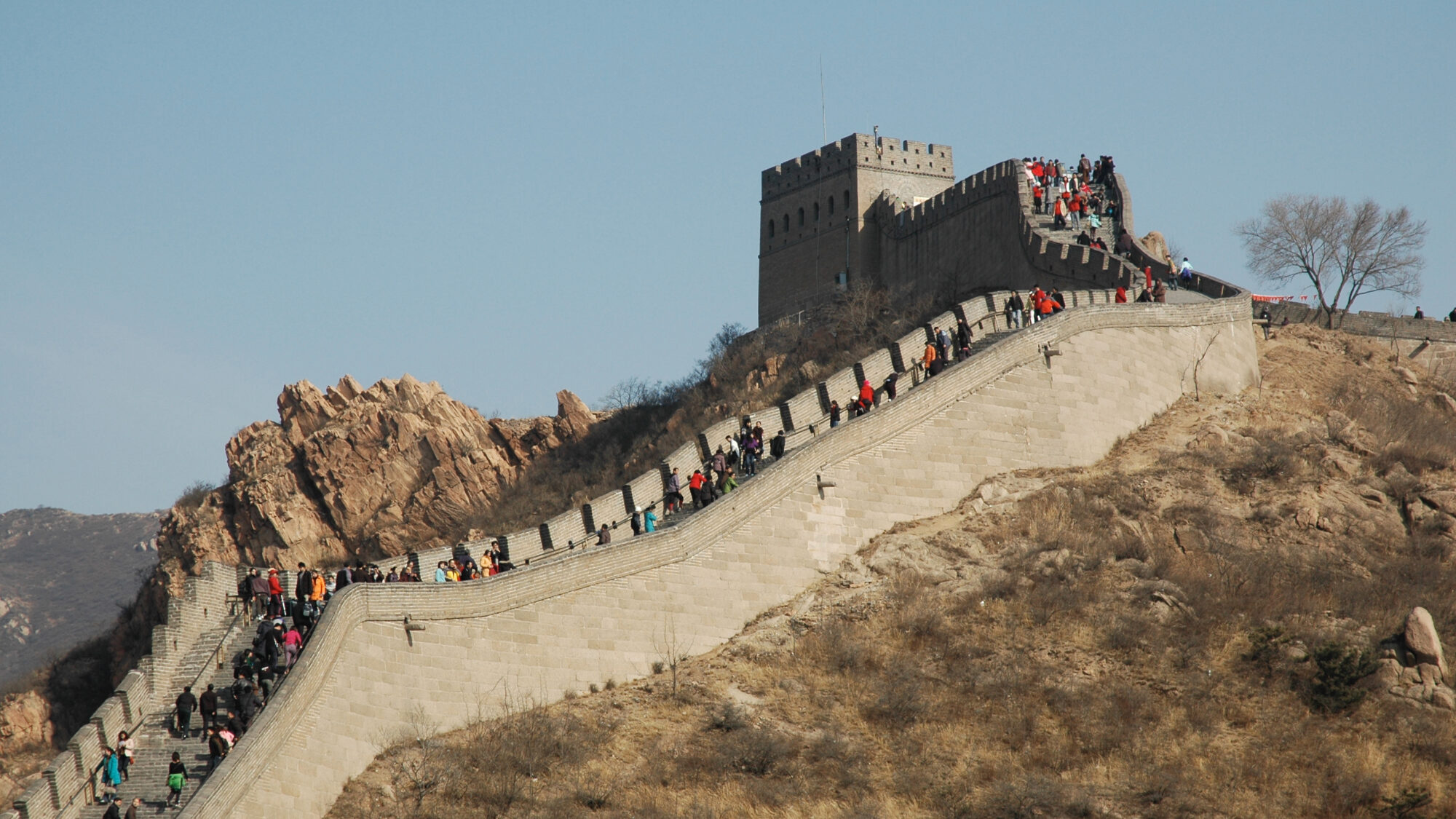
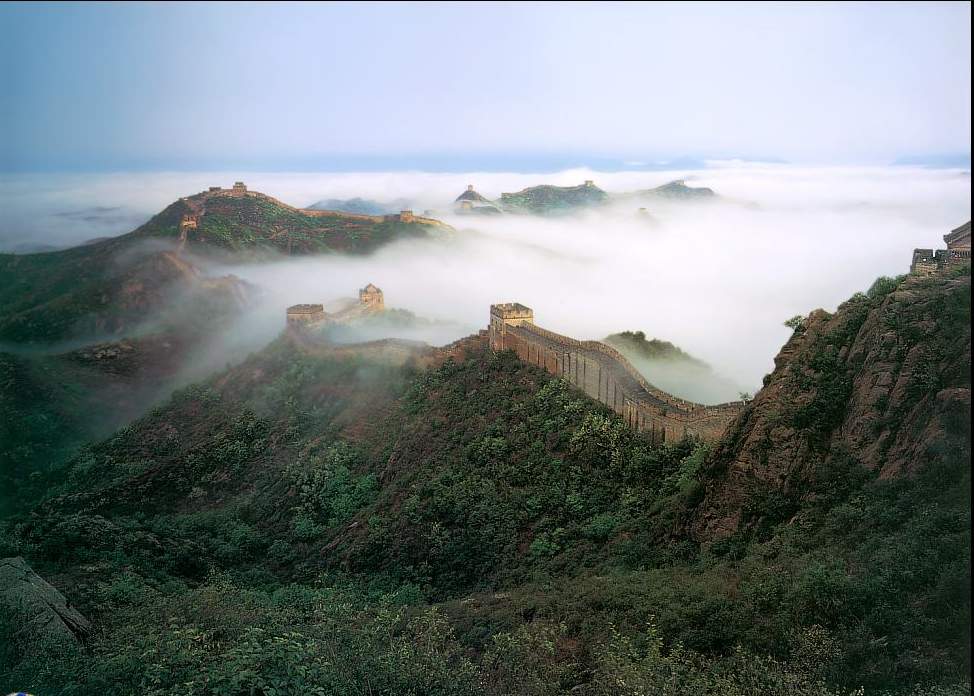
The Great Wall of China is a series of fortifications that were built, rebuilt, and maintained over the course of several centuries to protect the Chinese Empire from invasions by barbarian tribes. It stretches over 13,000 miles and is one of the most iconic symbols of China.
The Great Wall was first constructed during the Warring States period (475-221 BC), when rival states built walls to defend their borders. The first emperor of a united China, Qin Shi Huang, ordered the walls to be connected and strengthened in the 3rd century BC. The wall was then further extended and fortified during the Ming dynasty (1368-1644), when it took on much of the form that it has today.
The Great Wall is made up of a series of walls, fortresses, and watchtowers built from a variety of materials, including brick, tamped earth, and stone. It was designed to be both a physical barrier and a psychological deterrent to potential invaders. The wall was also used to control trade and immigration, as well as to maintain law and order within the empire.
Throughout its history, the Great Wall has undergone numerous repairs and renovations. In the 20th century, the Chinese government began a campaign to restore and preserve the Great Wall, which had fallen into disrepair in many places. Today, the Great Wall is a popular tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors each year.
Despite its iconic status, the Great Wall is not a single, continuous structure. Rather, it is made up of many different sections built at different times and for different purposes. Some sections are more well-preserved and popular with tourists, while others are more remote and less visited.
Despite its impressive size and history, the Great Wall was not always successful in its primary purpose of defending the Chinese Empire. It was breached by invaders on several occasions, and in some cases, the Chinese were able to repel the invaders only with the help of other defensive measures, such as floods or ambushes.
Overall, the Great Wall of China is a fascinating and complex historical monument that has played a significant role in the history and culture of China. It continues to be an important symbol of the country's past and present, and a source of pride for the Chinese people.