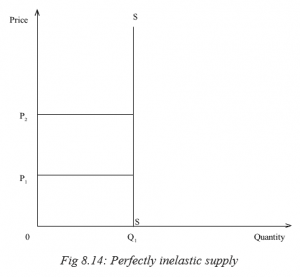
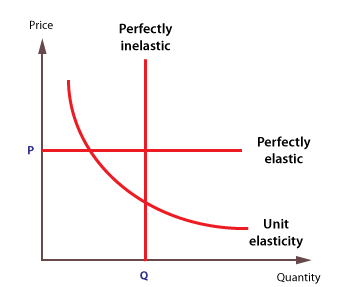
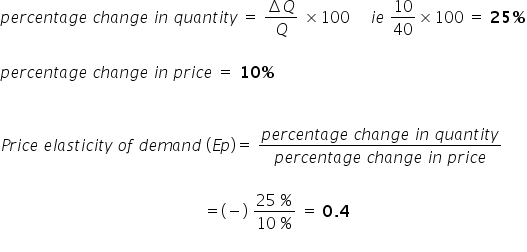An inelastic commodity is a type of good or resource whose demand does not change significantly in response to changes in price. In other words, the quantity demanded of an inelastic commodity is relatively constant, regardless of changes in its price. This can be contrasted with elastic commodities, which are goods whose demand changes significantly in response to price changes.
There are several factors that can influence the elasticity of demand for a commodity. One of the most important is the availability of substitutes. If a commodity has many substitutes, then consumers may be more likely to switch to a different good if the price of the original commodity increases. This can make the demand for the original commodity more elastic. On the other hand, if there are few substitutes for a commodity, then consumers may have little choice but to continue purchasing it, even if the price increases. This can make the demand for the commodity more inelastic.
Another factor that can affect the elasticity of demand for a commodity is the percentage of an individual's budget that is spent on the commodity. If a commodity makes up a small percentage of an individual's budget, then they may be more likely to continue purchasing it, even if the price increases. This can make the demand for the commodity more inelastic. On the other hand, if a commodity makes up a large percentage of an individual's budget, then they may be more sensitive to price changes and may reduce their consumption if the price increases. This can make the demand for the commodity more elastic.
Inelastic commodities are often essential goods, such as medicine or gasoline, that people need to purchase regardless of changes in price. For this reason, producers of inelastic commodities may have more pricing power, as they can increase prices without significantly affecting demand. However, it is important to note that all commodities have some degree of elasticity, and even inelastic commodities can experience changes in demand if the price changes enough.
In summary, an inelastic commodity is a good or resource whose demand does not change significantly in response to changes in price. This can be influenced by the availability of substitutes, the percentage of an individual's budget spent on the commodity, and other factors. Understanding the elasticity of demand for a commodity can be important for producers, as it can influence their pricing strategies and ability to increase prices.