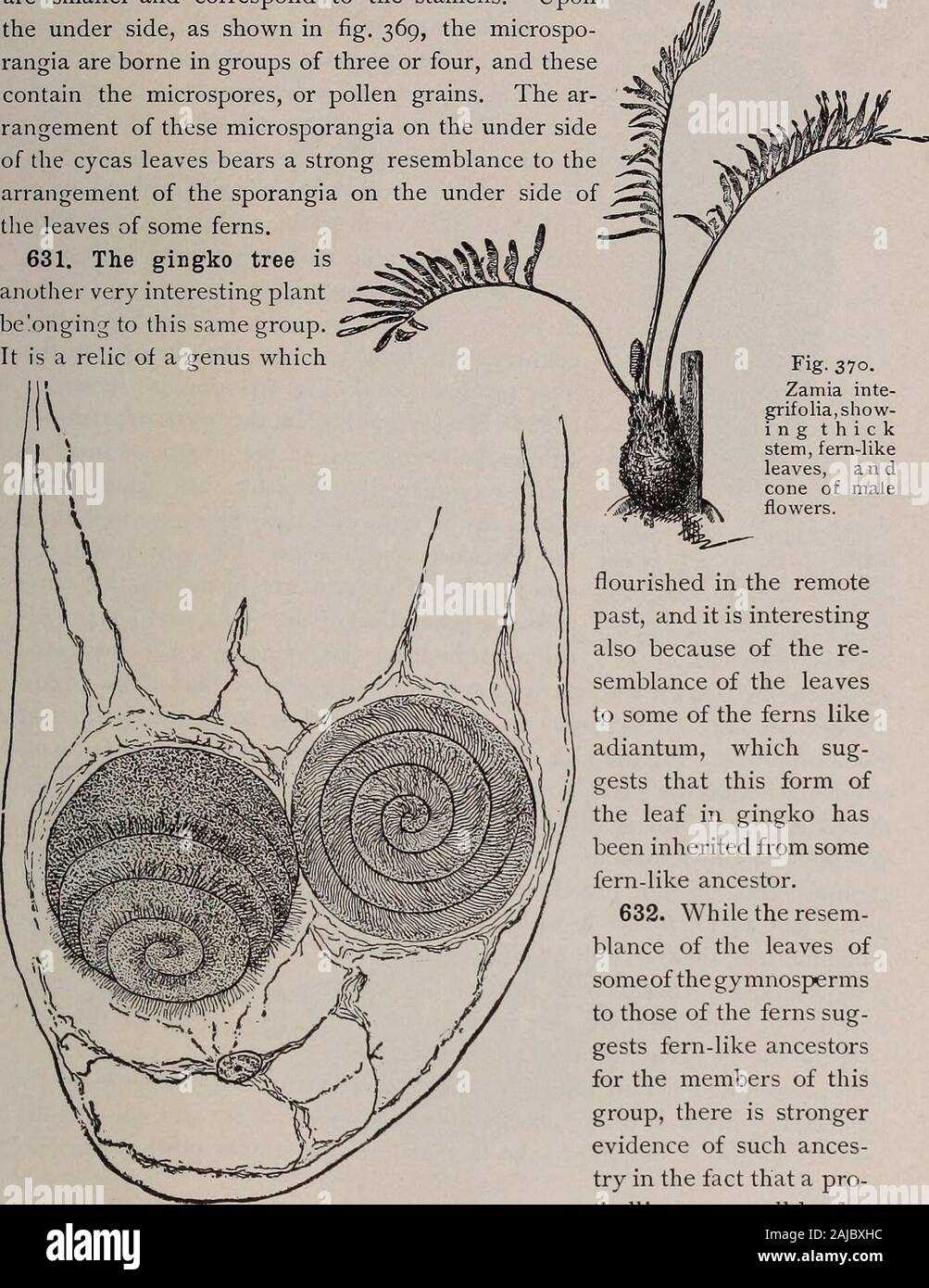
Gymnosperms are a group of plants that reproduce using seeds, but unlike angiosperms, which are the other major group of seed plants, gymnosperms do not produce flowers or fruit. Instead, they produce seeds on the surface of scales or leaves, or in cones. One of the key features of gymnosperms is the production of pollen, which is used to fertilize the female gametophytes, or ovules, and create seeds.
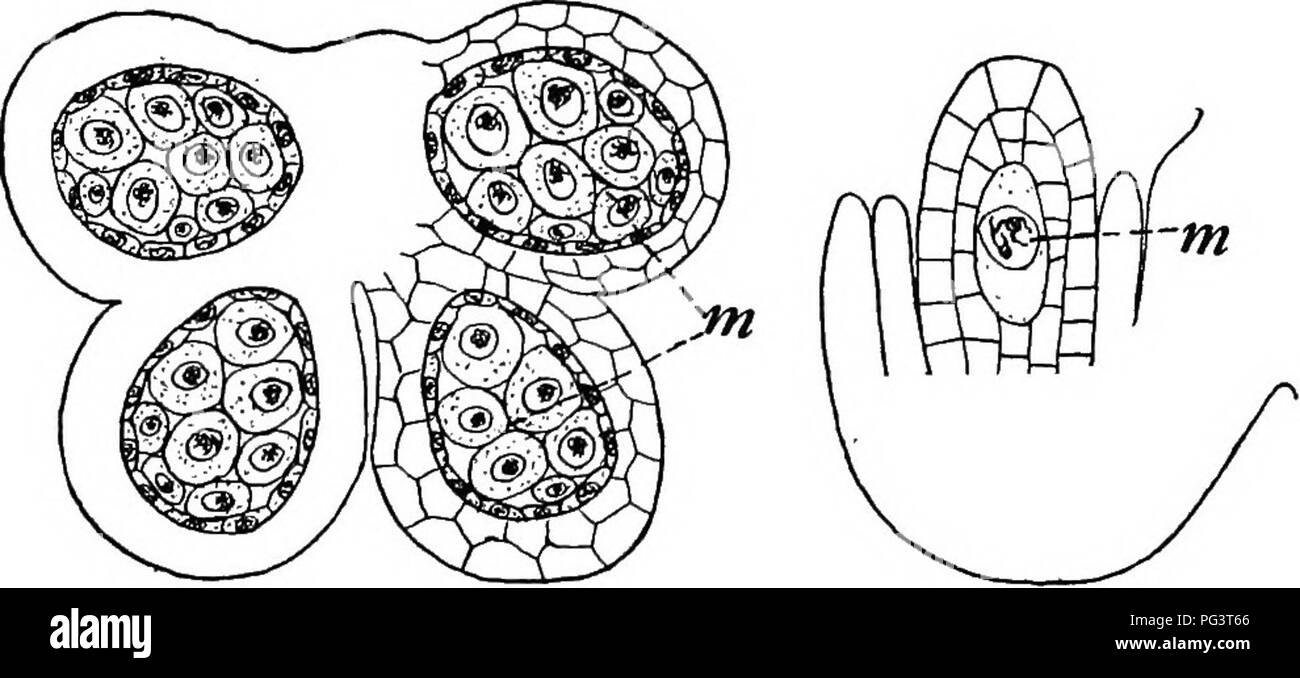
The process of pollen production in gymnosperms begins with the development of male gametophytes within the pollen sacs, which are located on the underside of the microsporophylls, or male sporophylls. The microsporophylls are modified leaves that contain microsporangia, which are structures that produce microspores. These microspores then develop into male gametophytes, or pollen grains, within the pollen sacs.
The development of the male gametophytes within the pollen sacs involves a series of cell divisions and differentiation, which results in the formation of the various structures that make up the pollen grain. The pollen grain has a protective outer wall called the exine, which is made up of a highly resistant material called sporopollenin. The exine helps to protect the pollen grain as it travels to the female gametophytes, and also helps to prevent the pollen grain from drying out.
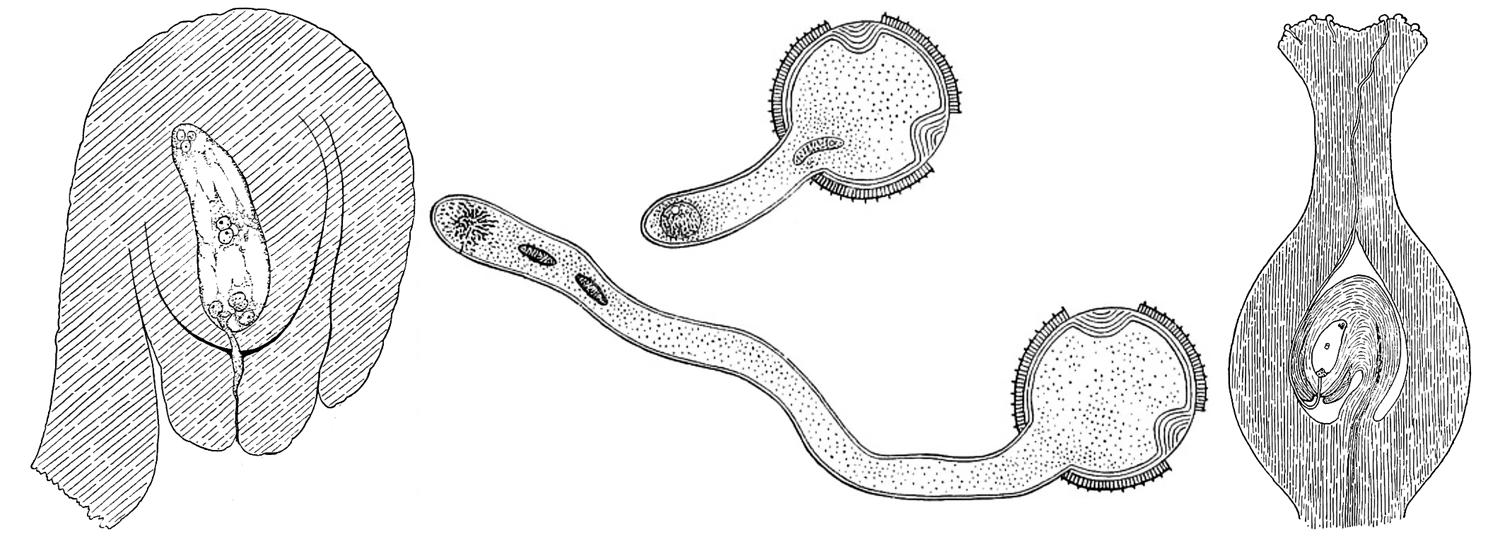
Inside the exine, there are two main cell types: the generative cell and the tube cell. The generative cell is responsible for producing the male gametes, or sperm cells, while the tube cell is responsible for growing the pollen tube, which carries the sperm cells to the ovules.
Once the pollen grains have fully developed, they are released from the pollen sacs and dispersed by wind or animals. If a pollen grain lands on a receptive female gametophyte, it will germinate and grow a pollen tube, which carries the sperm cells down to the ovules. If fertilization is successful, the fertilized ovule will develop into a seed.
In summary, the production of pollen in gymnosperms involves the development of male gametophytes within the pollen sacs, which are then released and dispersed to fertilize the female gametophytes. This process is essential for the reproduction and continuation of gymnosperm species.