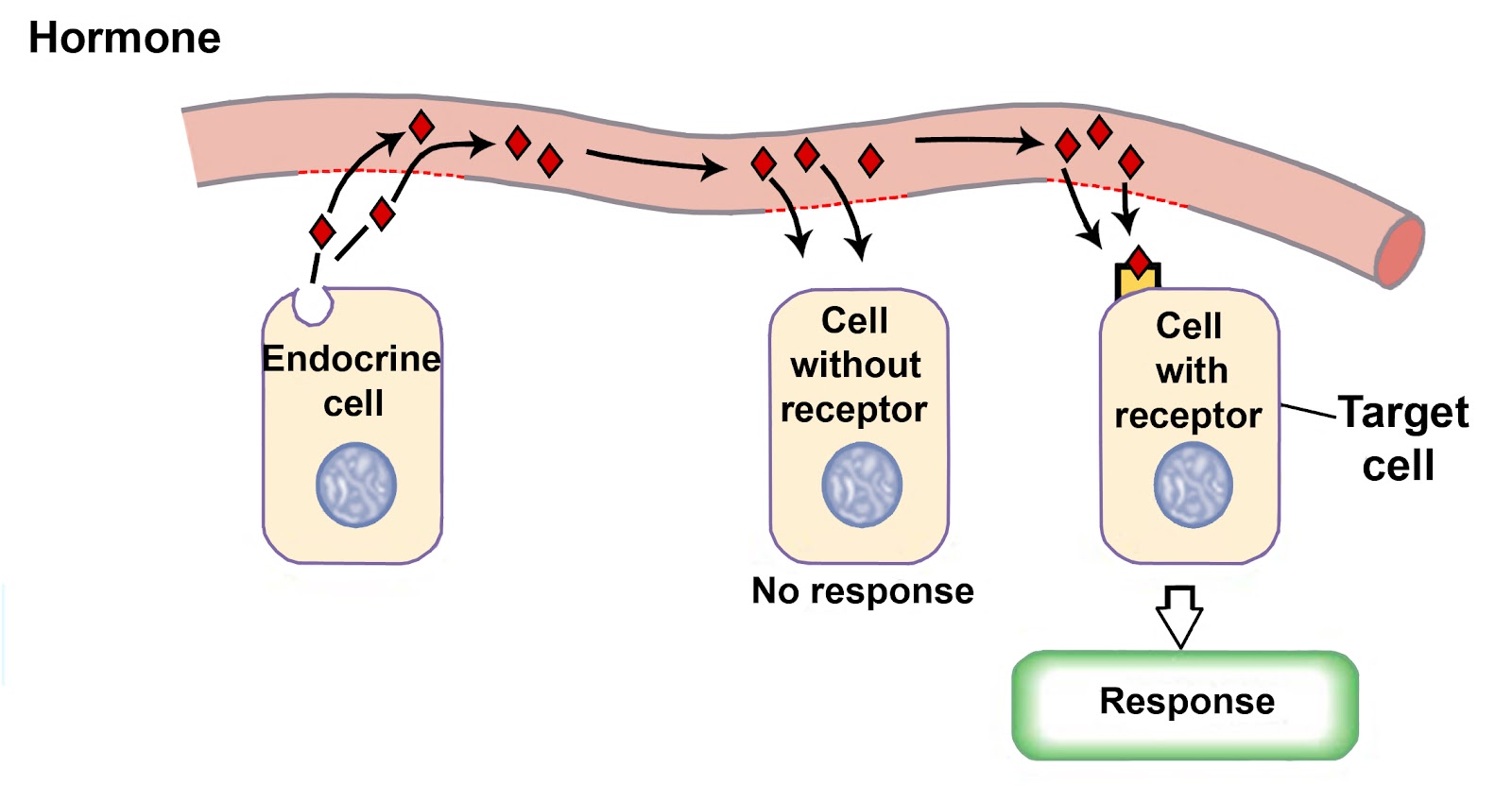
Hormones are chemical signaling molecules produced by specialized cells in the body that regulate various physiological processes. While hormones are best known for their role in regulating the endocrine systems of vertebrates, they are also present and play important roles in invertebrates, such as insects, worms, and mollusks. In this essay, we will explore the hormones of invertebrates and their functions in the body.
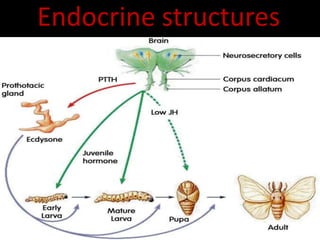
One of the main hormones in invertebrates is ecdysone, which is produced by the prothoracic gland and plays a crucial role in the molting process. Ecdysone is responsible for triggering the synthesis of enzymes that break down the cuticle, or outer layer of the exoskeleton, allowing the invertebrate to shed its old exoskeleton and grow a new one. This process occurs several times throughout the invertebrate's life cycle, and the secretion of ecdysone is regulated by other hormones, such as juvenile hormone and insulin-like peptides.
Another important hormone in invertebrates is juvenile hormone (JH), which is produced by the corpora allata, a pair of glands located in the head of insects. JH is responsible for inhibiting the development of adult characteristics and maintaining the juvenile form, allowing the invertebrate to continue growing and molting. In addition, JH plays a role in regulating the reproductive system, as it is involved in the activation of ovaries and the production of eggs in females.
In addition to ecdysone and JH, invertebrates also produce a variety of other hormones that regulate various physiological processes. For example, insulin-like peptides (ILPs) are produced by the insulin-producing cells (IPCs) and play a role in regulating metabolism and growth. In insects, ILPs have been shown to interact with ecdysone and JH, and may play a role in the molting process and the regulation of metabolism.
Another hormone that is important in invertebrates is serotonin, which is produced by the brain and is involved in the regulation of behavior and mood. In invertebrates, serotonin has been shown to play a role in learning and memory, as well as in the control of feeding and digestion.
In conclusion, hormones play important roles in the physiology of invertebrates, regulating processes such as molting, growth, and reproduction. Further research into the hormones of invertebrates may provide insight into the complex endocrine systems of these animals and could potentially lead to the development of new treatments for diseases and disorders in humans.