Functionalism is a sociological perspective that focuses on the ways in which social institutions, such as the family, contribute to the stability and cohesion of society as a whole. According to functionalist theorists, the family performs several important functions that help to maintain social order and ensure the smooth functioning of society.
One of the main functions of the family is socialization, or the process by which children learn the values, norms, and behaviors of their culture. The family is the primary agent of socialization, as it is through interactions with parents, siblings, and other family members that children learn how to behave and interact with others.
Another important function of the family is economic production and consumption. In many societies, the family serves as the basic unit of economic production, with members working together to provide for the needs of the group. In addition, the family is responsible for consuming goods and services, which helps to fuel economic growth and stability.
The family also serves as a source of social support and emotional well-being for its members. In times of crisis or stress, family members can provide emotional support and assistance to one another, helping to alleviate feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Finally, the family helps to transmit cultural values and traditions from one generation to the next. Through the transmission of cultural practices and beliefs, the family helps to preserve the continuity and stability of society.
In conclusion, functionalism emphasizes the important role that the family plays in maintaining social order and stability. By performing functions such as socialization, economic production and consumption, providing social support, and transmitting cultural values, the family helps to ensure the smooth functioning of society as a whole.
10 Functionalism Examples (in Schools, Families & Religion)

He notes that most parents take primary responsibility for their children's health - such as by teaching them hygiene and caring for and treating minor illnesses. It also teaches people about right and wrong, and how they should behave towards each other. Similarly, the practice of charity and helping the poor are institutionalized in the form of obligatory practice in many religions such as Sikhism. Therefore , Parsons' claim that Michael Anderson 1971 found that due to geographical mobility and high urban costs in industrial times, nuclear families would move in with their extended families to save costs and strengthen social ties. Other non-Functionalist sociologists have argued, however, that the existence of the Nayar, the single matrifocal families common among Afro- Caribbeans and increasingly common more generally and of gay and lesbian families all suggest that the nuclear family is not in fact universal which in turn suggests that Functionalist theories of the family focus excessively on the nuclear family form and insufficiently on other family forms.
Functionalism In Families And Societies

There has been a dramatic rise in divorce, single parent households and child poverty. First, low-income families are much more likely to experience negative events, such as death, poor health, unemployment, divorce, and criminal victimization. T he Functionalist View of Society Functionalists regard society as a system made up of different parts which depend on each other. Kinship and mode of production. They bear the primary responsibility for the education and socialization of children as well as instilling values of citizenship and belonging in the society. For example, in order to become a doctor, one must first study medicine at university. In order for this system to work effectively, there must be trust between the physician and the patient University of Minnesota, 2022.
Functionalism and the Family

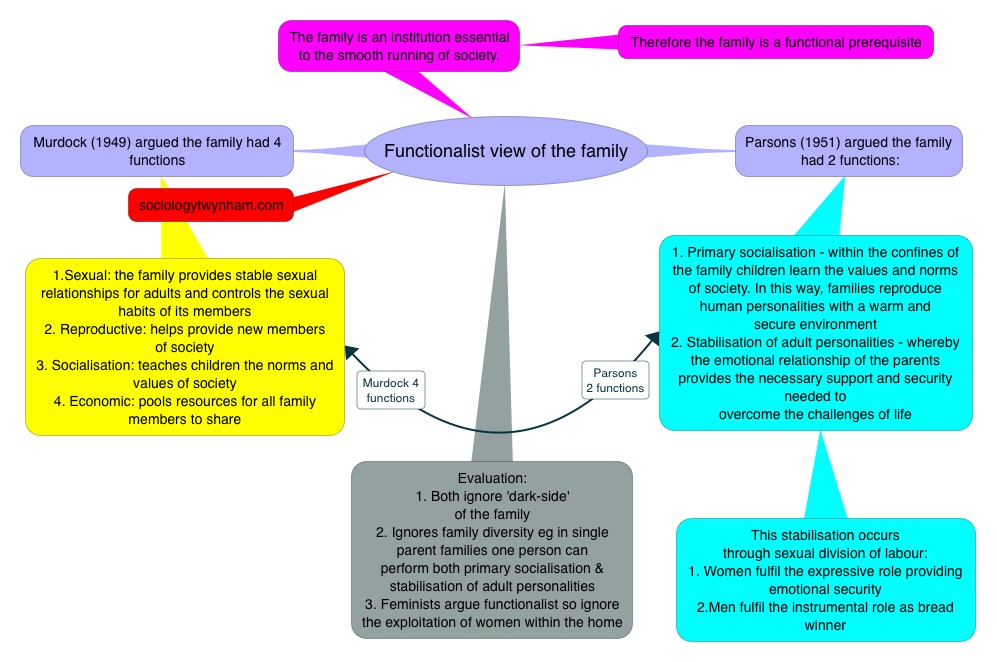
How does functionalism view family? Thus, the essence of the functionalist view of the family is that the family performs several essential functions for society. In particular, feminists argue that families exist largely for the benefit of men. Within the family unit, the children also take on important social roles. In making comparisons between small scale , pre-industrial societies and large scale industrial ones, the anthropologist Edmund Leach claims that the decline of the extended family has isolated the nuclear family and placed emotional demands upon it which are unbearable. The three main functionalist sociologists in this topic are Murdock, Parsons and Fletcher, who all have a different view towards family but main argument is the functions it provides for society.
Functionalist Perspectives on the Family: Overview

Over the last 200 years, society has moved from pre-industrial to industrial — and the main family type has changed from the extended family to the nuclear family. Further information on the continued existence of extended family ties in the late 20th and early 21st Centuries will be provided in a future document. Functionalists posit that successful societies have a stable social structure in which different institutions perform unique functions that contribute to the maintenance of all of society. The husband works outside the home while the wife does the housework and child care. Also they believe society is like the human body, that if one aspect is removed such as the family, it will not function properly or at all. For example, the parents in a family provides for the children, who will in turn care for the parents when they become elderly. For another reason that there are benefit in women, marriage is that some women probably convey their gratitude to their husbands for providing the security they and the children need, and this cements a men 's place in the world.
Free Essay: FUNCTIONALIST AND THE FAMILY
These parts make up the entirety of society and therefore, if one part changes, society is impacted. Wives and husbands have different styles of communication, and social class affects the expectations that spouses have of their marriages and of each other. Also according to Michael Anderson, extended families were common well into the mid 19 th century. Parsons' Warm Bath theory suggests that when a man comes home from a busy day of work, his family provides him with stress relief and relaxation; just as a warm bath would. Even today, women still end up being the primary child carers in 90% of families, and suffer the burden of extra work that this responsibility carries compared to their male partners. However, the emergence of factory labor shifted this dynamic, provoking families to serve complementary roles in providing support for workers. This means it sees the individual as less important as the social structure of society.