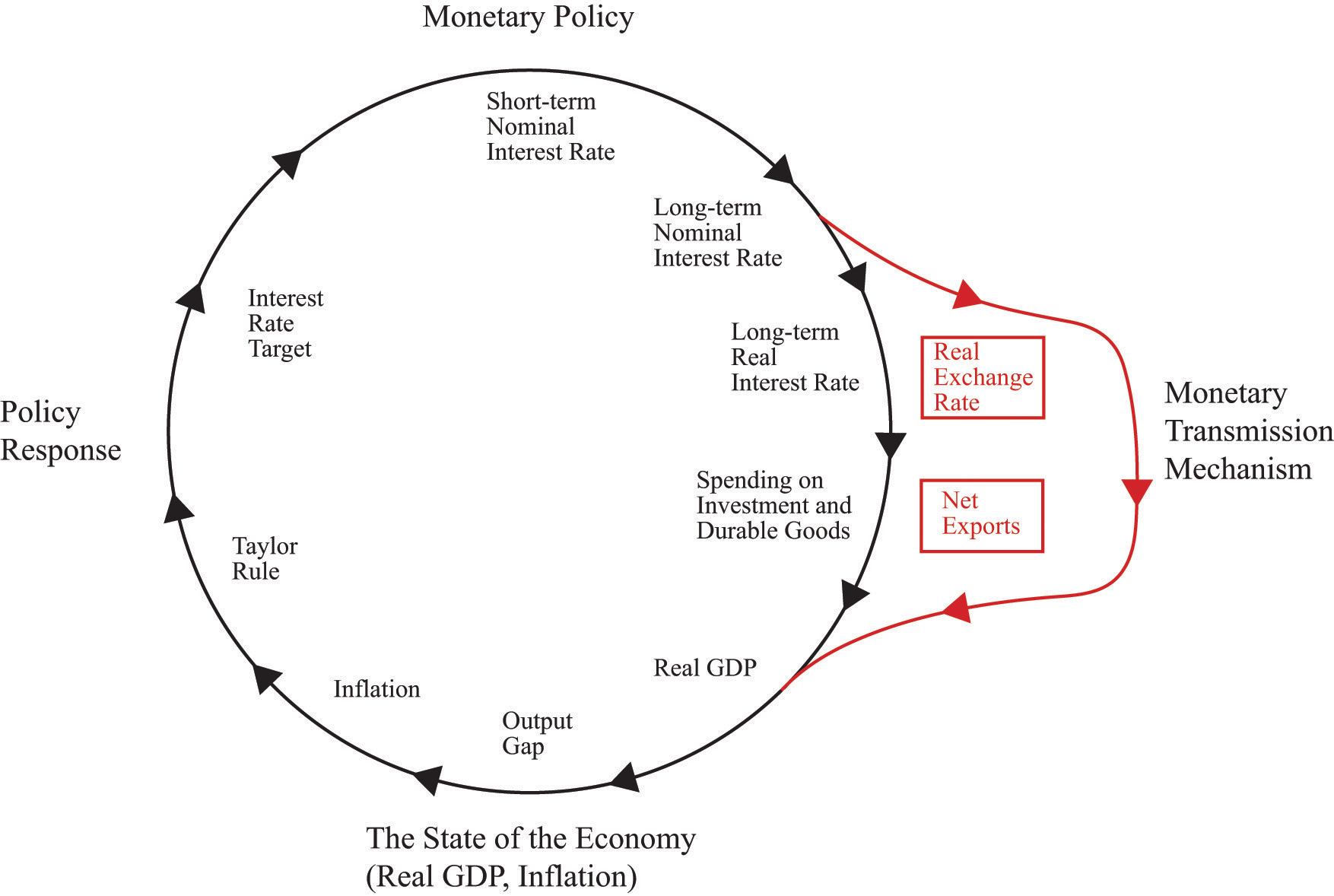
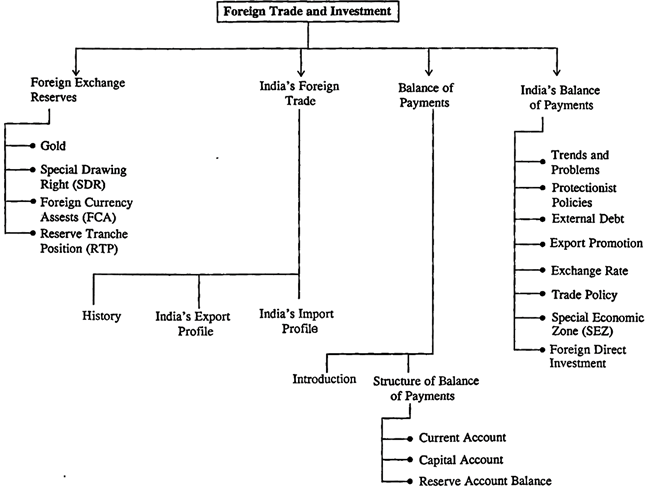
Foreign exchange rate policy in India is the policy followed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the central bank of India, in managing the exchange rate of the Indian rupee (INR) against other currencies. The exchange rate of a currency is the rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another. It is an important aspect of a country's economic policy as it affects the country's trade and financial transactions with other countries.
India follows a managed float exchange rate system, where the RBI intervenes in the foreign exchange market to manage the exchange rate of the INR. The RBI has the authority to buy or sell foreign exchange in the market to maintain the exchange rate within a certain band. The RBI also sets the daily reference rate for the INR, which is based on the market demand and supply of foreign exchange.
The RBI uses a variety of tools to manage the exchange rate of the INR, including foreign exchange reserves, open market operations, and foreign exchange market intervention. The RBI maintains a certain level of foreign exchange reserves, which it can use to buy or sell foreign exchange in the market to maintain the exchange rate. The RBI also uses open market operations, where it buys or sells government securities in the open market to influence the supply of money in the economy. This, in turn, affects the demand for foreign exchange and helps the RBI maintain the exchange rate.
The RBI also intervenes in the foreign exchange market to maintain the exchange rate. It does so by buying or selling foreign exchange in the market. The RBI may intervene in the market if it feels that the exchange rate is not in line with the country's economic fundamentals or if there is excessive volatility in the exchange rate.
The exchange rate policy in India has undergone several changes over the years. Prior to 1991, India followed a fixed exchange rate system, where the exchange rate was pegged to a particular currency or basket of currencies. However, due to the balance of payments crisis in 1991, India had to shift to a floating exchange rate system. Under this system, the exchange rate is determined by the market demand and supply of foreign exchange.
In recent years, the exchange rate policy in India has been aimed at maintaining the stability of the INR. The RBI has been trying to maintain a balance between the demand for and supply of foreign exchange in the market to keep the exchange rate within a certain band. The RBI has also been trying to reduce the volatility in the exchange rate to ensure that it does not adversely affect the country's trade and financial transactions with other countries.
In conclusion, foreign exchange rate policy in India is an important aspect of the country's economic policy. It is managed by the RBI, which uses a variety of tools to maintain the exchange rate within a certain band and reduce the volatility in the exchange rate. The exchange rate policy in India has undergone several changes over the years, with the current focus being on maintaining the stability of the INR.