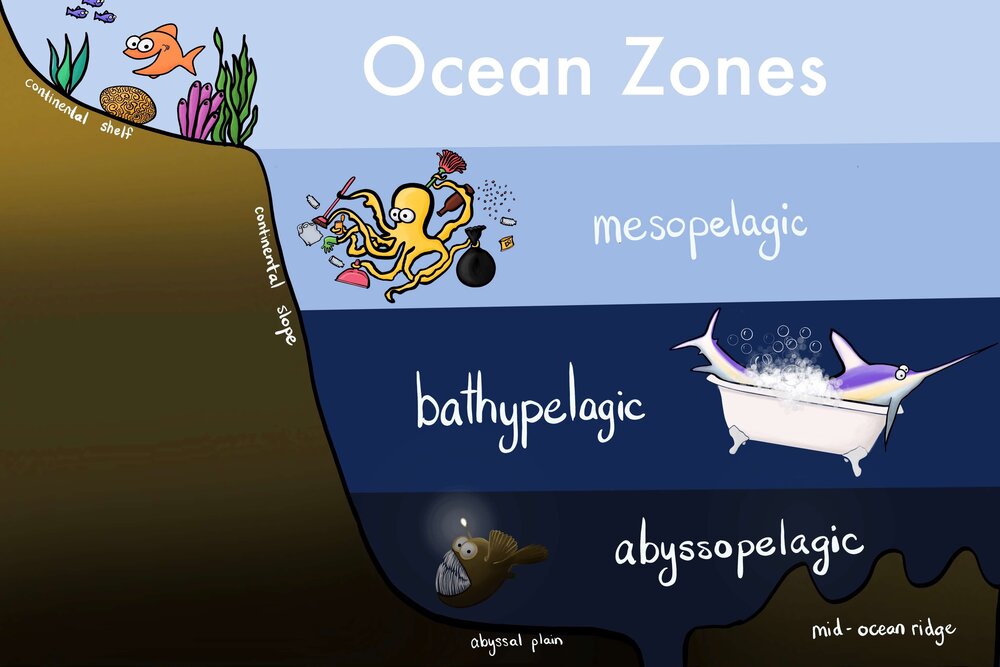
The abyssal zone, also known as the abyssopelagic zone, is the deepest part of the ocean, typically found at depths of 4,000 meters (13,123 feet) or more. It is a harsh and inhospitable environment, with high pressure, extreme cold, and complete darkness. Despite these challenges, a number of fish species have adapted to thrive in the abyssal zone.
One of the most well-known fish species that inhabit the abyssal zone is the lanternfish. These small, slender fish are found in great numbers throughout the abyssal zone, and are an important food source for larger predatory species. Lanternfish are adapted to life in the deep ocean, with large eyes to help them see in the darkness and bioluminescent organs that they use to communicate and attract mates.
Another common fish species found in the abyssal zone is the snailfish. These small, translucent fish are well-suited to life in the deep sea, with a slimy, gelatinous body that allows them to move easily through the water and a high tolerance for the extreme pressures found at these depths. Snailfish are often found in large schools, and are an important part of the food chain in the abyssal zone.
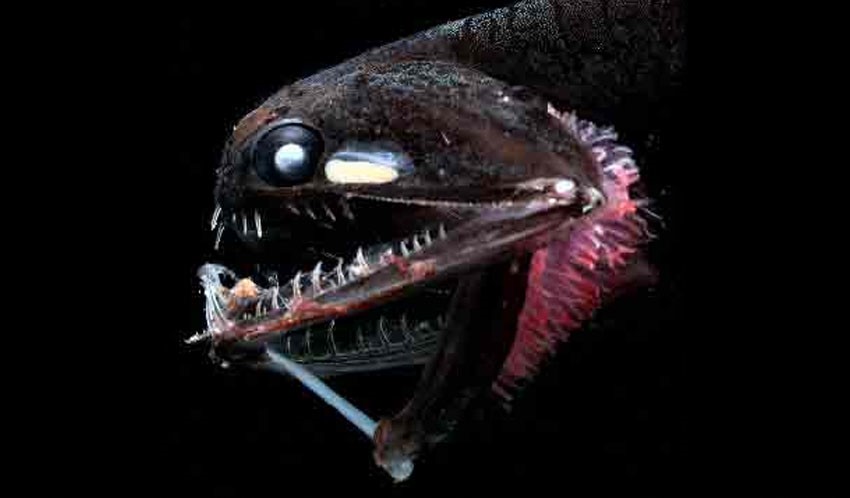
In addition to lanternfish and snailfish, a number of other fish species can be found in the abyssal zone, including the deep-sea eel, the fangtooth, and the viperfish. These species are all adapted to life in the deep ocean, with specialized physical characteristics that allow them to survive in this harsh environment.
Despite the challenges posed by the abyssal zone, these fish species have found ways to thrive in this extreme environment. Their ability to adapt and survive in the depths of the ocean is a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of life on our planet.
What lives in the abyssal zone?
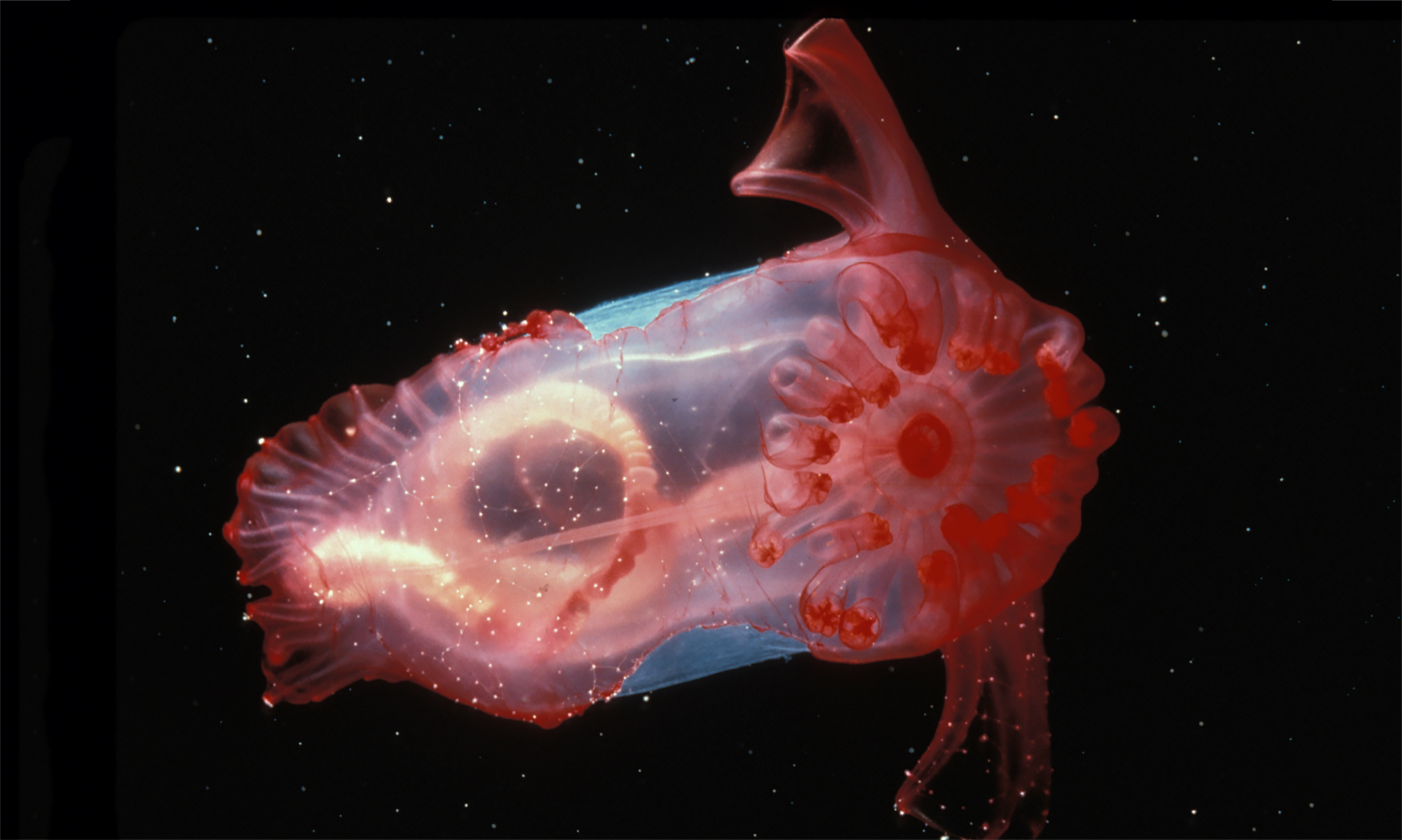
The bacteria actually convert the chemicals from the hydrothermal vents into organic molecules that provide food for the worm. Most animals cope with this by being very small and needing less to eat or by growing very slowly. These survive on organic matter, and provide a much needed food source for many of the other creatures that call the zone their home. Last update:28 May, 2021 Abyssal fish have developed different adaptations over time to take advantage of the limited resources available to them. The development of the mouth and stomach allows them to feed on larger prey. Roughly speaking, the deepest point is around 20,000 feet deep, which is roughly the size of 20 Empire State Buildings stacked end to end. This zone covers approx 300,000,000 square km that is 115,000,000 square miles.
Weird Creatures in Abyssal Zone

What animals live at the bottom of the sea? This includes deep seas, extreme water temperatures between 0º-4ºC, high concentration of nutritional salts, as well as a significant increase in pressure and lack of oxygen. This zone extends from 700 feet down to about 3,280 feet. The Bathyal zone is 1000 — 4000 meters below the surface of the ocean. Sediments of certain abyssal plains contain abundant mineral resources, notably polymetallic nodules. Did you know that abyssal fish have much more interesting characteristics than just their strange shapes? Telescope Octopus: The telescope octopus is a species of pelagic octopus found in tropical and subtropical regions of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. They can rise above the water layer closest to the bottom, where oxygen is scarce.
Abyssal fish, incredible sea creatures
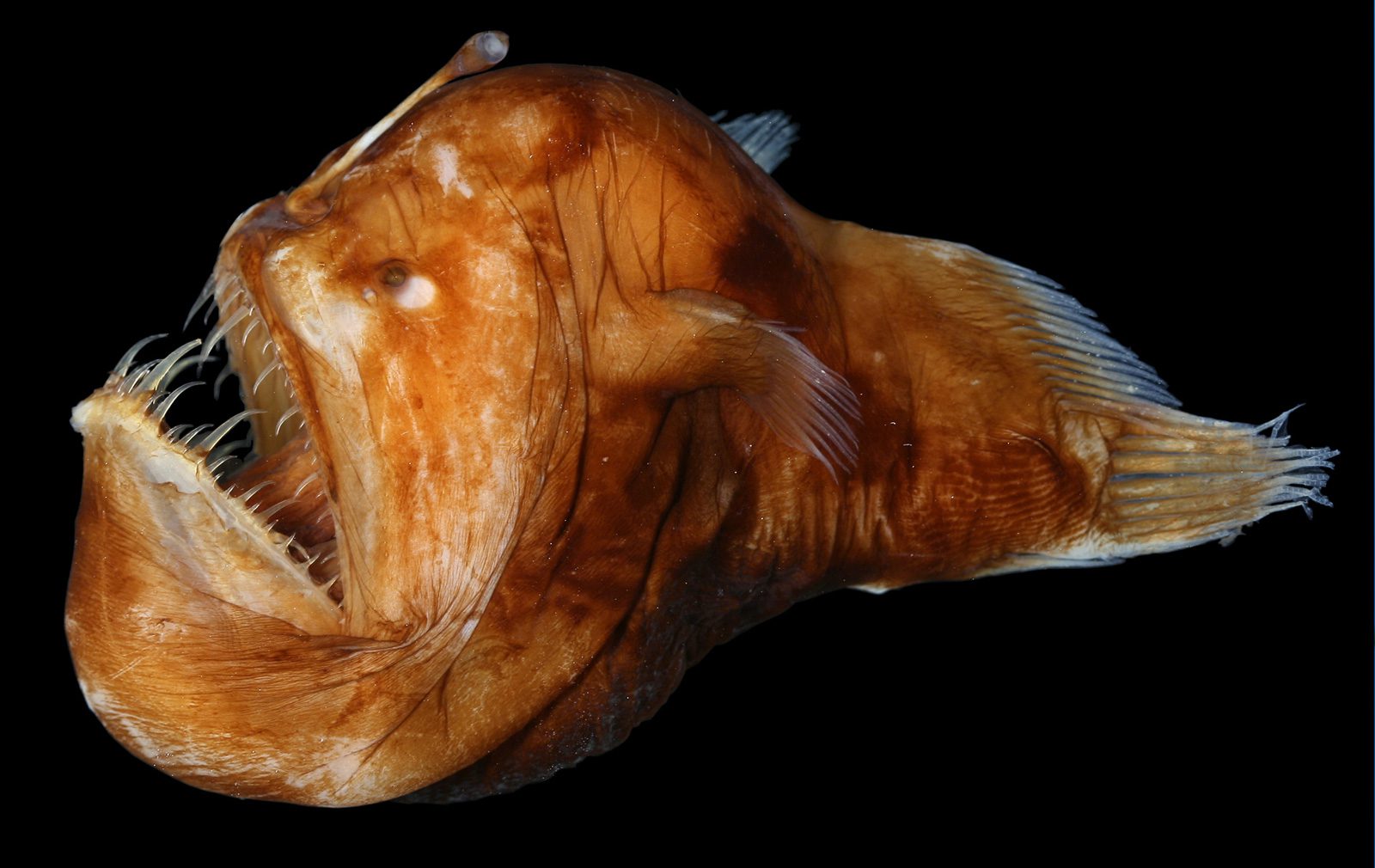

What ocean zone do whales live in? The abyssal zone is surprisingly made up of many different types of organisms, including microorganisms, crustaceans, molluscan bivalves, snails, and cephalopods , different classes of fishes, and a number of others that might not have even been discovered yet. In comparison to continental shelves, the deep sea is also very sparsely populated, owing to the scarcity of food. There are about 28,000 species of fish around the world. They are frequently distinguished by their colossal size and enormous variability in appearance. However, there may be some undiscovered animals. Anglerfish Perhaps the most terrifying species residing in the abyssal zone is the anglerfish. As organisms living in these upper layers die, their remains drift toward the ocean floor like soft snow.
What fish live in the abyssal zone?

The viperfish, for example, has a hinged skull that can rotate upwards so it can eat large fish, as well as a large stomach to store plenty of food and a set of fangs that look ferocious to chomp down on its prey. How do animals survive in the abyssal zone? And yet it is the area that we least know. A striking detail of all the species that make up the abyssal fauna is that they are clearly carnivorous. Hagfish, for example, can go as long as seven months without eating because their metabolism is so slow. Where are abyssal plains most likely to be found? Echinoids are sea urchins — in their many species — and while often confused for plantlife, they are sentient, living creatures capable of feeding and moving, the latter of which is done by moving their tube feet — similar to the starfish. It is a slow drift of mucus, fecal pellets, and body parts that sinks down from the surface waters. This zone remains in perpetual darkness at depths of 4,000 to 6,000 meters 13,300 to 20,000 feet.