Fiscal deficit and inflation are two important economic concepts that are closely related to each other and have significant impacts on a country's economy.
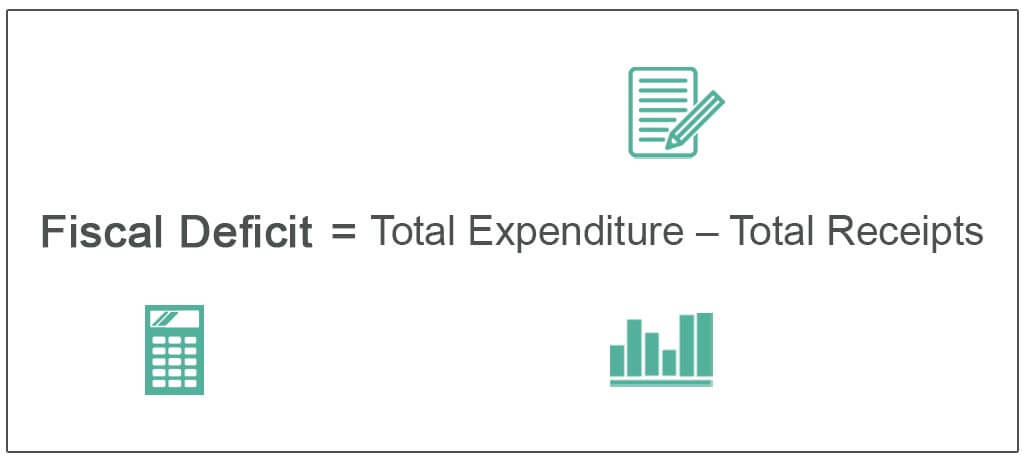
Fiscal deficit refers to the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue. When the government spends more money than it earns, it results in a fiscal deficit. This deficit can be financed by borrowing money from external sources or by printing more money.
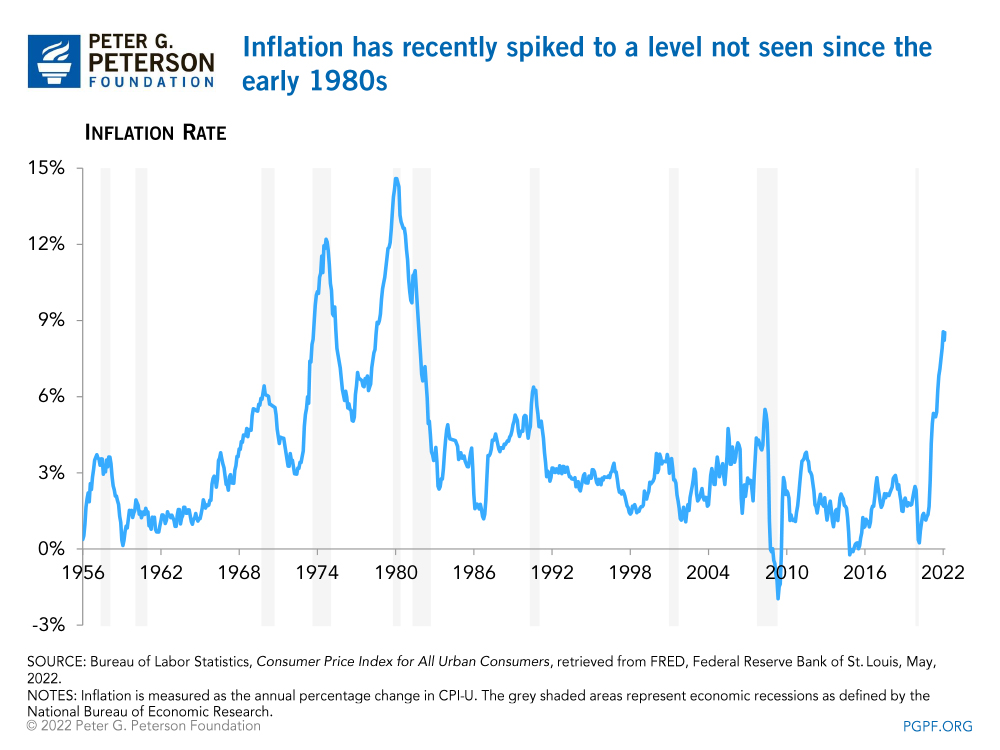
Inflation, on the other hand, is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. It is measured by the percentage change in the price index, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI). Inflation can be caused by various factors, including an increase in the demand for goods and services, a decrease in the supply of money, and an increase in production costs.
One of the ways in which fiscal deficit can lead to inflation is through the financing of the deficit. If the government borrows money to finance its deficit, it can lead to an increase in the demand for credit, which can push up interest rates. Higher interest rates can discourage borrowing and investment, leading to a slowdown in economic activity. On the other hand, if the government prints more money to finance its deficit, it can lead to an increase in the supply of money, which can lead to an increase in demand for goods and services. This can result in higher prices, leading to inflation.
Another way in which fiscal deficit can contribute to inflation is through government spending. If the government increases its spending, it can lead to an increase in demand for goods and services, which can drive up prices. This can be particularly true if the increase in government spending is not matched by an increase in the supply of goods and services.
It is important to note that fiscal deficit and inflation are not necessarily always linked. In some cases, a fiscal deficit can lead to deflation, which is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. This can occur if the increase in government spending is accompanied by an increase in the supply of goods and services, or if the increase in government spending is offset by a decrease in private sector spending.
In conclusion, fiscal deficit and inflation are two important economic concepts that are closely related to each other. A fiscal deficit can lead to inflation through the financing of the deficit and through government spending, but this is not always the case. It is important for governments to carefully manage their fiscal deficit and inflation to ensure stability and growth in the economy.