The circular flow of the economy is a model that describes the movement of goods, services, and money between different parts of the economy. It is called a "circular" flow because the movement of these economic elements is continuous and ongoing.
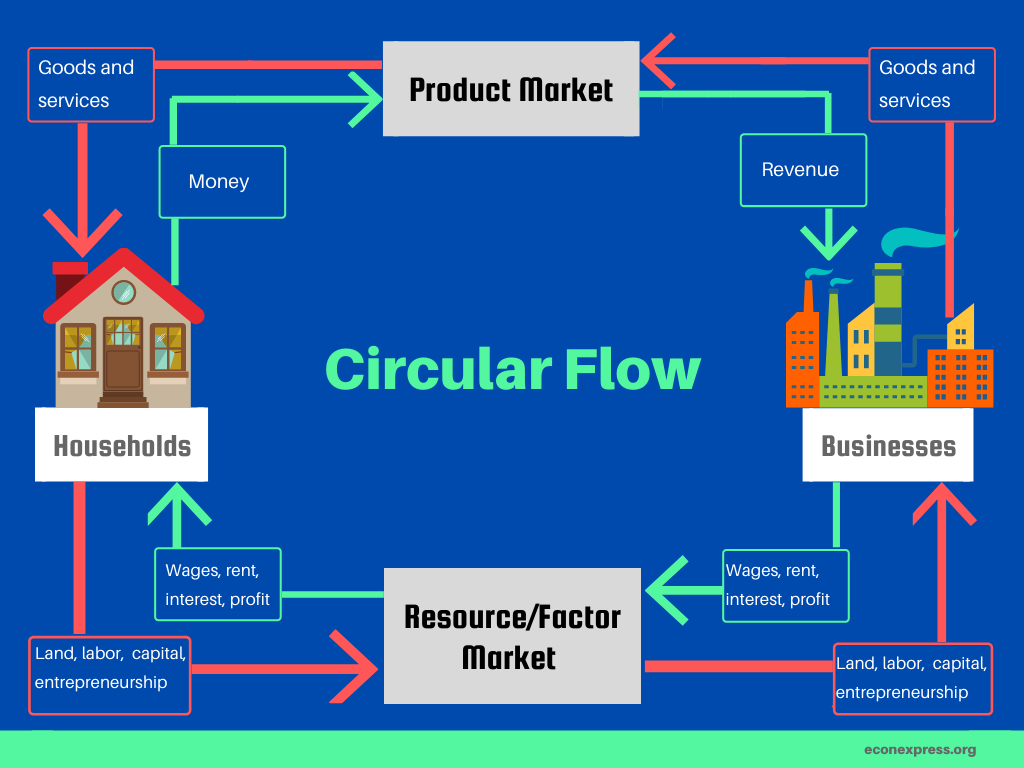
In the circular flow model, there are two main parts: households and firms. Households are the consumers in the economy and firms are the producers. These two groups are connected by two types of flows: the flow of goods and services and the flow of money.
The flow of goods and services begins when households buy goods and services from firms. This flow is represented by the arrows in the model that point from households to firms. As households buy goods and services, firms receive money from the households in exchange. This flow of money is represented by the arrows that point from firms to households.
The flow of money then returns to the firms as they use it to pay for the factors of production, such as labor and raw materials, needed to produce the goods and services that they sell to households. This flow is represented by the arrows that point from households back to firms.
The circular flow of the economy is an important concept because it helps to explain how the different parts of the economy are connected and how they interact with each other. It shows how the actions of households and firms influence each other and how the economy as a whole functions.
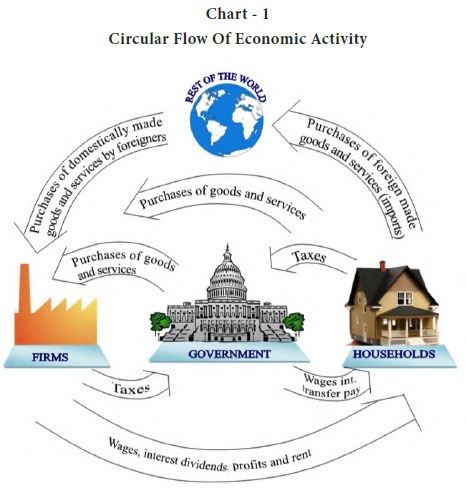
There are also two other components in the circular flow model: the government and foreign sectors. The government sector includes all levels of government, from local to federal, and the foreign sector includes all economic interactions with other countries. These sectors interact with the households and firms in the economy through taxes, subsidies, and trade.
In conclusion, the circular flow of the economy is a model that explains the movement of goods, services, and money between households and firms. It shows how the actions of these two groups influence each other and how the economy as a whole functions. Understanding the circular flow of the economy is essential for understanding how the economy works and how it can be improved.
Explain the circular flow of income in an open economy?
Imports, on the other side, are leaks in the circular flow. ADVERTISEMENTS: The model depicts circular flow in two-sector simple economy, where household sector earns Rs. These days financial markets around the world have become well integrated. This results in a circular income flow. The price of a haircut, chicken sandwich, car, video game, streaming service, etc. Savings can either be hoarded or loaned out to others. For a macro-level understanding, the two-sector model is not sufficient as many complex factors are not considered to explain the flow of income and expenditure.
Circular Flow Model in Economics: Definition & Examples

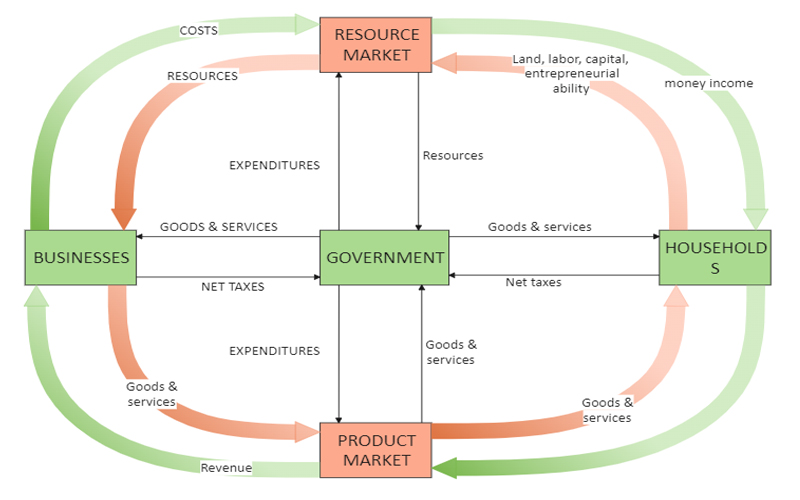
~ These comprise of households, business firms, financial sector, government sector and foreign sector. These public expenditure decisions are injections into the cycle. The government finances its deficit by borrowing from the capital market which receives funds from the household sector in the form of saving. Circular Flow of Income in 2 Sector Economy Like we said before, the two-sector economy is a fundamental model consisting of only two sectors, firms, and households. More expenditure means more income and greater production. Since all the value produced must belong to someone in the form of a claim on the value, national product is equal to national income. Two Sectoral Economy or Simple Economy assumes only two sectors: Household and Firms.
Circular Flow of Income: 2 Sector, 3 Sector and 4 Sector Economy
Payments Foreign sectors need to make payment to the business sector from where imports have been made. Image 15-1 In the diagram, there are two primary actors in the economy — households and businesses. Their ultimate aim is to satisfy the wants of their members with their limited budgets. ADVERTISEMENTS: Similarly, the government receives payments from foreigners when they visit the country as tourists and for receiving education, etc. ADVERTISEMENTS: Let us make in-depth study of the circular flow of income in two sector, three sector and four sector economy. In year of depression, the circular flow of money income will contract, i.
Circular Flow of Income and Expenditure
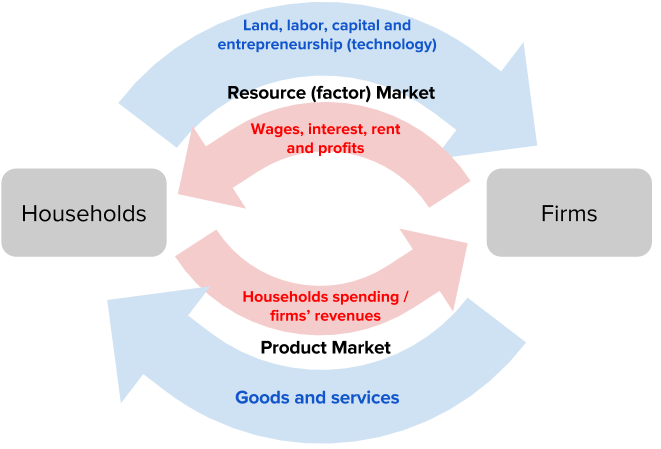
It is often represented with a circular flow model like the one seen in Image 15-1. As such, the role of government cannot be ignored in any economy because of such a huge control it possesses over the economic cycle. Let us understand these different circular sectors in detail. But the government purchases the services of the households, makes transfer payments in the form of old age pensions, unemployment relief, sickness benefit, etc. Business produces goods utilizing the resources provided by the households, which are then sold in the product market. Government expenditure G , which provides public services and welfare payments to the community, on the other hand, is the injection into the circular flow.