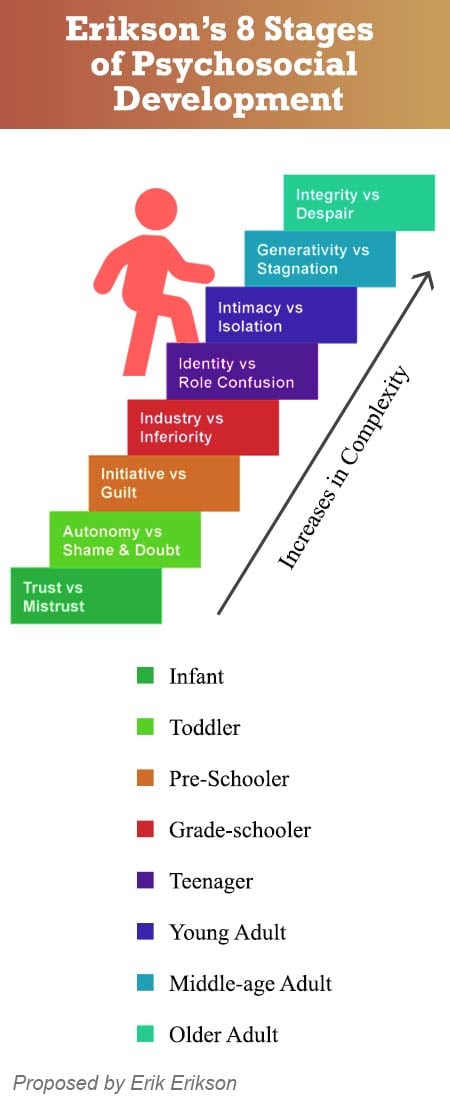
Erikson's stages of development, also known as Erikson's psychosocial stages, were proposed by psychoanalyst Erik Erikson in the 1950s. Erikson believed that each person goes through a series of eight stages over the course of their lifetime, each of which involves a different psychological conflict. These conflicts are resolved through a process of "psychosocial moratorium," or a temporary suspension of one's identity, which allows for the exploration and resolution of the conflict.
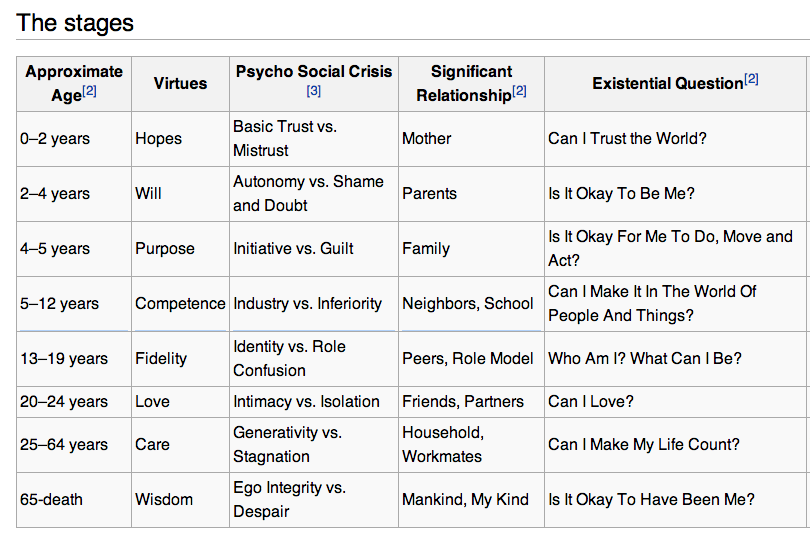
The first stage is the "Trust vs. Mistrust" stage, which occurs in infancy and early childhood. During this stage, children develop a sense of trust in the world and in the people around them, or they may develop a sense of mistrust if their basic needs are not met.
The second stage is the "Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt" stage, which occurs during early childhood. During this stage, children develop a sense of independence and control over their own bodies, or they may feel shame and doubt about their abilities.
The third stage is the "Initiative vs. Guilt" stage, which occurs during play age. During this stage, children develop a sense of initiative and purpose, or they may feel guilty for their actions.
The fourth stage is the "Industry vs. Inferiority" stage, which occurs during school age. During this stage, children develop a sense of competence and the ability to contribute to the world, or they may feel inferior to their peers.
The fifth stage is the "Identity vs. Role Confusion" stage, which occurs during adolescence. During this stage, adolescents develop a sense of their own identity and the roles they will play in society, or they may feel confused about their place in the world.
The sixth stage is the "Intimacy vs. Isolation" stage, which occurs during young adulthood. During this stage, young adults develop close relationships with others and a sense of intimacy, or they may feel isolated and alone.
The seventh stage is the "Generativity vs. Stagnation" stage, which occurs during middle adulthood. During this stage, individuals develop a sense of caring for and contributing to the next generation, or they may feel stagnant and unfulfilled.
The eighth and final stage is the "Ego Integrity vs. Despair" stage, which occurs during late adulthood. During this stage, individuals reflect on their lives and either feel a sense of ego integrity and contentment, or they may feel despair about their accomplishments and the meaning of their lives.
Erikson's stages of development provide a framework for understanding the psychological conflicts that people encounter at different points in their lives. Understanding these stages can help individuals identify their own challenges and seek out ways to resolve them. It is important to note that not everyone experiences each stage in the same way and that individuals may revisit and revisit different stages throughout their lives.