Effects of the structural adjustment program. The Effects of the Structural Adjustment Programs on Economic Growth … 2022-10-22
Effects of the structural adjustment program
Rating:
5,1/10
1273
reviews
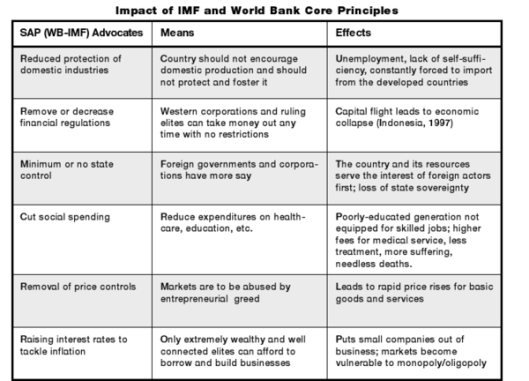
Structural adjustment programs (SAPs) are economic reform packages implemented by countries in response to financial crises or as a condition for receiving financial assistance from international organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) or World Bank. These programs are designed to address macroeconomic imbalances and improve the competitiveness of a country's economy by implementing a range of structural and policy reforms.
The effects of structural adjustment programs can be complex and varied, and the outcomes of these programs depend on a number of factors, including the specific measures included in the program, the broader economic and political context in which the program is implemented, and the effectiveness of the program in addressing the underlying causes of the economic crisis.
One of the key aims of structural adjustment programs is to reduce the size of the government budget deficit and improve the balance of payments position of the country. This is often achieved through measures such as reducing government spending, increasing taxes, and liberalizing trade and capital markets. These measures can help to reduce the demand for imported goods, which can help to improve the balance of payments position of the country. However, these measures can also have negative effects, such as reducing the availability of social services and increasing the burden of taxes on low-income households.
Structural adjustment programs can also have an impact on the structure of the economy, including the industrial base and the distribution of income. For example, liberalizing trade and capital markets can lead to an increase in exports and foreign investment, which can help to stimulate economic growth and create new job opportunities. However, these measures can also lead to the decline of certain sectors of the economy and an increase in income inequality as some sectors of the economy benefit more from these changes than others.
Another potential effect of structural adjustment programs is their impact on social welfare. Reducing government spending on social services such as education, health care, and social protection can lead to a decline in the living standards of the most vulnerable members of society. This can have negative long-term effects on the overall welfare of the population, as access to education and health care are important determinants of human development.
Overall, the effects of structural adjustment programs can be complex and varied, and the outcomes of these programs depend on a range of factors. While these programs can help to address macroeconomic imbalances and improve the competitiveness of an economy, they can also have negative impacts on social welfare and the distribution of income. It is important for countries implementing structural adjustment programs to carefully consider the potential impacts of these measures and to take steps to mitigate any negative effects on the most vulnerable members of society.
The Effects of the Structural Adjustment Programs on Economic Growth …

H Industrial roundwood production national level, 000 CUM. The main proximate direct causes of forest loss, include fire, mining, quarry-ing, plantation strategy, but more importantly log-ging and farming ITTO 1993. Moreover the public was encouraged to take part in construction of clinics, hospitals and medical training. The Structural Adjustment Programs was a financing mechanism of the international monetary fund to support macroeconomic policies and reforms in low-income countries through low interest subsidizations and loans. Health services were improved with an increase of hospitals leading to an increase of life expectancy from 44 years at independence to 68 years in the 1980s whereas infant mortality had dropped significantly from about 220 deaths per 1000 new born to 70 per 1000 new born. To mitigate such ef-fect, the cost of logging, in one or the other must beincreased.
Next
The Effects of Structural Adjustment Programs

Cocoa land expansion in Ghana in that period wasmore influenced by factors other than the producerprice of cocoa. This led to reductions in the fiscal deficit and balance of payments deficit to a certain extent, but also resulted in increasing poverty. Why is structural adjustment so bad for Africa? Changes in the relative output and input prices due to the SAP may have played a significant role in the reduced impact of agricultural and timber related deforestation in the post-adjustment period. B ogo~ Center for International Forestry Research CIFOR. Consequently, it can be deduced that the first decade after Kenya gained independence was a period of high aspirations and economic prosperity Swamy 1994. However, despite the implementation of these programs, economic growth in SSA has been disappointing, and SAP programs earned a negative reputation because of these failures. Al-though all subsidies on inputs were removed in thepost-adjustment period, because of expected in-creases in the producer price of cocoa, farmersfound it relatively cheaper to rehabilitate existingfarms by using insecticides rather than opening upnew lands.
Next
(DOC) Impacts of STRUCTURAL ADJUSTMENT PROGRAM

This result indicates that if timber extrac-tion is inefficient, price increases which may leadto increased timber extraction may lead to in-creased forest loss in Ghana. The control variables in the modelare Xc, Xm, Xfi, t, and i? Themodel is comprised of a three-sector approach toforest land use in Ghana. This was as a result of the high prices of primary commodities that Kenya exported for example tea and coffee, therefore the country acquired a huge sum of foreign exchange which it reserved and thus could afford to deal any instability in the economy. The first equation is a function of the last three, and the last three are functions of mainly prices. Ifthe price of maize increases in the previous year,farmers expect it to stay the same or even rise inthe current year, and they therefore modify theirdemand for all inputs, including maize land, inorder to increase production. Journal of Social Development in Africa, 17 1 , 81-98.
Next
What are the impacts of structural adjustment program?

The State of the Ghanaian Economy in 1996. Logging also makes the forest more susceptible tofire, and accessible to farmers Hawthorne 1989;Martin 1991. However, the impact on forest loss in the post-adjustment period was reduced. Estimation Procedure and Discussion ofEmpirical Analysis The hypothesized relationship between deforesta-tion in Ghana and its proximate and underlyingcauses is examined through estimating for the196595 period a modified form of equations 25 - 28 above. These results reflect the importance of maize as afood crop in Ghana.
Next
What are the effects of structural adjustment?

Average price of exported industrial roundwood data from FPIB and TEDB. Therefore, the components Structural Adjustment Programs as advocated by the IMF and the World Bank include: the devaluation of local currency, balance of payments management, government reduction of social services through cutting of public spending, social spending and budget deficit, reduction of tax on high earners, reduction of inflation, suppression of wages, lowering of import tariffs, tightened monetary policy. This, however, need not be thecase if the increased returns from these activities,due to the SAP, increase the incentives of produc-ers to adopt efficient methods of production. Environment and Development Economics 4 1 :91 8. For timberproduction, higher prices in the post-adjustmentperiod may have increased timber production andtimber-related deforestation.
Next
[PDF] The Effects of the Structural Adjustment Program on Deforestation in Ghana

Benhin and Edward B. First, thedata were separated into pre-adjustment 1965-82 and post-adjustment 198395 periods. Beyond Capitalism verses Socialism in Kenya and Tanzania, Nairobi, East African Educational Publishers. How does structural adjustment worsen poverty? In response, the International Monetary Fund IMF and the World Bank undertook the implementation of a trade liberalization policy through structural adjustment programs SAPs to ease the debt crisis in SSA. . Piecewise linear and switching regression approaches are used to distinguish between the influence of the post from the pre… Expand A need to find a win—win situation to control the spate of tropical deforestation is suggested, which may imply improved technologies in the agriculture sector in the developing world, which would lead both to increased production in the agricultural sector, and would also help control the use of tropical forest as an input in agriculture production.
Next
The Effects of the Structural Adjustment Program on webapi.bu.edu and Barbier The Effects of the Structural Adjustment Program 67 SAP

L Maize land area harvested national level, 000 ha. The forest reserves nowcontain most of the countrys remaining tropicalmoist forest, most of which even exist in isolatedfragments. STRUCTURAL ADJUSTMENT PROGRAMS IN KENYA Kenya gained independence in 1963, a period when the global economy was expanding and stable. Given the uncertain impact of SAP reforms onforest loss, it is important to investigate this poten-tial relationship on a case-by-case basis. These results support the hypothesis that, in thepost-adjustment period timber production but notcocoa land expansion is an important proximatefactor determining forest loss in Ghana. Moreover, the loan was given with conditions which required Kenya to reduce budget deficit, promote exports, liberalize trade, reform interest rate regime and cut down its funding on social services.
Next
The Effects of the Structural Adjustment Program on Deforestation in Ghana
As a result, life expectancy increased from 44 years at independence to 68 years in the 1980s whereas infant mortality dropped significantly from about 220 deaths per 1000 new born to 70 per 1000 new born Rono, 2002. The hypothesis that cocoa land expansionand timber production are important proximatefactors in forest loss in Ghana is therefore sup-ported by the model in the pre-adjustment period. The dummy variable is negative and very significant as ex-pected, indicating that the re-demarcation of new forest reserves led toincreased total closed forest area and helped reduce the total amount offorest 10ss. Accra: Policy Planning, Monitoring and Evalua- tion Department PPMED , Ministry of Agriculture. Thus there is not yet a shortage of avail-able land for agricultural production in Ghana Ministry of Agriculture 1991. Data: Life expectancy at birth, total years.
Next




