DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that carries the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA is essential for the reproduction, function, and evolution of life, and it is the blueprint for the structure and function of the cells in which it is found.
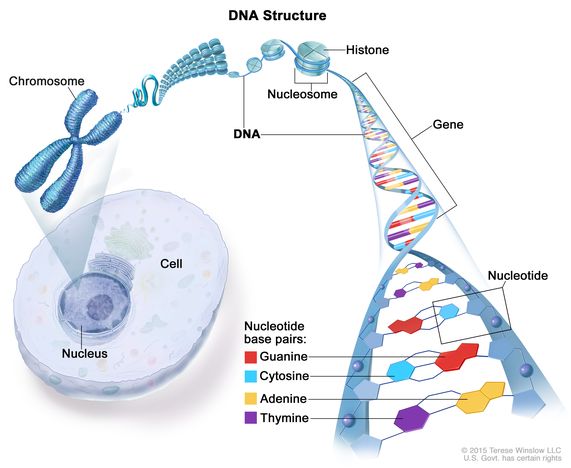
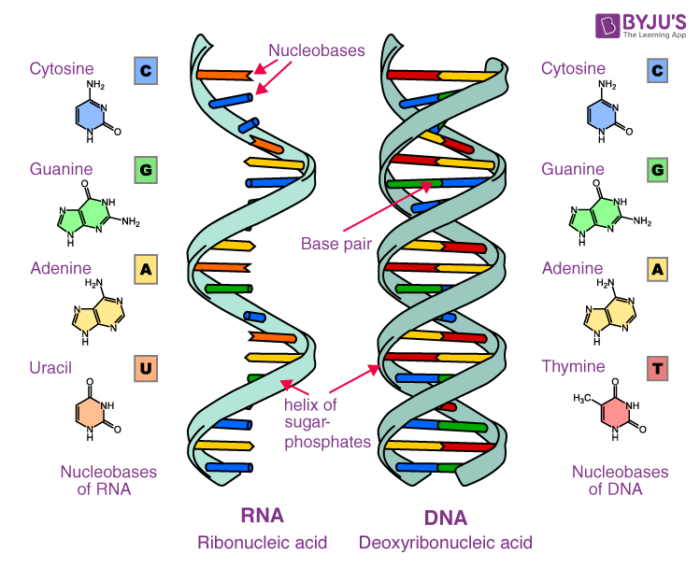
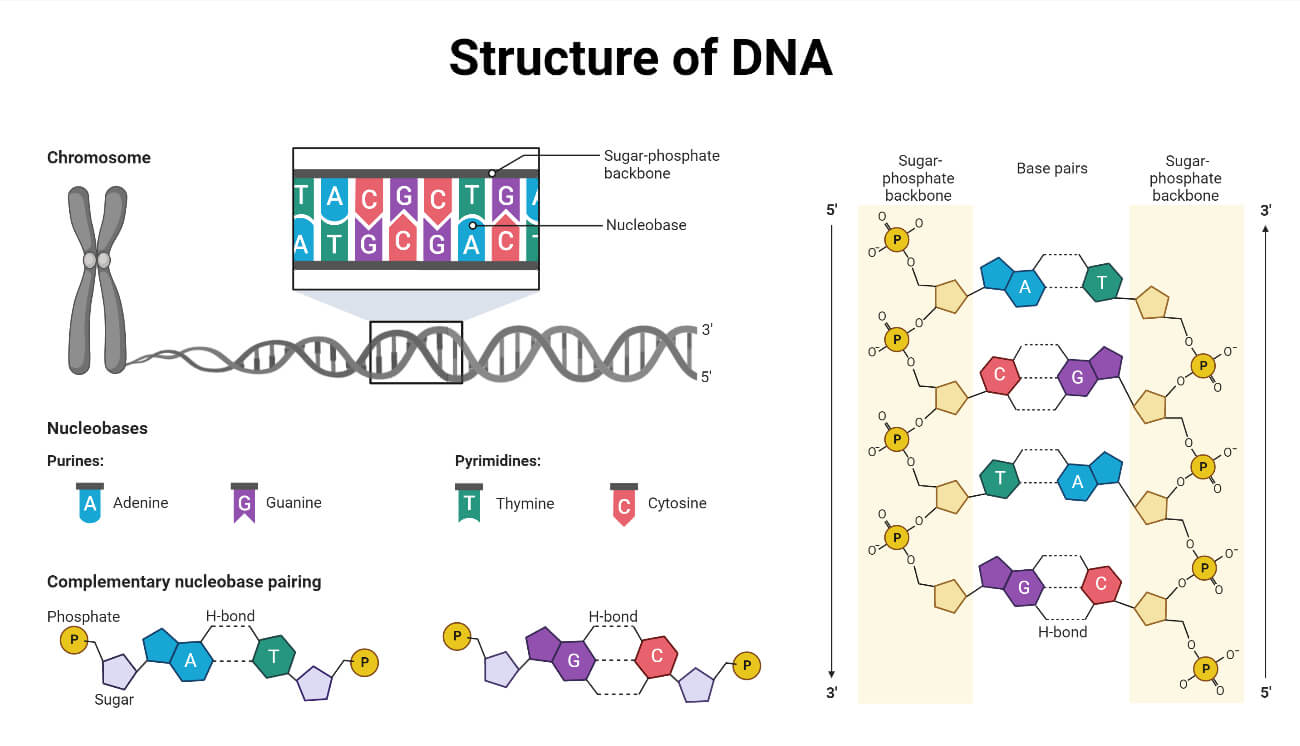
DNA is made up of four nucleotide bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. These bases are arranged in a specific order, or sequence, that determines the genetic information carried by the DNA molecule. The sequence of these bases is unique to each individual organism, and it is this uniqueness that makes DNA an important tool for identifying individuals and for understanding the genetic basis of inherited traits.
DNA is found in the nucleus of cells, where it is organized into structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is a long, linear structure made up of DNA and proteins, and each chromosome carries a unique set of genetic instructions. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes.
DNA is composed of two strands that are twisted together in a helical structure known as a double helix. The strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases, with adenine bonding specifically with thymine, and cytosine bonding with guanine. This base pairing is what allows DNA to replicate and pass genetic information from one generation to the next.
DNA plays a critical role in the functioning of cells and organisms. It is the genetic material that provides the instructions for the synthesis of proteins, which are the building blocks of cells and the functional units of life. DNA also controls the expression of genes, which determines the traits and characteristics of an organism.
In summary, DNA is a molecule that carries the genetic instructions for the development and functioning of all known living organisms. It is composed of four nucleotide bases and is organized into chromosomes in the nucleus of cells. DNA is essential for the reproduction, function, and evolution of life, and it plays a critical role in the synthesis of proteins and the expression of genes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotides-5c253d8cc9e77c0001d9b089.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/3-D_DNA-56a09ae45f9b58eba4b20266.jpg)