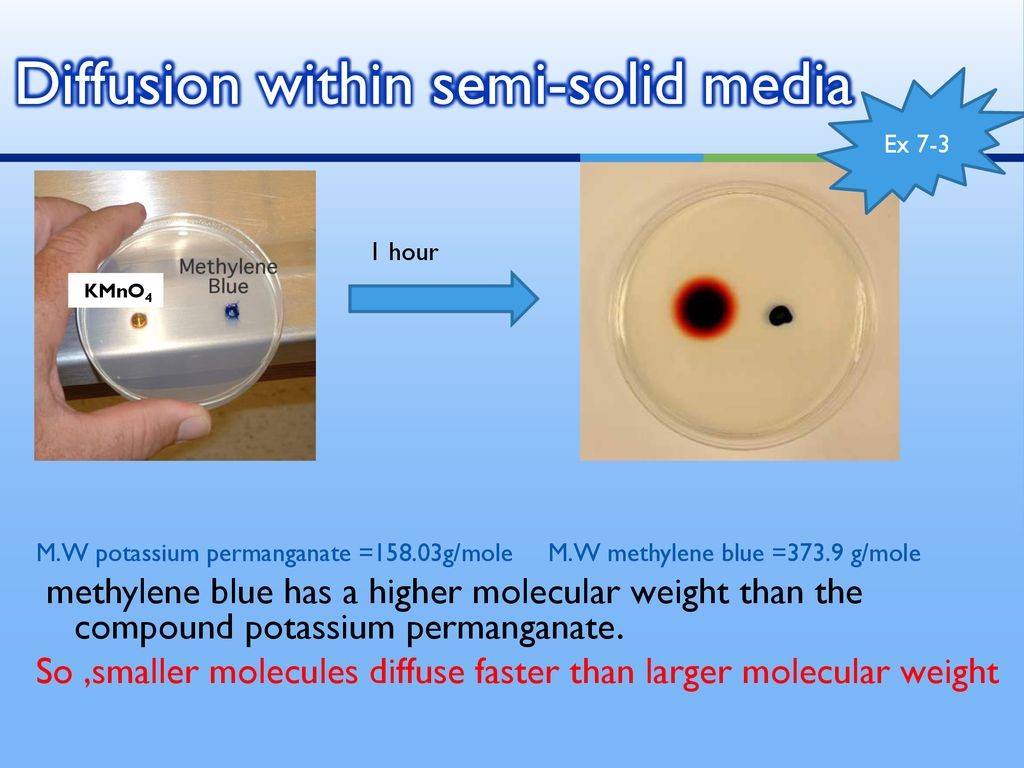
Diffusion and osmosis are important biological processes that play a vital role in the movement of substances across cell membranes. These processes are essential for maintaining homeostasis in the body and are involved in many physiological processes, including the transport of nutrients and waste products, the regulation of water balance, and the regulation of ion concentrations.
In a diffusion and osmosis lab, students can observe and experiment with these processes in order to better understand how they work and their significance in living organisms.
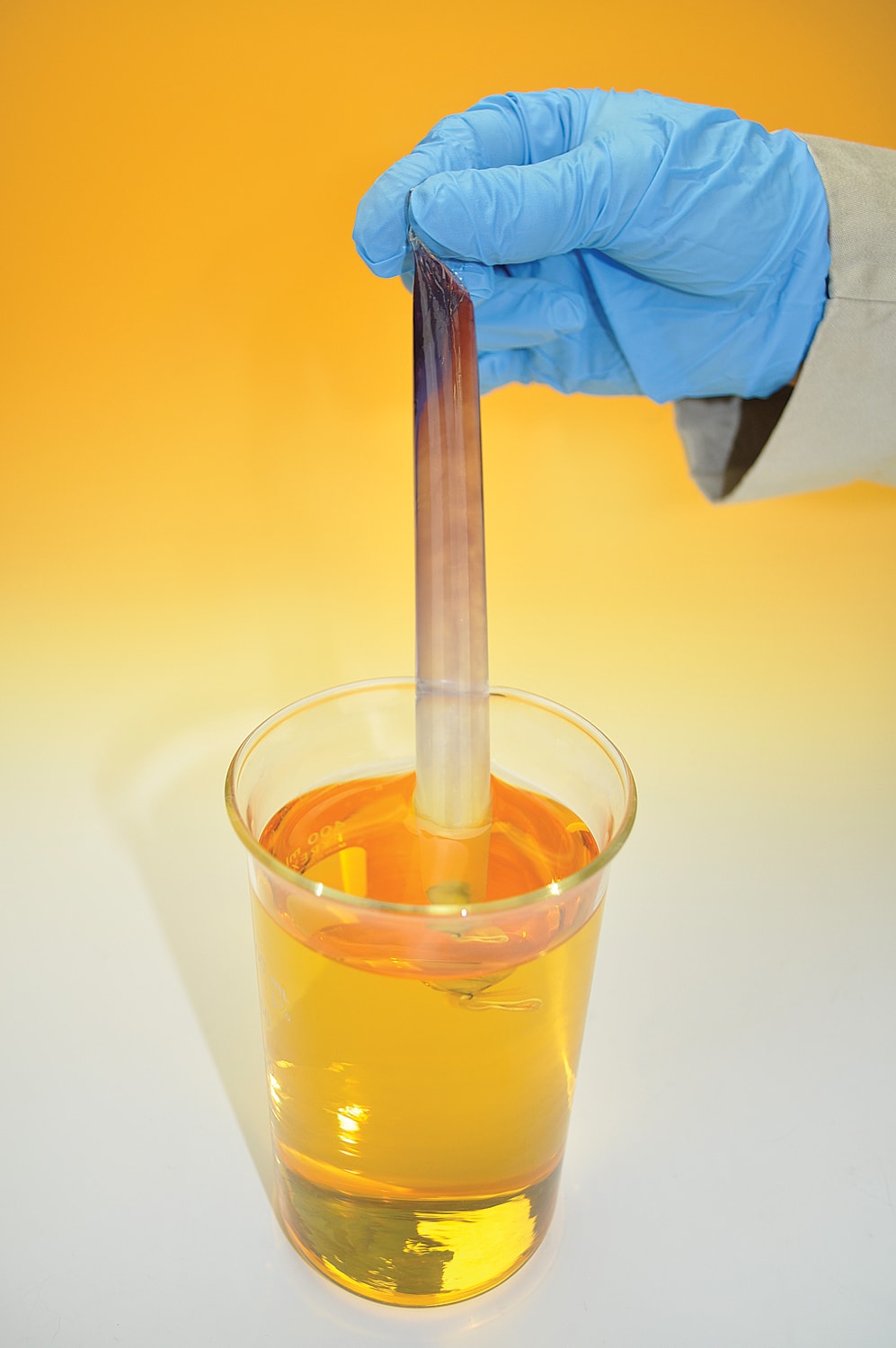
One common experiment in a diffusion and osmosis lab involves the use of a semipermeable membrane, such as dialysis tubing, to demonstrate the movement of substances across a membrane. In this experiment, a solution of different concentrations is placed in the dialysis tubing, and the tubing is then placed in a beaker containing a different solution. As the molecules of the solution in the tubing diffuse across the membrane into the beaker, the concentration of the solution in the tubing becomes more dilute, while the concentration of the solution in the beaker becomes more concentrated. This process can be observed using a spectrophotometer, which measures the absorbance of light by the solution and can be used to determine the concentration of the solution.
Another experiment that can be conducted in a diffusion and osmosis lab is the study of osmosis in plant cells. In this experiment, a potato is cut into small slices and placed in a solution of different concentrations. As the water moves across the cell membrane of the potato cells by osmosis, the potato slices will either gain or lose weight, depending on the concentration of the solution. By weighing the potato slices before and after the experiment, students can observe the effects of osmosis on plant cells and how it affects their size and shape.
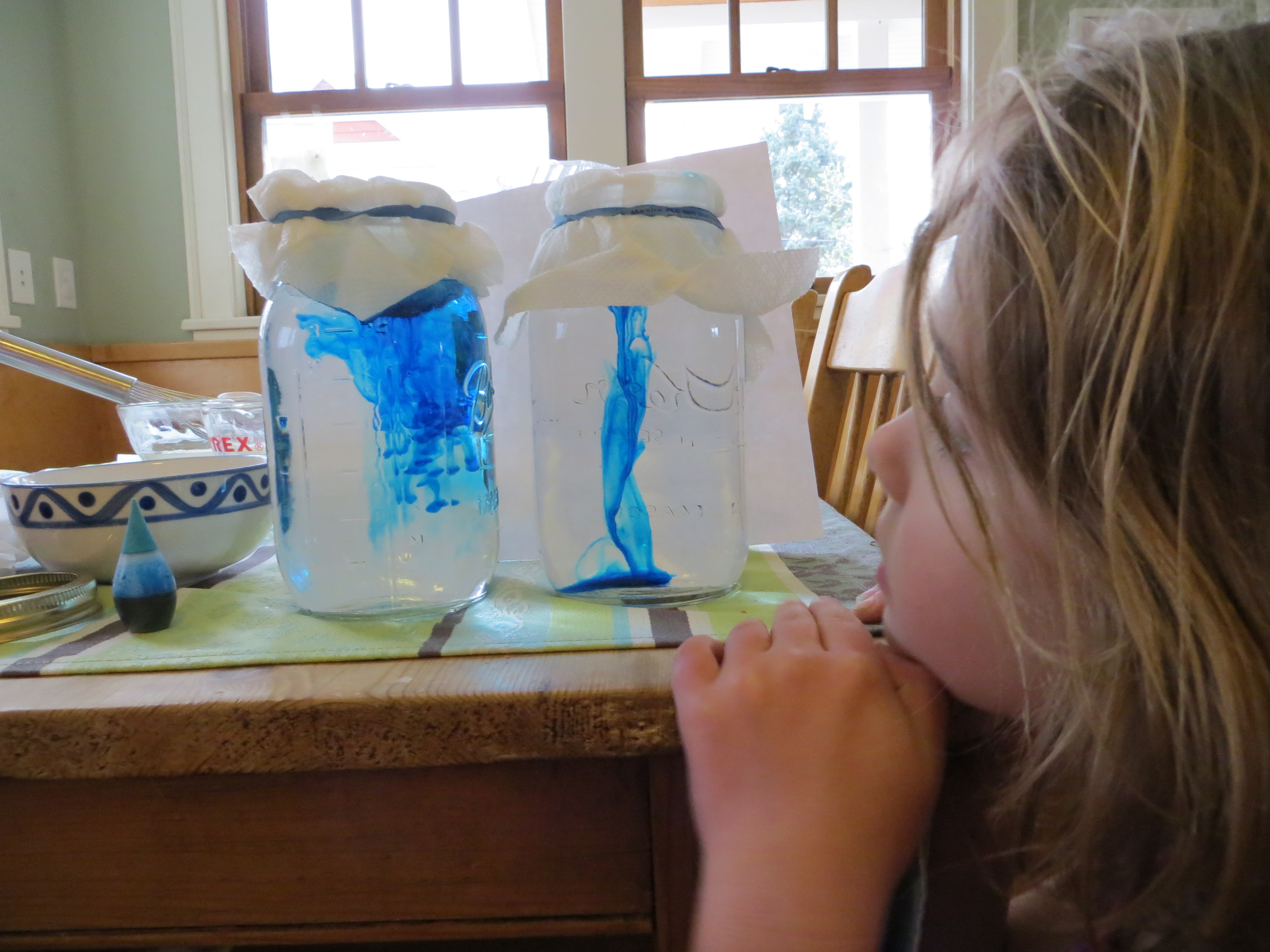
In addition to these hands-on experiments, students in a diffusion and osmosis lab may also learn about the theories and principles that underlie these processes. For example, they may learn about the concept of concentration gradients, which describes the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, and how this drives the diffusion and osmosis of substances across membranes.
Overall, a diffusion and osmosis lab provides an engaging and interactive way for students to learn about these important biological processes and their role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. Through hands-on experiments and discussions of the underlying principles, students can gain a deeper understanding of how diffusion and osmosis work and how they are important for the functioning of living organisms.