Classical conditioning and operant conditioning are two important concepts in the field of psychology that were developed by Ivan Pavlov and B.F. Skinner, respectively. While both approaches involve the learning of behaviors through the consequences of those behaviors, there are some key differences between classical and operant conditioning that are worth exploring.
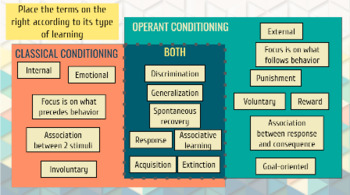
Classical conditioning involves the association of a neutral stimulus with a reflexive response. For example, if a dog salivates at the sound of a bell because it has been conditioned to associate the bell with the presentation of food, then the bell is the neutral stimulus and the salivation is the reflexive response. In classical conditioning, the reflexive response is elicited by the neutral stimulus through the process of association.
On the other hand, operant conditioning involves the learning of a behavior through the consequences of that behavior. In operant conditioning, an animal or person will perform a behavior in order to receive a reward or avoid punishment. For example, if a child is given a toy as a reward for picking up their toys, they are more likely to perform the behavior in the future because it has been reinforced.
One key difference between classical and operant conditioning is the type of response that is being learned. In classical conditioning, the response is reflexive and involuntary, while in operant conditioning, the response is voluntary and under the control of the learner.
Another difference is the role of the reinforcing stimuli. In classical conditioning, the reinforcing stimuli are presented after the response has occurred, while in operant conditioning, the reinforcing stimuli are presented before the behavior in order to increase the likelihood of the behavior occurring again in the future.
A third difference is the role of attention in the learning process. In classical conditioning, attention is not necessary for learning to occur, while in operant conditioning, attention is required for the reinforcing stimuli to have an effect on behavior.
Overall, classical and operant conditioning are two different approaches to understanding how behaviors are learned and modified. While they share some similarities, they also have some key differences that are worth considering when attempting to understand and modify behavior.
Difference Between Classical vs Operant Conditioning
Since involuntary responses i. If the behavior is punished, it is likely to decrease; if it is reinforced, it is likely to increase. Contrary to this, the occurrence of the reinforcer is under the control of organism and thus, the organism acts actively. They mistake this bell for their food bell and begin salivating in response to it. You can see In contrast to classical conditioning, operant conditioning involves encouraging or discouraging a specific behavior using reinforcement. You move your hand back in a split second; courtesy, automatic reflex. The response rate is fast, but the extinction rate is slow as the trainee likely realizes there is still a chance to be rewarded.
Difference Between Classical Conditioning and Operant Conditioning

No wash equals no treat. The unconditioned stimulus in this example are the sights and sounds of the rollercoaster you don't want to ride, and the elevated heart rate is the unconditioned response. Classical conditioning takes a previously neutral stimulus, such as the bell, and pairs it with an unconditioned stimulus, such as the taste of food, and uses them to condition a desired response, such as the salivation. If you smell this scent somewhere else conditioned stimulus it can trigger that same happy feeling conditioned response even though your grandmother is not present. By associating a harmful behaviour with an undesirable or negative consequence, operant conditioning can help reduce or eliminate them. Students study hard, when the teacher is present. This approach may result in children demonstrating honesty because they can expect the reward of praise from parents.
Operant Conditioning vs. Classical Conditioning: 8 Main Distinctions To Know

When you touch a door handle to open the door, you get an electric shock. However, after repeated pairing of that song with the anxiety of getting on the ride, your brain will start to think, 'I hear that song, so something scary must be going to happen soon! Another term is extinction burst. Definition: Classical conditioning is defined as a type of learning in which a neutral stimulus, when paired with an unconditioned stimulus which naturally generates a response, becomes conditioned and starts generating a response similar to that generated by unconditioned stimulus. Students can then turn in these tokens to receive some type of reward, such as a treat or extra playtime. There are also two types of punishment that occur in operant conditioning.
The difference between operant and classical conditioning
In classical conditioning, the UCR salivation to food and the CR salivation to bell show a great deal of similarity. Quitting destructive habits Operant conditioning is another effective method of influencing the tendency to indulge in destructive habits. The CS and the UCS are connected together so that the animal learns to respond to the CS just as it does to the UCS. Skinner, an American Psychologist. Classical Conditioning Classical conditioning, alternatively called respondent conditioning or Pavlovian conditioning, was developed by Ivan Pavlov, a Russian physiologist and researcher. Also, classical conditioning always works with involuntary responses, while operant conditioning works with voluntary behaviors.







