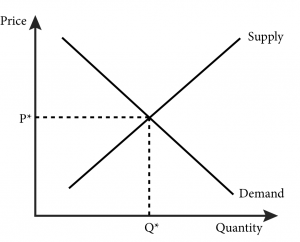
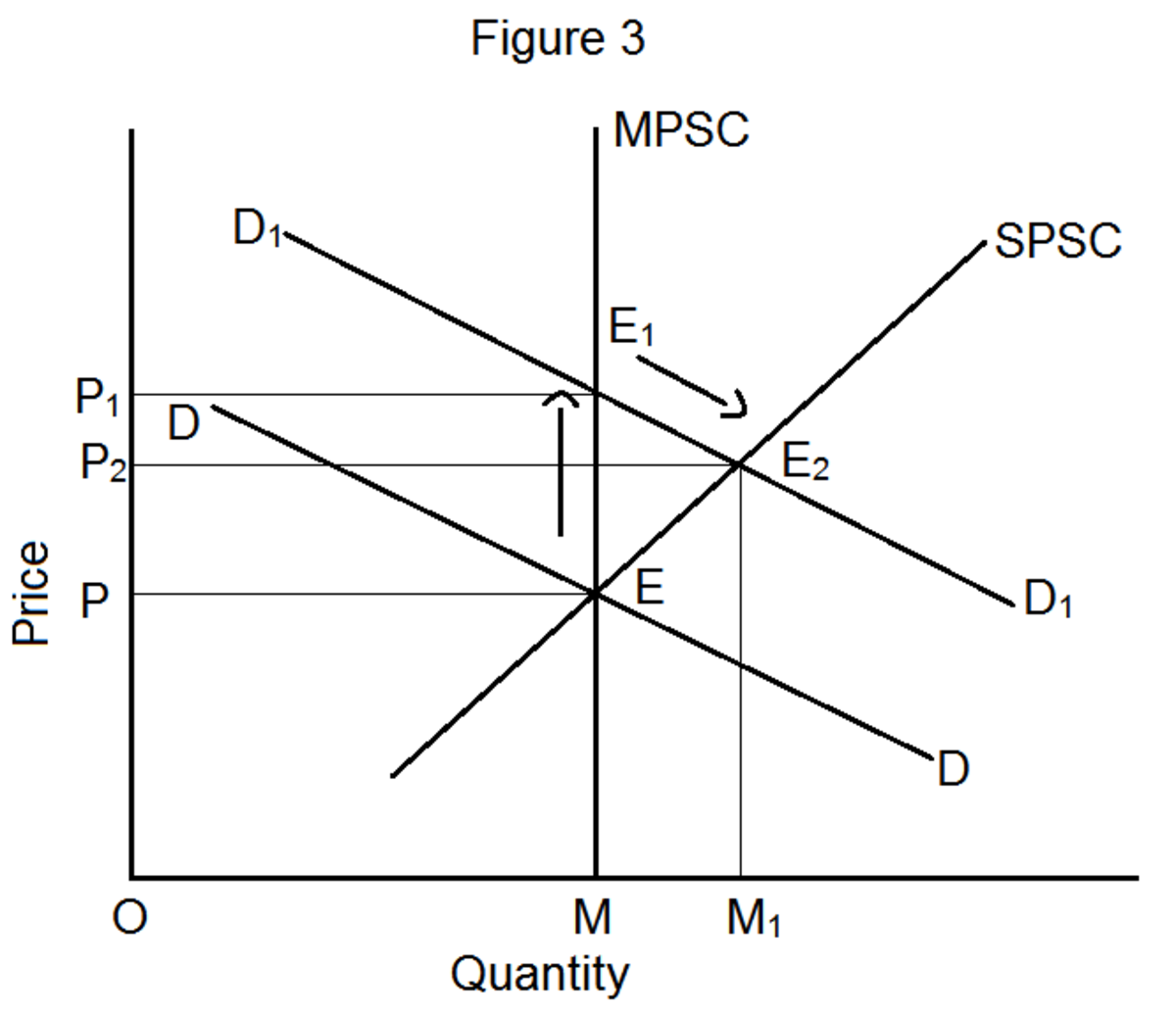
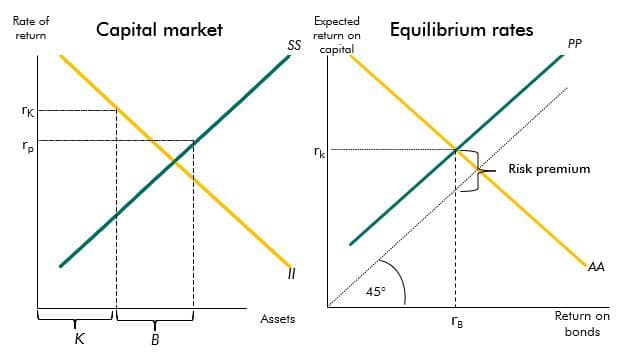
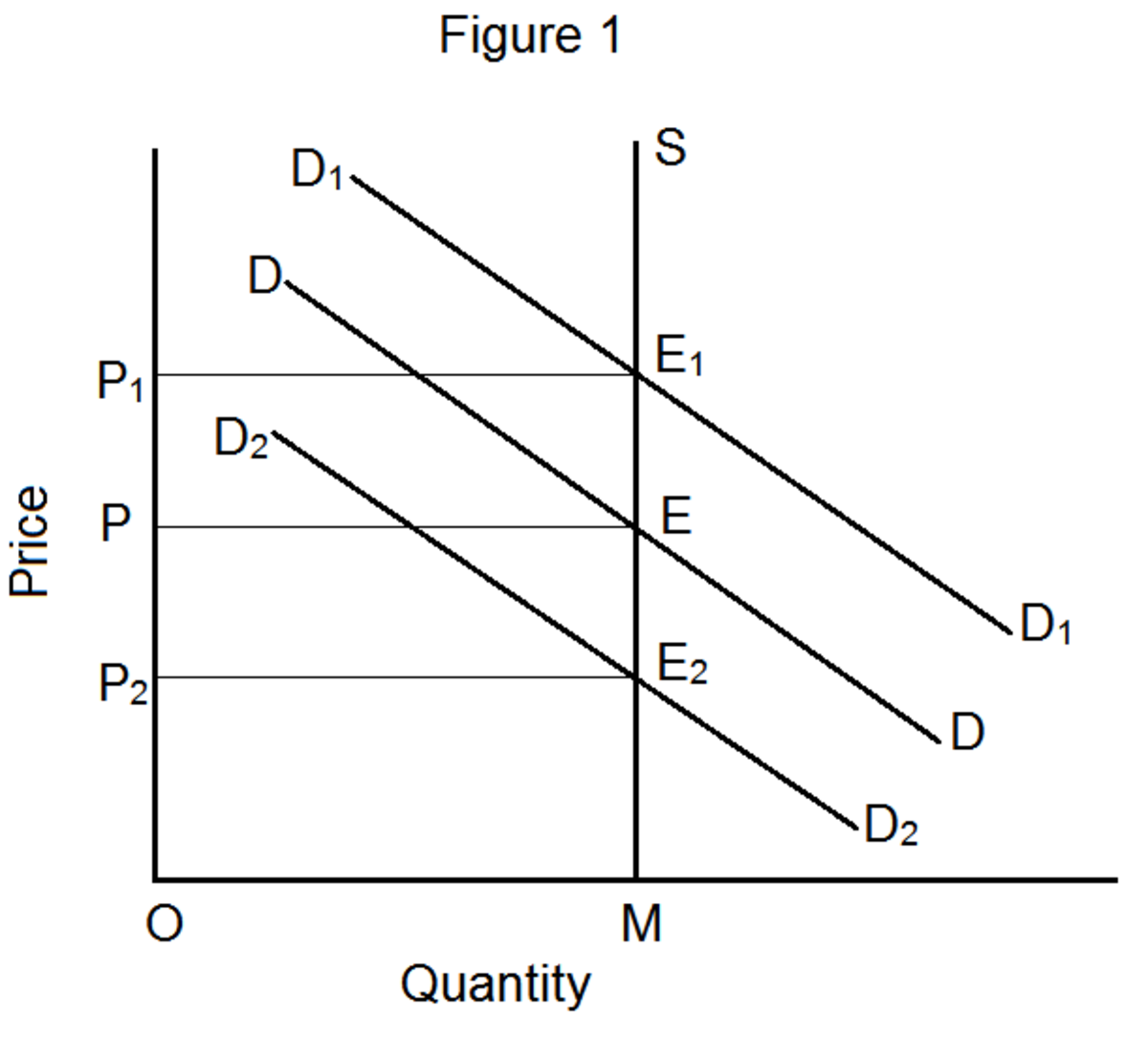
Market equilibrium is a state in which the supply of a good or service is equal to the demand for it, resulting in a stable price for that good or service. Determining market equilibrium is an important aspect of economics, as it helps to understand the underlying forces that drive the prices of goods and services in a market.
There are several factors that can influence the determination of market equilibrium. One of the most important factors is the price of the good or service itself. If the price of a good or service is too high, there will be fewer buyers, leading to a surplus of the good or service. On the other hand, if the price is too low, there will be more buyers than sellers, leading to a shortage.
Another factor that can affect the determination of market equilibrium is the cost of production. If the cost of production is high, it may be difficult for sellers to make a profit, leading to a decrease in the supply of the good or service. Conversely, if the cost of production is low, sellers may be able to increase the supply of the good or service, leading to a decrease in the price.
In addition to price and cost of production, other factors that can influence the determination of market equilibrium include consumer preferences, government regulations, and the level of competition in the market. All of these factors can affect the supply and demand for a good or service, ultimately impacting the market equilibrium.
To determine market equilibrium, economists use supply and demand curves. These curves show the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity of that good or service that is either supplied or demanded at that price. When the supply and demand curves intersect, it indicates the market equilibrium price and quantity.
In summary, market equilibrium is a state in which the supply of a good or service is equal to the demand for it, resulting in a stable price. The determination of market equilibrium is influenced by a variety of factors, including price, cost of production, consumer preferences, government regulations, and competition. Economists use supply and demand curves to understand and analyze market equilibrium.