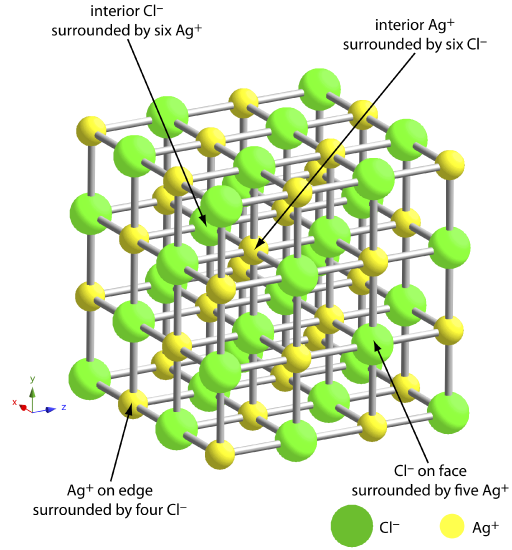
Gravimetric analysis is a method of chemical analysis in which the mass of an element or compound is measured to determine its quantity. One of the common methods for gravimetric analysis is the determination of chloride ions, which are anions (negatively charged ions) with the chemical formula Cl-. Chloride ions are present in a variety of compounds, including sea water, brines, and many inorganic and organic substances. In this essay, we will discuss the determination of chloride ions by gravimetric analysis, including the principle behind the method, the experimental procedure, and the potential sources of error.
The principle behind the gravimetric determination of chloride ions is based on the formation of a precipitate with a known composition. Chloride ions can be quantitatively precipitated as silver chloride (AgCl) by adding a solution of silver nitrate (AgNO3) to a sample containing chloride ions. The reaction between silver nitrate and chloride ions is shown below:
AgNO3 + Cl- → AgCl + NO3-
The mass of the precipitate, AgCl, can then be measured and used to calculate the mass of chloride ions in the sample. The mass of chloride ions is calculated using the following equation:
Mass of chloride ions (g) = Mass of AgCl (g) x (atomic weight of Cl / formula weight of AgCl)
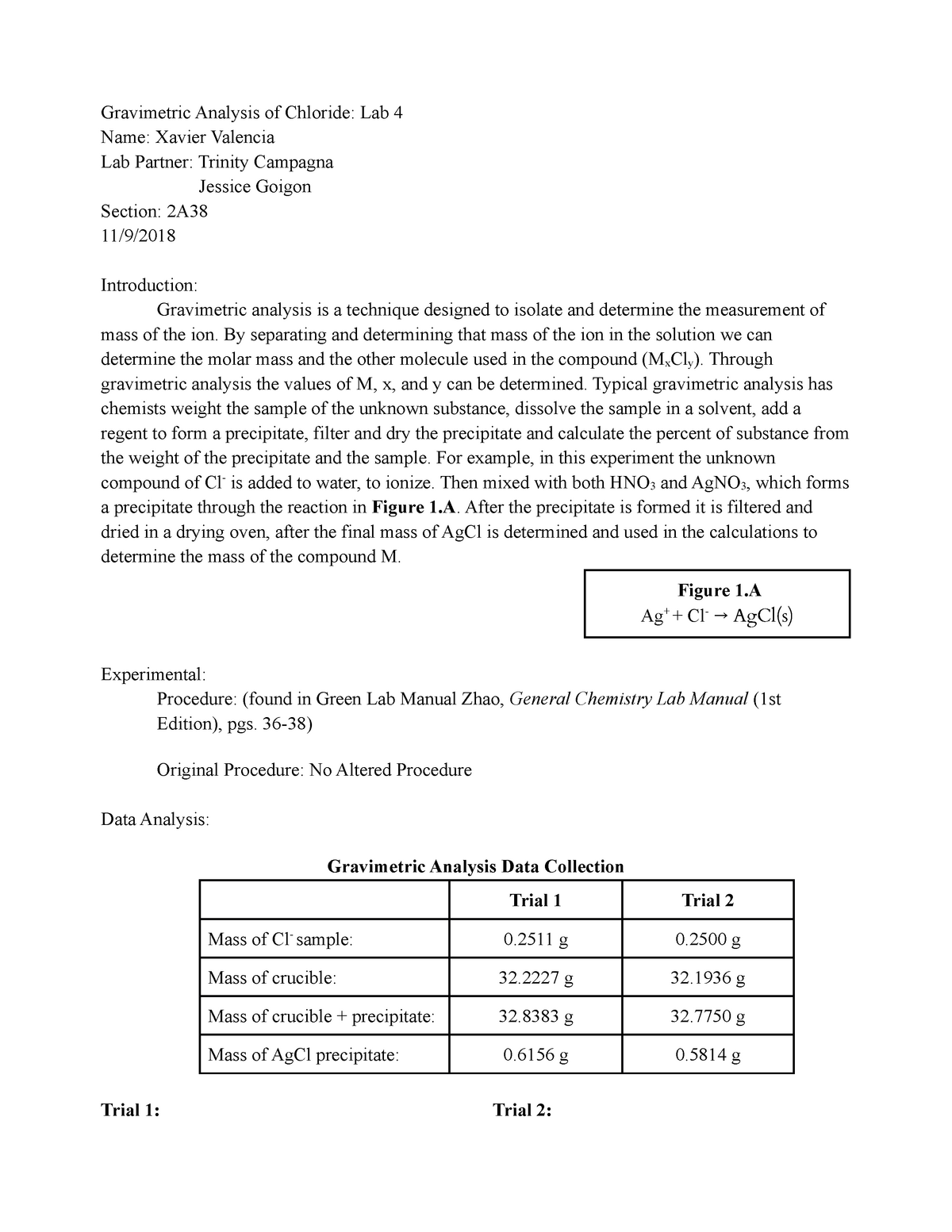
The experimental procedure for the gravimetric determination of chloride ions involves several steps. First, a known volume of the sample containing chloride ions is taken and diluted with water to a known concentration. Next, a solution of silver nitrate is added to the sample until all of the chloride ions are precipitated as silver chloride. The precipitate is then collected by filtration, washed with water to remove any excess silver nitrate, and dried in an oven at a temperature of 110°C for at least 1 hour. The mass of the dried precipitate is then measured using a balance and used to calculate the mass of chloride ions in the sample.
There are several potential sources of error in the gravimetric determination of chloride ions. One common source of error is incomplete precipitation of the silver chloride, which can occur if the concentration of silver nitrate is too low or if the reaction time is not sufficient. Another potential source of error is the loss of the precipitate during the filtration and washing steps, which can occur if the precipitate is not properly collected or if it dissolves in the wash water. Finally, errors can also occur in the measurement of the mass of the precipitate, which can be influenced by factors such as the sensitivity of the balance and the accuracy of the temperature control in the oven.
In conclusion, the gravimetric determination of chloride ions is a widely used method for the quantitative analysis of chloride ions in a variety of compounds. The method is based on the formation of a precipitate with a known composition, and the mass of the precipitate is used to calculate the mass of chloride ions in the sample. However, there are several potential sources of error in the method, including incomplete precipitation, loss of the precipitate during the filtration and washing steps, and errors in the measurement of the mass of the precipitate.