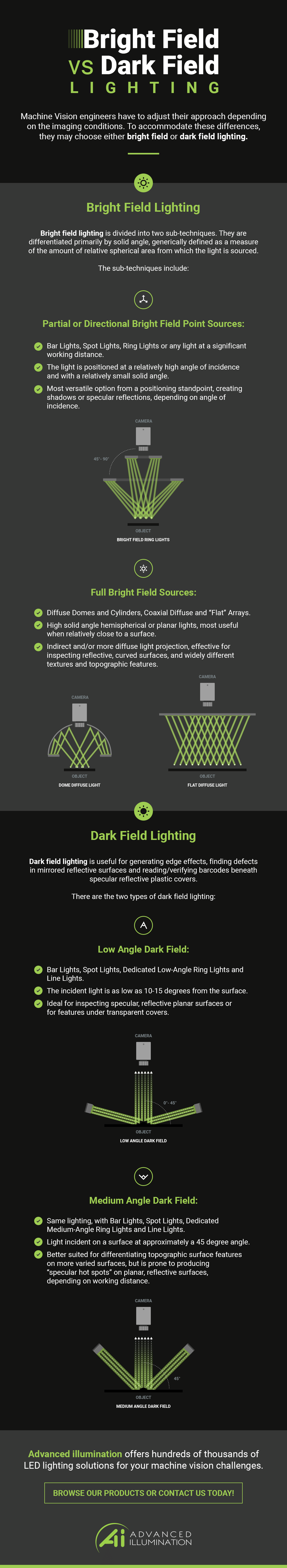
Dark field microscopy and bright field microscopy are two common techniques used in microscopy to visualize samples and obtain detailed images of their structures. Both techniques use light to illuminate the sample, but they differ in how the light is collected and analyzed to form the image.
Dark field microscopy is a technique that utilizes oblique illumination to visualize samples. In this technique, the light source is positioned at an angle to the microscope objective, so that the light is not directly transmitted through the sample. Instead, the light is scattered by the sample, and the scattered light is collected by the objective and focused onto the detector. This results in an image that appears dark, with the sample appearing as bright structures against a dark background.
Dark field microscopy is particularly useful for visualizing transparent or transparent samples, as well as for observing small particles or structures that may be difficult to see under bright field conditions. It is also useful for identifying the shape, size, and arrangement of cells and other structures within a sample.
Bright field microscopy, on the other hand, is a technique that uses direct illumination to visualize samples. In this technique, the light source is positioned directly above the sample, and the light is transmitted through the sample and the objective, and then focused onto the detector. This results in an image that appears bright, with the sample appearing as dark structures against a bright background.
Bright field microscopy is the most common technique used in microscopy, and it is particularly useful for visualizing samples that are opaque or have a high contrast with the surrounding medium. It is also useful for identifying the overall structure and organization of a sample.
In conclusion, both dark field microscopy and bright field microscopy are important techniques in microscopy, and they are used to visualize and study the structure and organization of samples at the microscopic level. Each technique has its own strengths and limitations, and the choice of which technique to use depends on the specific properties of the sample and the information that is desired.