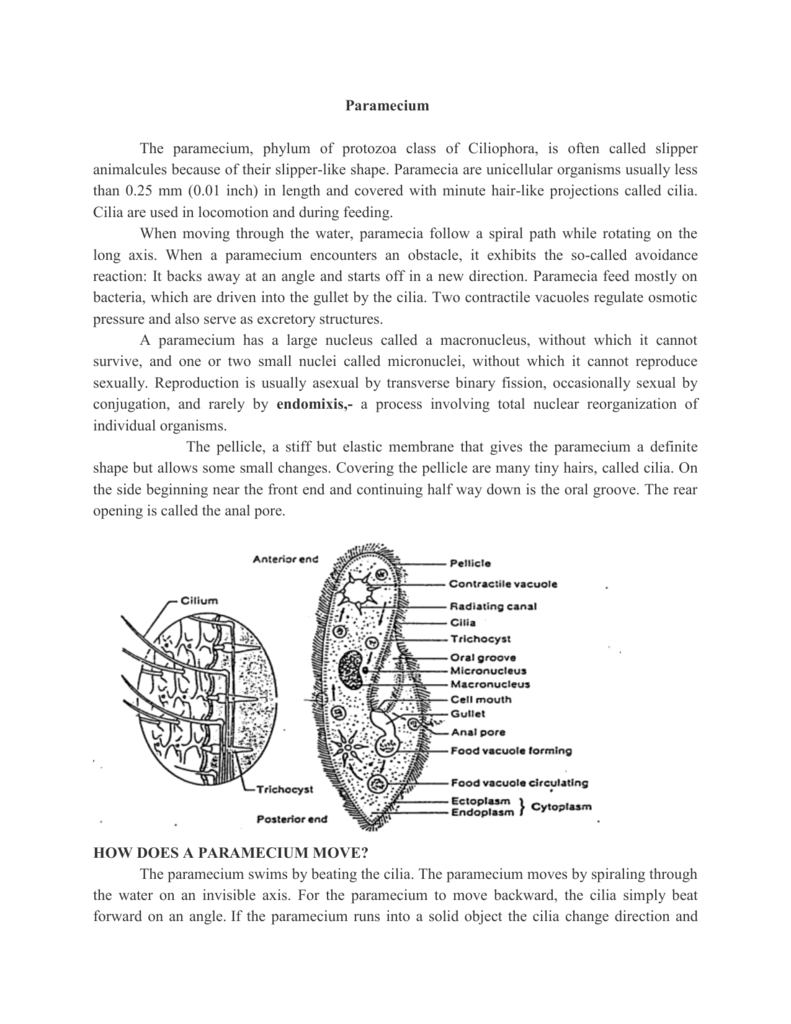
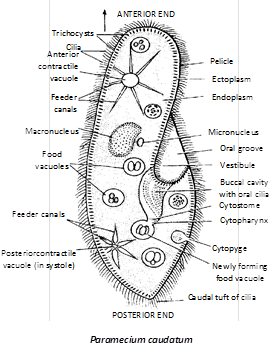
Cytogamy is a term that refers to the fusion of gametes, or reproductive cells, during sexual reproduction. This process occurs in many different types of organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi, and is an essential step in the reproduction and continuation of these species.
In plants, cytogamy typically occurs during fertilization, when the male gametes, or pollen, are transferred to the female gametes, or ovules, inside the flower. The pollen grains germinate on the surface of the ovule and produce a tube that grows down through the style and into the ovule. At the end of this tube is the male gamete, which fuses with the female gamete inside the ovule, forming a zygote. The zygote then divides and grows into a new plant, which will eventually produce its own flowers and seeds.
In animals, cytogamy occurs when the male gametes, or sperm, are fertilized by the female gametes, or eggs. This process can occur either internally, as in mammals, or externally, as in many fish and amphibians. In internal fertilization, the male deposits his sperm inside the female's reproductive tract, and the sperm swim up the female's fallopian tubes to reach the egg. Once the sperm reaches the egg, it penetrates the egg's outer layers and fuses with the egg's nucleus, forming a zygote. The zygote then begins to divide and grow, eventually developing into a baby animal.
In fungi, cytogamy occurs when two different individuals fuse their cells together, forming a new individual that contains the genetic material of both parents. This process is known as heterokaryosis, and it allows fungi to exchange genetic material and increase their genetic diversity.
Overall, cytogamy plays a critical role in the reproductive biology of many different types of organisms, and is an essential step in the continuation of these species. It allows for the exchange of genetic material between individuals, which can increase genetic diversity and help organisms adapt to changing environments.