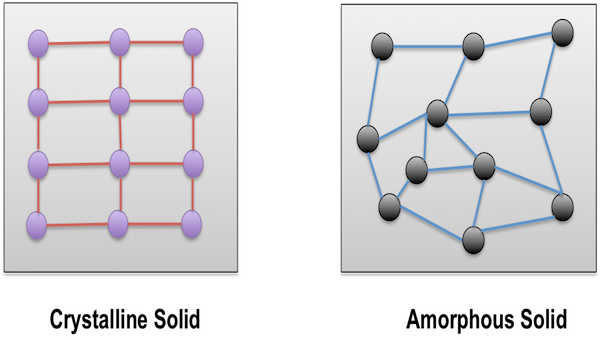
A crystalline substance is a solid material in which the atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly, repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. Crystalline substances are characterized by their high degree of symmetry and regularity, which results in distinctive physical and chemical properties. They are also known for their ability to form well-defined crystals, which are three-dimensional structures with a repeating arrangement of atoms.
There are two types of crystalline substances: inorganic and organic. Inorganic crystalline substances are those that do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and are typically found in minerals. Examples of inorganic crystalline substances include salt (sodium chloride), quartz, and diamond. Organic crystalline substances, on the other hand, are those that contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and are typically found in living organisms. Examples of organic crystalline substances include sugar, cholesterol, and DNA.
Crystalline substances have a number of important properties that make them useful in a wide range of applications. For example, they are often hard and strong, making them suitable for use in construction and other structural applications. They also tend to be good thermal and electrical conductors, which makes them useful in electronics and other technologies. In addition, many crystalline substances have unique optical properties, such as the ability to refract or reflect light in specific ways, which makes them useful in optoelectronic devices and other optical applications.
One of the most interesting and useful properties of crystalline substances is their ability to form well-defined crystals. Crystals are three-dimensional structures that have a repeating arrangement of atoms, which gives them a high degree of symmetry and regularity. This regularity results in distinctive physical and chemical properties, such as a specific melting point or solubility in a particular solvent. Crystalline substances also have a characteristic crystal structure, which is the arrangement of atoms in the crystal. The crystal structure of a substance determines many of its physical and chemical properties, such as its density, electrical conductivity, and melting point.
In conclusion, crystalline substances are solid materials that are characterized by their high degree of symmetry and regularity. They are found in both inorganic and organic forms and have a number of useful properties, including their ability to form well-defined crystals. These properties make crystalline substances important in a wide range of applications, from construction and electronics to optoelectronic devices and more.