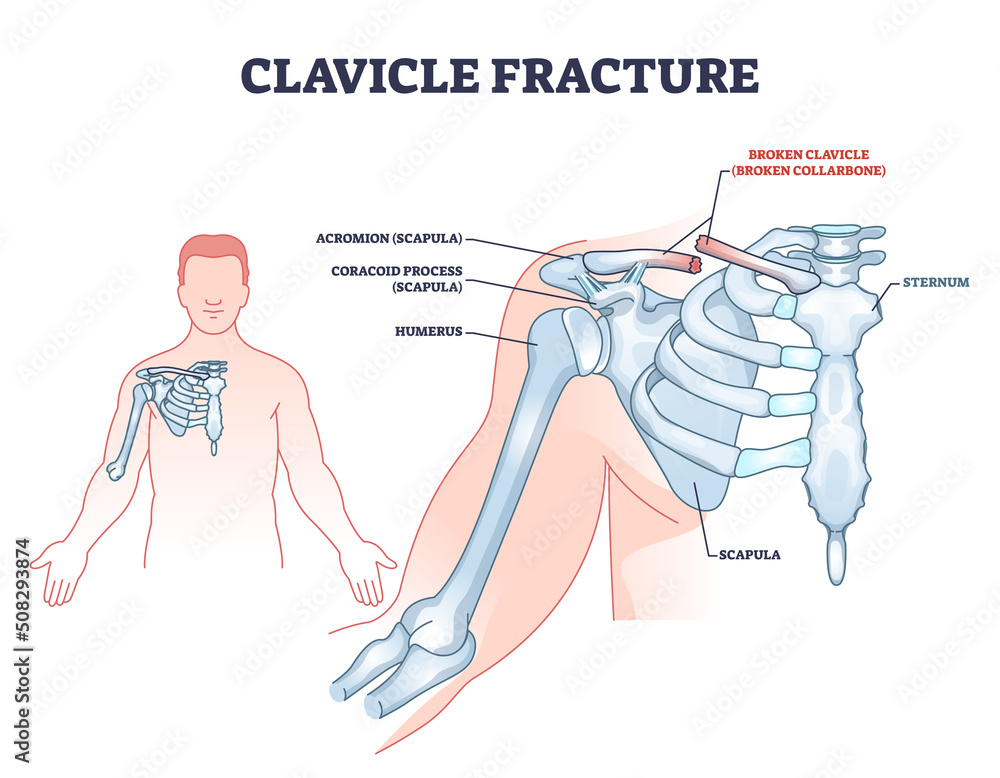
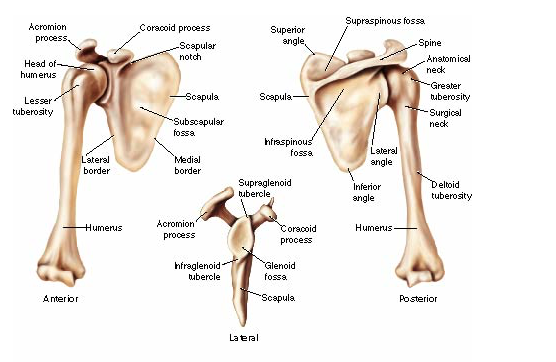
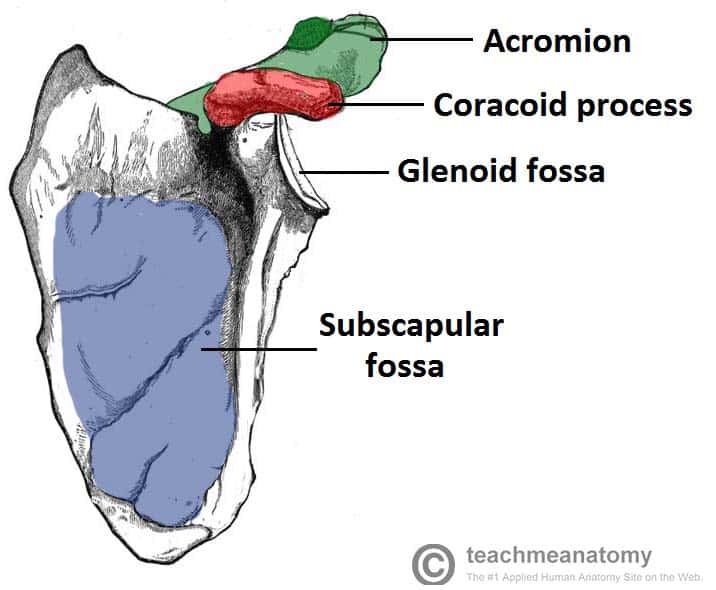
The coracoid process of the scapula, also known as the coracoid bone or coracoid process, is a small, hook-like projection that extends from the superior border of the scapula, the bone that forms the shoulder blade. It is located just above the glenoid cavity, which is the socket that articulates with the head of the humerus, the bone of the upper arm.
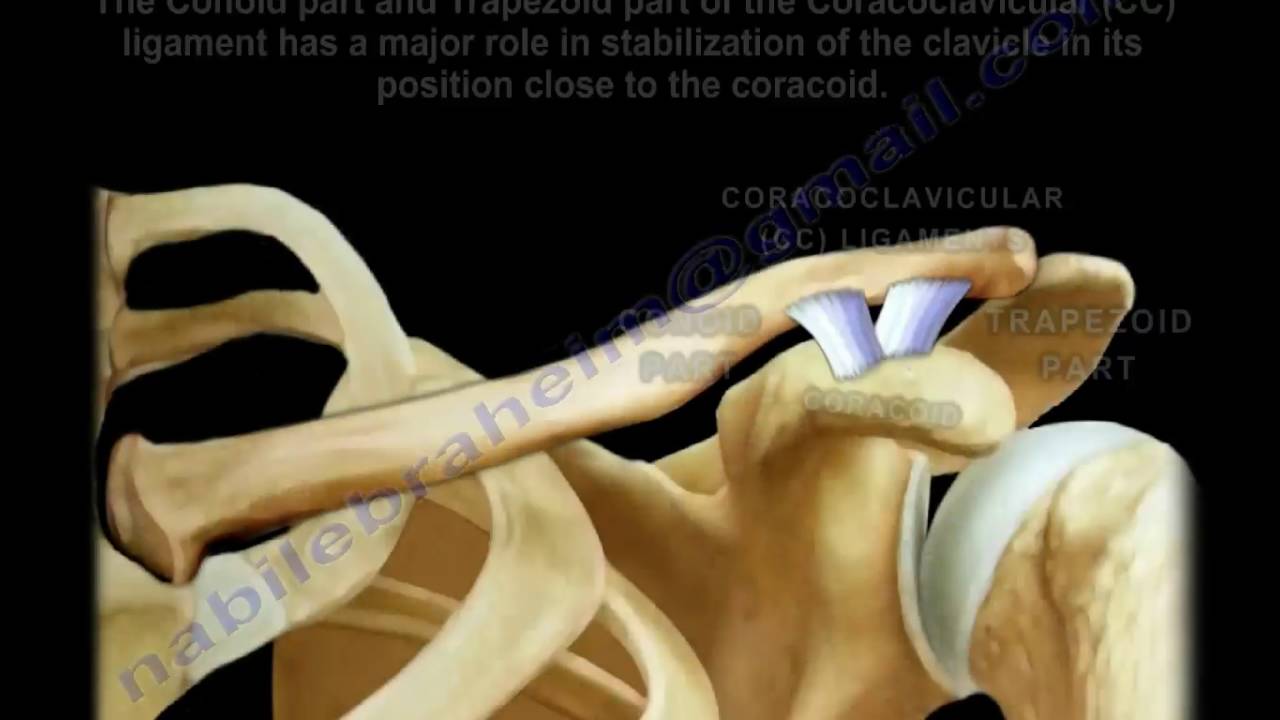
The coracoid process has several important functions in the human body. It serves as an attachment site for several muscles and tendons that are important in shoulder movement and stability. These muscles and tendons include the pectoralis minor, the coracobrachialis, the short head of the biceps brachii, and the conoid and trapezoid ligaments.
The pectoralis minor muscle, which is located in the chest, attaches to the coracoid process and helps to move the shoulder forward and downward. The coracobrachialis muscle, which is located in the upper arm, also attaches to the coracoid process and helps to flex the shoulder joint. The short head of the biceps brachii muscle, which is located in the upper arm, attaches to the coracoid process and helps to flex and rotate the shoulder joint. The conoid and trapezoid ligaments, which are located in the shoulder joint, attach to the coracoid process and help to stabilize the shoulder joint.
In addition to its role in muscle and tendon attachment, the coracoid process also plays a role in the movement and stability of the scapula. It serves as a pivot point for the scapula to rotate around as the arm is moved. This allows the scapula to move in a way that is coordinated with the movement of the arm, which is essential for proper shoulder function.
The coracoid process is a small but important structure in the shoulder joint. It plays a vital role in the movement and stability of the shoulder, and any injury or dysfunction of the coracoid process can result in reduced shoulder function. Treatment for coracoid process injuries or dysfunction may involve physical therapy, shoulder stabilization exercises, or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
In conclusion, the coracoid process of the scapula is a small, hook-like projection located on the superior border of the scapula. It serves as an attachment site for several muscles and tendons that are important in shoulder movement and stability, and it also plays a role in the movement and stability of the scapula. Any injury or dysfunction of the coracoid process can result in reduced shoulder function, and treatment may be necessary to restore proper shoulder function.