Education is a fundamental right guaranteed by many constitutions around the world. In the United States, the Constitution does not explicitly mention education, but the 14th Amendment, which guarantees equal protection under the law, has been interpreted by the courts to require the provision of education to all children.
The 14th Amendment states that "No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws." This amendment has been used to challenge laws and policies that discriminate against certain groups of people, including those that deny children access to education.
In addition to the 14th Amendment, other provisions of the Constitution also relate to education. The First Amendment guarantees freedom of speech, religion, and the press, which are important rights for students and educators. The Fourth Amendment protects against unreasonable searches and seizures, which can be relevant in cases involving student privacy and school searches.
At the federal level, the U.S. Department of Education is responsible for implementing education policies and providing funding to states and local school districts. The department was established in 1979 and is responsible for enforcing federal education laws, including the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and the No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB).
The IDEA guarantees a free and appropriate public education to students with disabilities, while NCLB aims to improve student achievement and close the achievement gap between different groups of students. These and other federal education laws set standards and guidelines for states and local school districts to follow in providing education to all students.
In conclusion, the Constitution of the United States provides several provisions related to education, including the 14th Amendment's guarantee of equal protection under the law and the First and Fourth Amendments' protections of individual rights. At the federal level, the U.S. Department of Education is responsible for implementing and enforcing education policies and laws. These provisions and policies ensure that all children have access to a quality education.
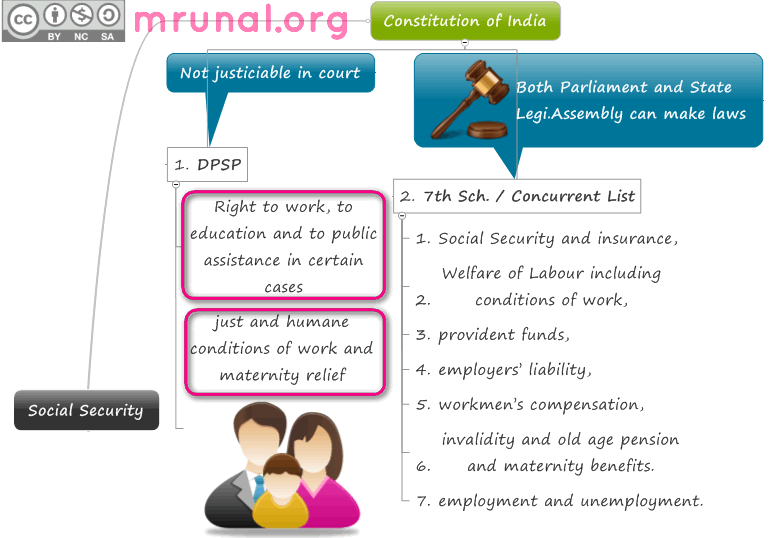
Major Constitutional Provisions on Education in India !

Until spring 2002 one huge unknown factor in the debate over using public funds to support private, parochial schools was whether such use of public funds violates the First Amendment of the Constitution, which prohibits government from unduly supporting religion or favoring one religion over another. In states where plaintiffs have been successful, often after many years or decades of litigation, such lawsuits have led to higher spending for education, including expenditures for school facilities, teacher's salaries, special programs, and technology. There would be no discrimintation on the basis of gender article 15 1. The Bias of the System The US political system is designed to prevent quick agreement within the legislature and between the branches. Dole, the Supreme Court in 1987 upheld a federal law withholding a percentage of federal highway funds from any state that declined to raise its minimum drinking age to twenty-one. Article 351 promoted Hindi for its development and propagation.
Constitutional Requirements Governing American Education

San Antonio Independent School District v. The wets asked for specially called state conventions and rapidly ratified repeal—on December 5, 1933. At the time, Texas, like most states, financed its schools primarily through local property taxes. This has been accomplished in many states by providing more state-level funding to property-poor districts to offset their lower local revenues, and less state funding to property-rich districts. Many school reform advocates believe that public schools suffer from a lack of competition and that states or school districts should provide vouchers to students, especially poor and minority students attending substandard inner-city schools, to enable them to attend a private school.
Aims and Purpose of Education Drawn from Constitutional Provisions
If provisions are to be changed, they must undergo a specific process, which requires approval by both the U. This practice of federalism as we explain in detail in Federalism aside, three key principles are the crux of the Constitution: separation of powers, checks and balances, and bicameralism. The government of India wants to provide inclusive education to all. How did the authors of the Constitution address the concerns of those who worried that the new federal government would be too strong? The highest courts of these states have struck down the state system for financing public schools and required the legislatures to appropriate significantly increased spending for public education. Intermediary institutions not mentioned in the Constitution have developed important governmental roles Ackerman, 2005. Since federal grants to the states may be conditioned upon the state's adoption of certain legal and regulatory structures, the federal government has been able to exercise substantial authority over K—12 education policy. To show causal effects, we exploit discontinuities in the procedure for adopting constitutional amendments to compare outcomes when an amendment passed with those when an amendment failed.
The Constitutional Provisions for Education in India

Amending Constitutional Provisions For a constitutional provision to be amended, it must be approved also known as ratified by two-thirds of the Congress in both the House and the Senate. The Constitutional Provisions for Education in India INTRODUCTION The Constitutional Provisions for Education in India, India got Independence on Assumption , 1947. We briefly summarize them here, leaving the details of the powers and responsibilities given to these branches to specific chapters. It took 2 years 11 month and 18 day to make our constitution. Article I of the Constitution establishes Congress, as well as its main powers. A story, possibly fanciful, depicts the logic: Thomas Jefferson, back from France, sits down for coffee with Washington. Under the Constitution, minorities, whether based on religion or language, are given full rights to establish educational institutions of their choice.







