A collusive oligopoly is a market structure in which a small number of firms cooperate with each other to achieve a common goal, usually to increase profits. In contrast to a competitive market, in which firms compete with each other for customers and market share, a collusive oligopoly involves firms working together to achieve their objectives.
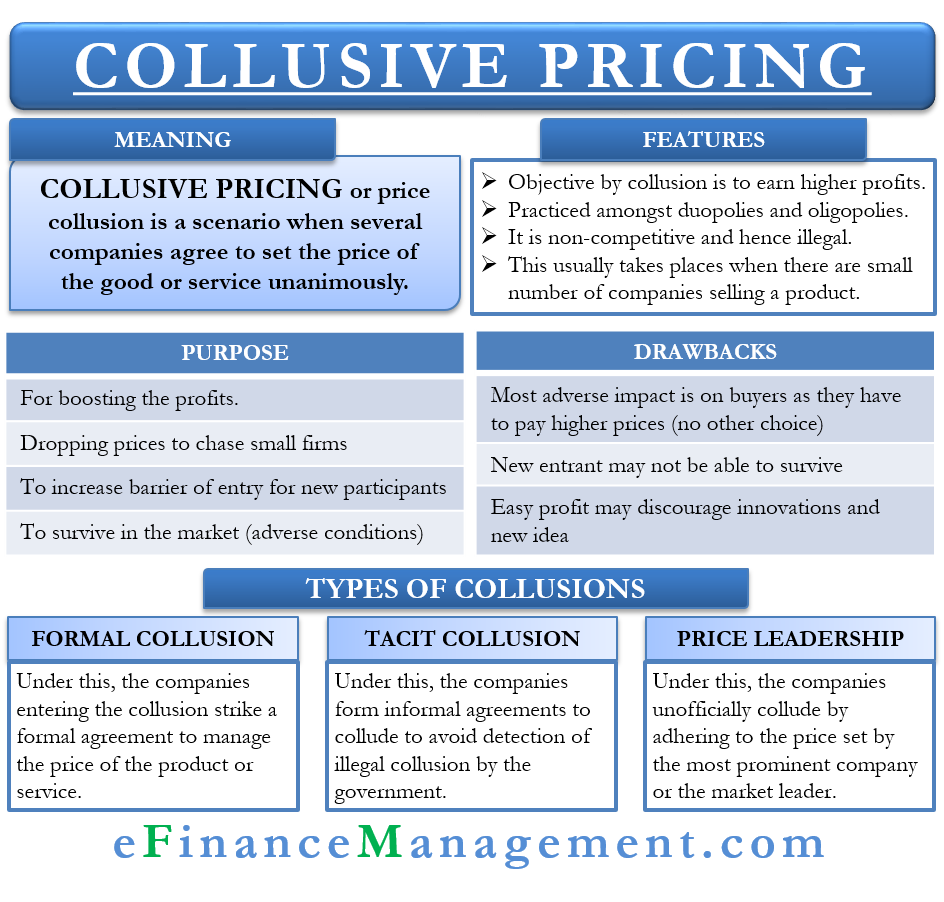
There are several ways that firms in a collusive oligopoly can cooperate with each other. One common form of collusive behavior is price fixing, in which firms agree to charge the same price for their products or services. This can be done directly, through explicit agreements between firms, or indirectly, through signaling or other forms of communication.
Another form of collusive behavior is called output restriction, in which firms agree to limit their production or sales in order to keep prices high. This can be done through a variety of mechanisms, such as quotas, production limits, or marketing agreements.
In addition to price fixing and output restriction, firms in a collusive oligopoly may also engage in other forms of cooperation, such as sharing information or coordinating their investments or operations.
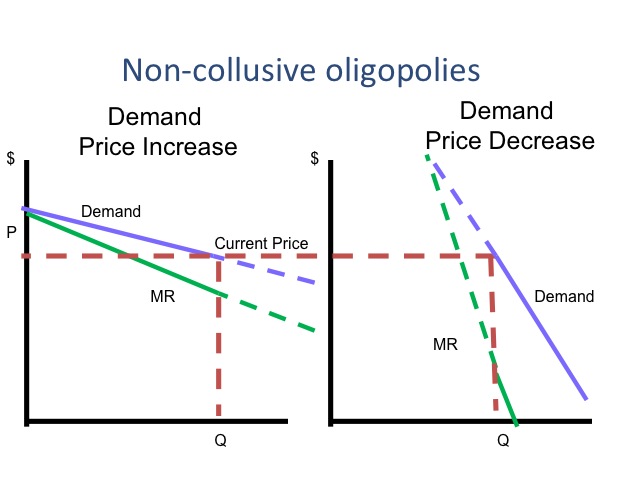
There are several reasons why firms in a collusive oligopoly might choose to cooperate with each other. One reason is to avoid price wars, which can be costly and destructive for all firms involved. By agreeing to charge the same price, firms can avoid the need to constantly adjust their prices in response to competitors' actions, which can lead to a more stable market.
Another reason is to reduce uncertainty and risk in the market. By coordinating their actions, firms can reduce the risk of unexpected changes in demand or supply, which can lead to more predictable profits.
However, collusive oligopolies can also have negative consequences for consumers and the broader economy. By limiting competition, collusive oligopolies can lead to higher prices and reduced innovation. In addition, they can create barriers to entry for new firms, making it harder for them to enter the market and compete with established firms.
Overall, a collusive oligopoly is a market structure in which a small number of firms cooperate with each other to achieve a common goal, typically to increase profits. While this type of market structure can provide some benefits for firms, it can also have negative consequences for consumers and the broader economy.