Classical humanism. Concepts of Classical Humanism 2022-10-24
Classical humanism
Rating:
6,1/10
180
reviews
Classical humanism is a philosophical and cultural movement that emerged in the Renaissance period in Europe and emphasizes the inherent worth and dignity of the individual. This movement is based on the belief that the study of classical literature, history, and philosophy can provide a foundation for living a fulfilling and meaningful life.
Classical humanism was influenced by the rediscovery of the works of ancient Greek and Roman writers, who were seen as models of human excellence and virtue. These writers, such as Plato, Aristotle, and Cicero, believed that humans have the capacity to reason and act with moral integrity, and that this capacity should be cultivated through education and self-improvement.
Classical humanism also emphasizes the importance of individual freedom and choice. It holds that each person has the right to pursue their own goals and interests, and that they are responsible for their own actions. This emphasis on individualism and self-determination is in contrast to the more collectivist and authoritarian values of the Middle Ages.
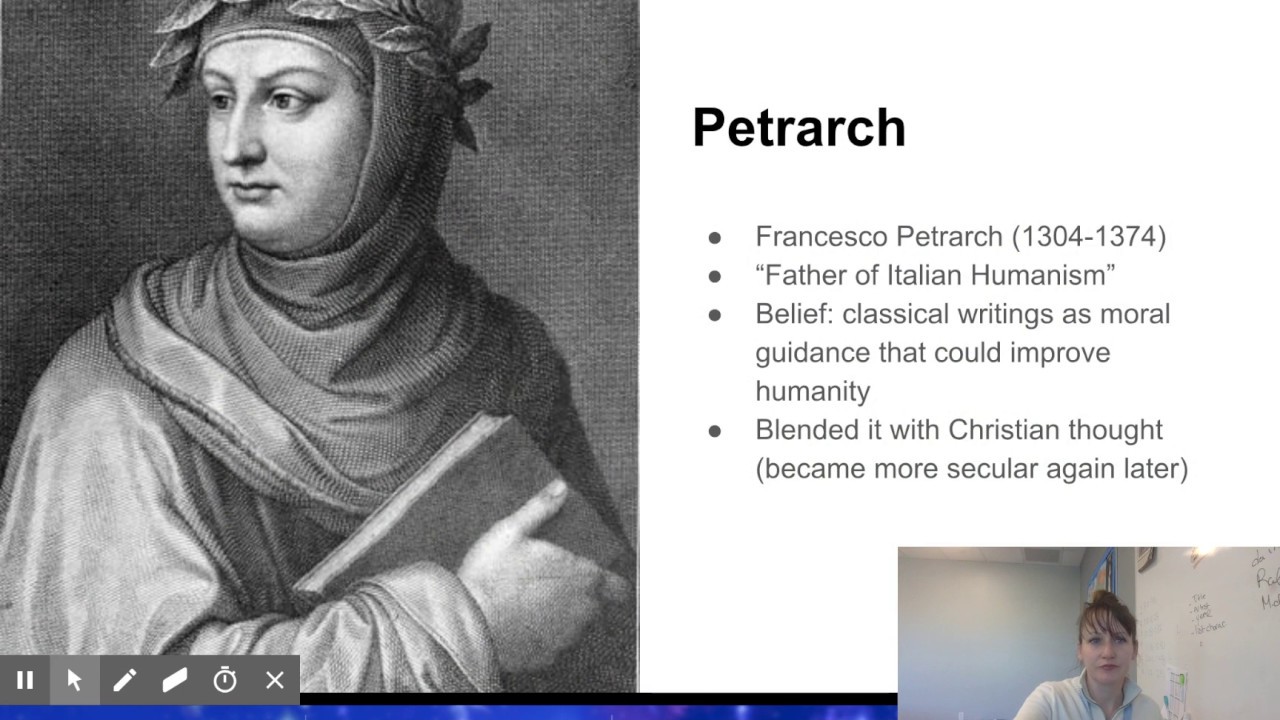
One of the key figures in the development of classical humanism was the Italian scholar and poet Francesco Petrarch, who is often considered the "father of humanism." Petrarch believed that the study of classical literature and history could provide a path to self-improvement and a more enlightened and virtuous life.
Another important figure in the development of classical humanism was the Italian philosopher and statesman Niccolò Machiavelli, whose work The Prince is seen as a key text in the tradition of classical humanism. Machiavelli argued that rulers should act in the best interests of their subjects, and that they should be guided by reason and practicality rather than by traditional moral values.
Classical humanism has had a lasting impact on Western culture and has influenced many of the values and ideals that are central to modern society, such as individual freedom, democracy, and human rights. It has also contributed to the development of the scientific and rational worldview that has shaped the modern world.
Overall, classical humanism represents a belief in the inherent worth and potential of the individual, and a commitment to the cultivation of knowledge and virtue as a means of improving the human condition.
What Was Renaissance Humanism?

. Inspired by their self belief as being the supreme citizens ofGreece, they confidently portrayed themselves among the gods. In general, we may say that humanism, because of its academic character, tends either to interpret the institutional problem in a narrow way or to give it only slight emphasis. Religion is associated with its socological bearers: the institution of the church, the priesthood, the officers and members of the church, the sacraments, and the special disciplines of the church. In other words, theonomy involves the transcending of the autonomous forms of culture and society. God's will was to be followed without question and any attempt to explain a phenomenon without God's involvement was heresy. In Conclusion, The Renaissance Humanists came to be symbolized by the idea of the unlimited potential of the individual.
Next
Free Essay: Classical Humanism And The Renaissance

Social, emotional, intellectual, artistic, practical, and other social skills are all used in humanistic theory as part of their education. . The Italian Renaissance was one of the most productive periods in the history of art, with large numbers of outstanding masters to be found in many centers and in all the major fields painting, sculpture, and architecture. In this connection, we must mention one other aspect of the Christian-humanist conception of human nature, namely, the assertion of the infinite value of the individual personality. Students and scholars came to Italy to study before returning to their homelands carrying humanistic messages. Although Petrarch grew up in Italy, he traveled widely and collected numerous ancient texts. The basic frame of reference or definition of value is valid for all.
Next
Concepts of Classical Humanism

Individualism, humanist philosophy, and the printing press were major components of humanism that made it a crucial influence on Europe during the renaissance period. This is equally true for Christian humanism, for the revolutionary humanism of the seventeenth century and of the late eighteenth century, for the romantic humanism of the twentieth century. Their supporters are themselves divided. Just as theonomy does not represent an orientation which replaces or exists alongside that of autonomy but rather one which goes through and beyond it, so Christianity does not demand a repudiation of culture but rather a deepening and transcending of it. Romantic humanism, as represented by German idealism, overstresses the likeness between the structure of the human mind and that of the absolute mind. Who Was the First Great Humanist? What is humanism as it relates to the Renaissance? This time was the Golden Age of Athens, with the institution of democracy in the city, with a new form of government, citizens were afforded the opportunity to view and understand themselves as constituents of a greater whole, the latter being Athens.
Next
Humanism

Such was, for example, the case of the Florentine Medici. Human realization can take place on earth. From Poets like Sophocles who's play "Antigone" speaks to their influence on humanity at the time. During the Renaissance, there was a great renewal of notice in education and ancient times. Indeed, the similarities between modern humanism and Christianity are for the most part the consequence of the dependence of modern humanism upon Christianity, due to the fact that the humanists of the Middle Ages and of the modern era were nurtured on Christian soil.
Next
What Is Classical Humanism

Retrieved 24 October 2022. The great intellectual movement of Renaissance Italy was humanism. Share this: Facebook Facebook logo Twitter Twitter logo Reddit Reddit logo LinkedIn LinkedIn logo WhatsApp WhatsApp logo The citizens of ancient civilizations lived in a world where the influence of nature and the influence of its rulers minimized the common mans efforts. But Greece in particular has influenced philosophy, which celebrates reason. There is the humanism of Greece and of Rome, colored by the general world-view and religious outlook of paganism. In contrast to this attitude, Christianity views the world as historical, as involved in a process of directed time rather than of cyclic time. In this connection, a very important distinction must be made, a distinction often overlooked by Roman Catholics and orthodox Protestants and also by many exponents of humanism.
Next
History of Humanism With Ancient Greek Philosophers
My advice to any young man is that he return to orthodox Catholicism or Protestantism. The illustration opted for human reason as a beacon to illuminate the darkness of existence, fighting ignorance, tyranny, superstition and betting on a world designed economically, socially and politically for man. These are but a few of the Greek philosophers, artists, and politicians whose ideas and actions not only represented a break from a superstitious and supernaturalistic past but also posed a challenge for the systems of religious authority in the future. Although modern humanism, as distinguished from ancient humanism, is largely dependent upon Christianity, we may identify certain elements as common to Christianity and ancient humanism. There is also another besetting sin of historical Christianity and of humanism which should be mentioned, for it will serve to bring into relief another aspect of the fundamental difference between Christianity and humanism. The humanistic identity stands in opposition to extreme forms of national, religious, racial, and gender identity. His reply was shockingly emphatic for a man of poise and vision.
Next
Understanding humanism

The study of old Latin and Greek literature was the subject of humanism. This was shown in many ways with their architecture at the time, none more evident than the Parthenon inAthenswhich proudly, and some may say arrogantly, displayed the Athenians as a higher class of citizen I Greece and throughout the region. Auguste Comte and the Religion of Humanity: The Post-theistic Program of French Social Theory. Humanism comes as a belief just as well as religion and can be interpreted in many ways. . .
Next
Humanism: Summary, Representatives and Characteristics

The Christian attitude towards nature grows out of the view that God is the Creator of nature, as well as of man, that the heavens and the hills declare the Glory of God. Mostly every person from the Renaissance believed in the humanism in one way or another, even people of the once strict church. This technique is introduced by Giotto who was one of the greatest figures in the history of Florentine painting, and his greatness was recognized very early on. The result is that there are as many types of Christianity or of humanism as there are of anti-Christianity or of anti-humanism. Shiban Khan, Ernst von Kimakowitz, Michael Pirson, Wolfgang Amann.
Next




