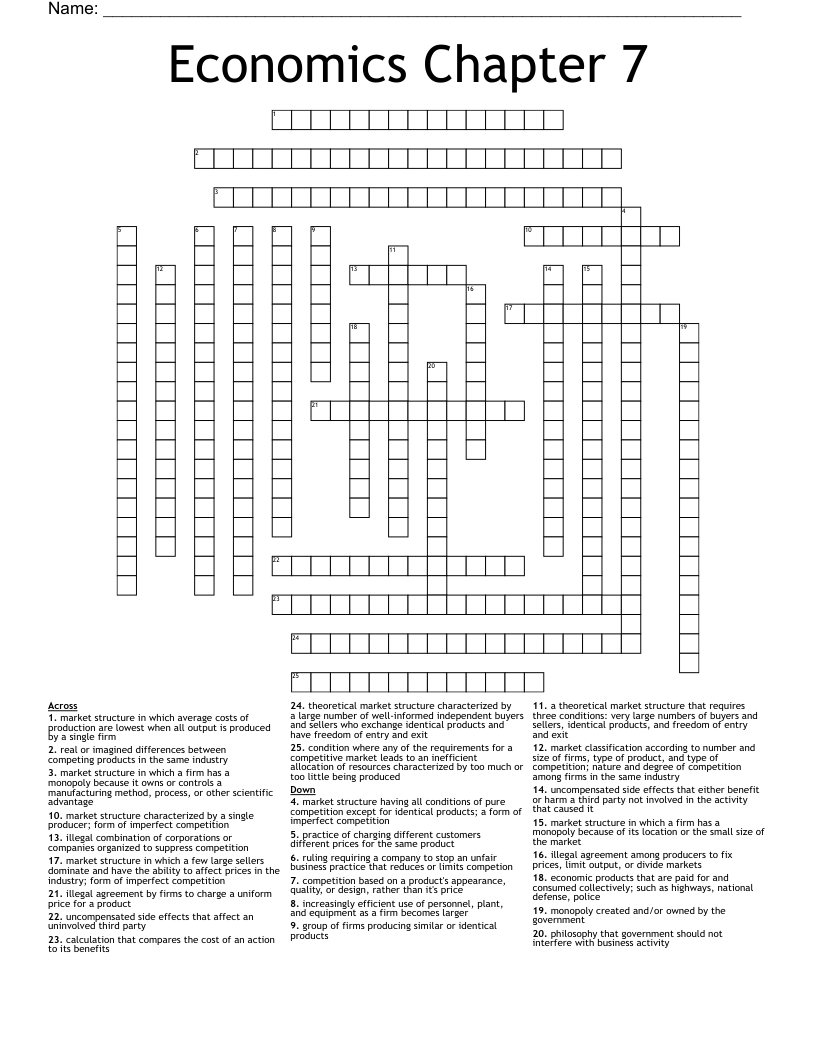
Market structures refer to the various ways in which the market for a particular product or service is organized. These structures can be characterized by the level of competition among firms, the type of goods or services being produced, and the degree of differentiation among products. Understanding the different market structures is important for firms as it helps them to determine the most appropriate strategies for pricing, production, and marketing. In this essay, we will explore the main types of market structures, including perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly, and discuss their key features and implications for firms operating in these markets.
Perfect competition is a market structure in which there are a large number of firms producing identical products and selling them to a large number of buyers. In this type of market, firms are price takers, meaning that they have no control over the price of their product and must accept the price set by the market. Firms in a perfectly competitive market are unable to differentiate their products from those of their competitors, and so they must compete on the basis of price alone.
One of the key features of a perfectly competitive market is that there are no barriers to entry or exit. This means that any firm can enter the market and start producing the same product as its competitors, and any firm can leave the market if it is not profitable. This constant flow of firms entering and exiting the market helps to ensure that supply and demand are in balance, and that prices remain stable.
While perfect competition is a theoretical concept that does not exist in reality, it serves as a useful benchmark for comparing other market structures. In practice, most markets fall somewhere between perfect competition and monopoly, with varying degrees of competition and differentiation among firms.
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which there are many firms producing similar, but not identical, products. This type of market is characterized by a high degree of differentiation among products, as firms try to distinguish their products from those of their competitors through branding, packaging, and other marketing strategies. Firms in a monopolistically competitive market have some control over the price of their product, but they still face significant competition from other firms.
Oligopoly is a market structure in which there are only a few firms producing a particular product or service. In an oligopoly, firms are interdependent, meaning that the actions of one firm can have a significant impact on the other firms in the market. This can lead to strategic behavior, such as price collusion or price leadership, in which firms coordinate their pricing decisions in order to maximize profits. Oligopoly markets are often characterized by high barriers to entry, which help to protect the incumbent firms from new competition.
Monopoly is a market structure in which there is only one firm producing a particular product or service. This firm has complete control over the price of its product and is the only supplier in the market. Monopolies can arise when a firm has a patent on a product, or when it is the only firm with the necessary resources or expertise to produce a particular product. Monopolies are often heavily regulated by governments in order to prevent abuse of market power and to ensure that consumers have access to reasonable prices.
In summary, market structures refer to the ways in which the market for a particular product or service is organized. The main types of market structures include perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Each of these market structures has its own characteristics and implications for firms operating in the market, and understanding these differences can help firms to develop appropriate strategies for pricing, production, and marketing.