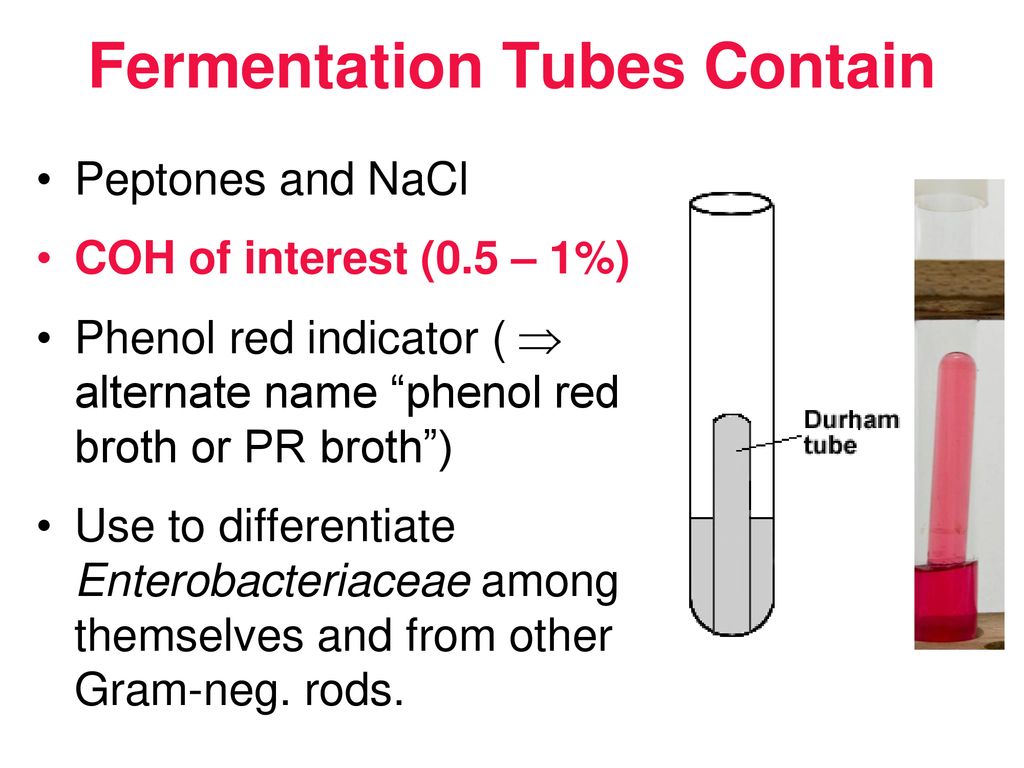
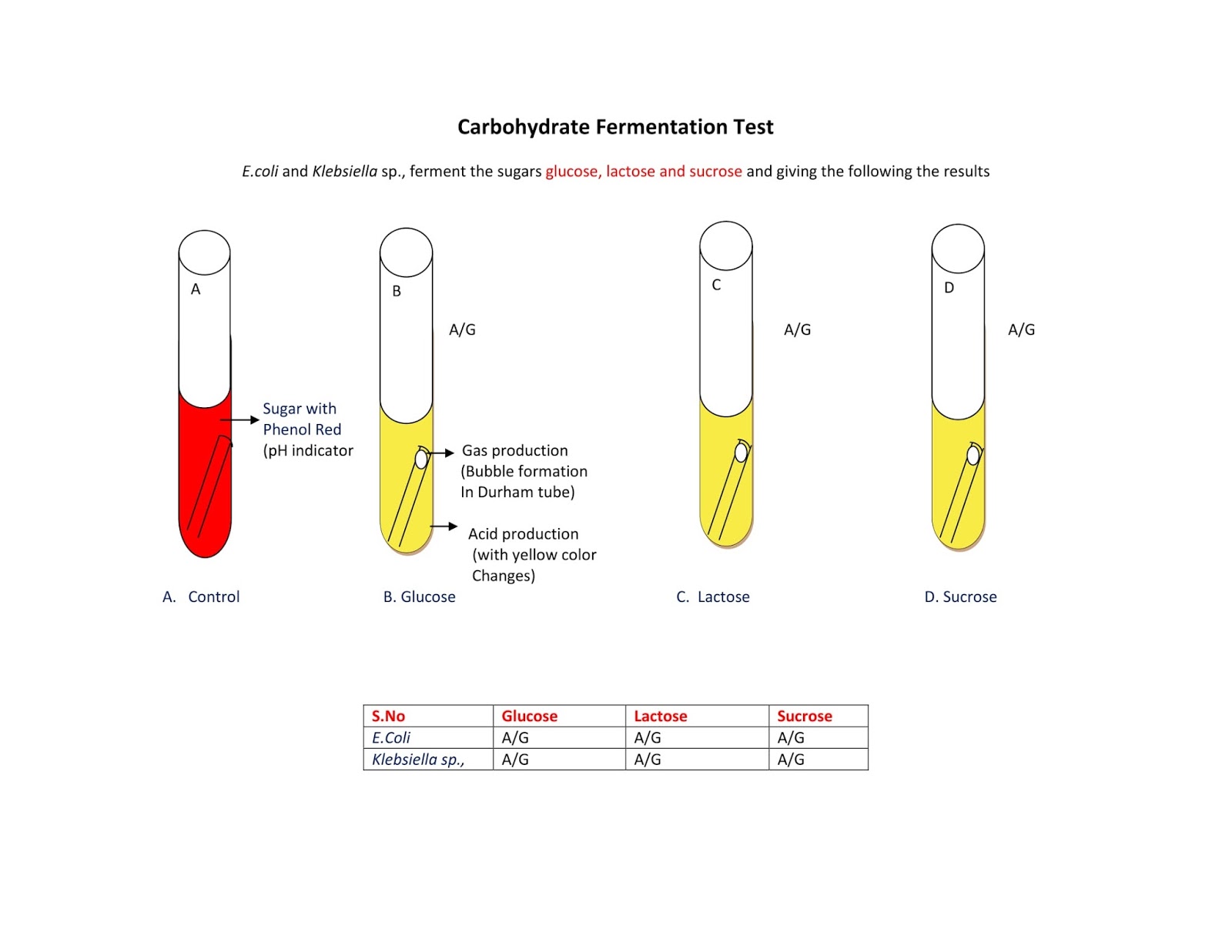
Carbohydrate fermentation tests are a type of laboratory procedure used to identify and classify microorganisms based on their ability to produce specific metabolic end products during the process of carbohydrate fermentation. These tests are commonly used in microbiology laboratories to identify and differentiate between different types of bacteria and yeast.
Carbohydrate fermentation involves the breakdown of sugars, such as glucose and lactose, by microorganisms using anaerobic respiration. During this process, the microorganisms consume the sugars as a source of energy and produce various metabolic end products, such as lactic acid, ethanol, and acetic acid. The presence and amount of these end products can be used to identify and classify different types of microorganisms.
There are several different types of carbohydrate fermentation tests that can be performed, including the methyl red test, Voges-Proskauer test, and citrate utilization test. Each of these tests is used to detect the production of specific end products during carbohydrate fermentation.
The methyl red test is used to detect the production of lactic acid and acetic acid during carbohydrate fermentation. In this test, a small amount of the test microorganism is grown in a liquid medium containing a specific carbohydrate. If the microorganism is able to produce lactic acid or acetic acid during carbohydrate fermentation, the pH of the medium will become acidic. A small amount of methyl red indicator is then added to the medium, and the presence of red color indicates a positive result for the production of lactic acid or acetic acid.
The Voges-Proskauer test is used to detect the production of acetylmethylcarbinol (AMC) and acetoin during carbohydrate fermentation. In this test, a small amount of the test microorganism is grown in a liquid medium containing a specific carbohydrate. If the microorganism is able to produce AMC and acetoin during carbohydrate fermentation, the medium will become alkaline. A small amount of potassium hydroxide and alpha-naphthol are then added to the medium, and the presence of a pink color indicates a positive result for the production of AMC and acetoin.
The citrate utilization test is used to detect the ability of microorganisms to utilize citrate as a sole source of carbon during carbohydrate fermentation. In this test, a small amount of the test microorganism is grown in a liquid medium containing citrate as the sole source of carbon. If the microorganism is able to utilize citrate as a sole source of carbon, it will produce a green color in the medium.
Overall, carbohydrate fermentation tests are a valuable tool in the identification and classification of microorganisms. These tests allow microbiologists to determine the metabolic capabilities of different microorganisms, which can be useful in a variety of applications, including food safety, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnosis.