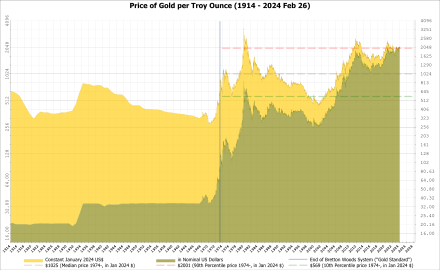
The Bretton Woods system was a monetary system established in 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference in New Hampshire, United States. It was designed to provide stability in the international monetary system following World War II and to facilitate international trade and economic growth. The system was based on the idea of fixed exchange rates, with the United States dollar serving as the world's reserve currency and the anchor for the system.
Under the Bretton Woods system, countries pegged their currencies to the US dollar, and the US dollar was pegged to gold at a fixed rate of $35 per ounce. This meant that the value of other currencies was fixed in relation to the US dollar, and the value of the US dollar was fixed in relation to gold. This system was designed to provide stability in the international monetary system and to prevent competitive devaluations of currencies that had occurred in the past.
The Bretton Woods system worked well for many years, and the international monetary system was relatively stable during this time. However, by the 1960s, a number of factors began to undermine the stability of the system. One of the main factors was the cost of the Vietnam War, which led to increased government spending and a resulting increase in the supply of US dollars. This led to a decline in the value of the US dollar, which put pressure on the Bretton Woods system.
Another factor that contributed to the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system was the emergence of new economic powers, such as Japan and Germany, which were rapidly growing and becoming more competitive in international trade. These countries began to accumulate large trade surpluses, which led to an increase in the demand for their currencies. This put pressure on the fixed exchange rate system, as countries with trade surpluses wanted to revalue their currencies to reflect their growing economic strength.
In 1971, the US government faced a crisis when it was unable to maintain the fixed exchange rate of the US dollar to gold. In response, President Nixon suspended the convertibility of the US dollar to gold, effectively ending the Bretton Woods system. This event, known as the Nixon Shock, marked the end of the Bretton Woods system and the beginning of a new era of floating exchange rates.
The breakdown of the Bretton Woods system had significant consequences for the international monetary system and the global economy. It marked the end of the era of fixed exchange rates and the beginning of an era of floating exchange rates, in which the value of currencies is determined by the forces of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. This has led to increased volatility in the value of currencies and has made it more difficult for countries to manage their exchange rates and maintain stability in their economies.
Overall, the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system was a significant event in the history of the international monetary system and had far-reaching consequences for the global economy. It marked the end of an era of fixed exchange rates and the beginning of an era of floating exchange rates, which has had both positive and negative effects on the global economy.