Bone regions united by fibrous connective tissue. Fibrous Connective Tissue Function & Types 2022-10-27
Bone regions united by fibrous connective tissue
Rating:
6,3/10
1937
reviews
Fibrous connective tissue is a type of tissue that plays an important role in the body by connecting and supporting various structures. One specific area where fibrous connective tissue is prevalent is in the bones.
There are several different regions of the bone that are united by fibrous connective tissue, including the epiphyseal plate, the periosteum, and the joint capsule.
The epiphyseal plate, also known as the growth plate, is a thin layer of hyaline cartilage located at the ends of long bones in growing children and adolescents. This plate is responsible for the growth of the bones, as it allows the bone to lengthen during periods of growth. The epiphyseal plate is surrounded by fibrous connective tissue, which helps to stabilize the bone and keep it in place as it grows.
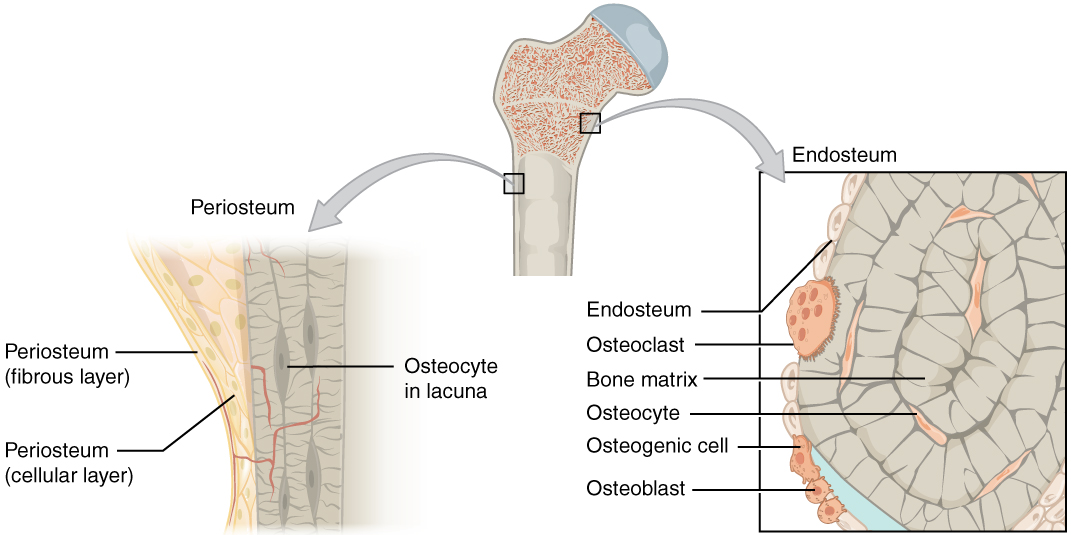
The periosteum is a thin layer of fibrous connective tissue that covers the outer surface of bones. It serves several important functions, including the formation of new bone tissue during the healing process and the attachment of tendons and ligaments to the bone. The periosteum is also rich in blood vessels, which helps to nourish the bone tissue and keep it healthy.
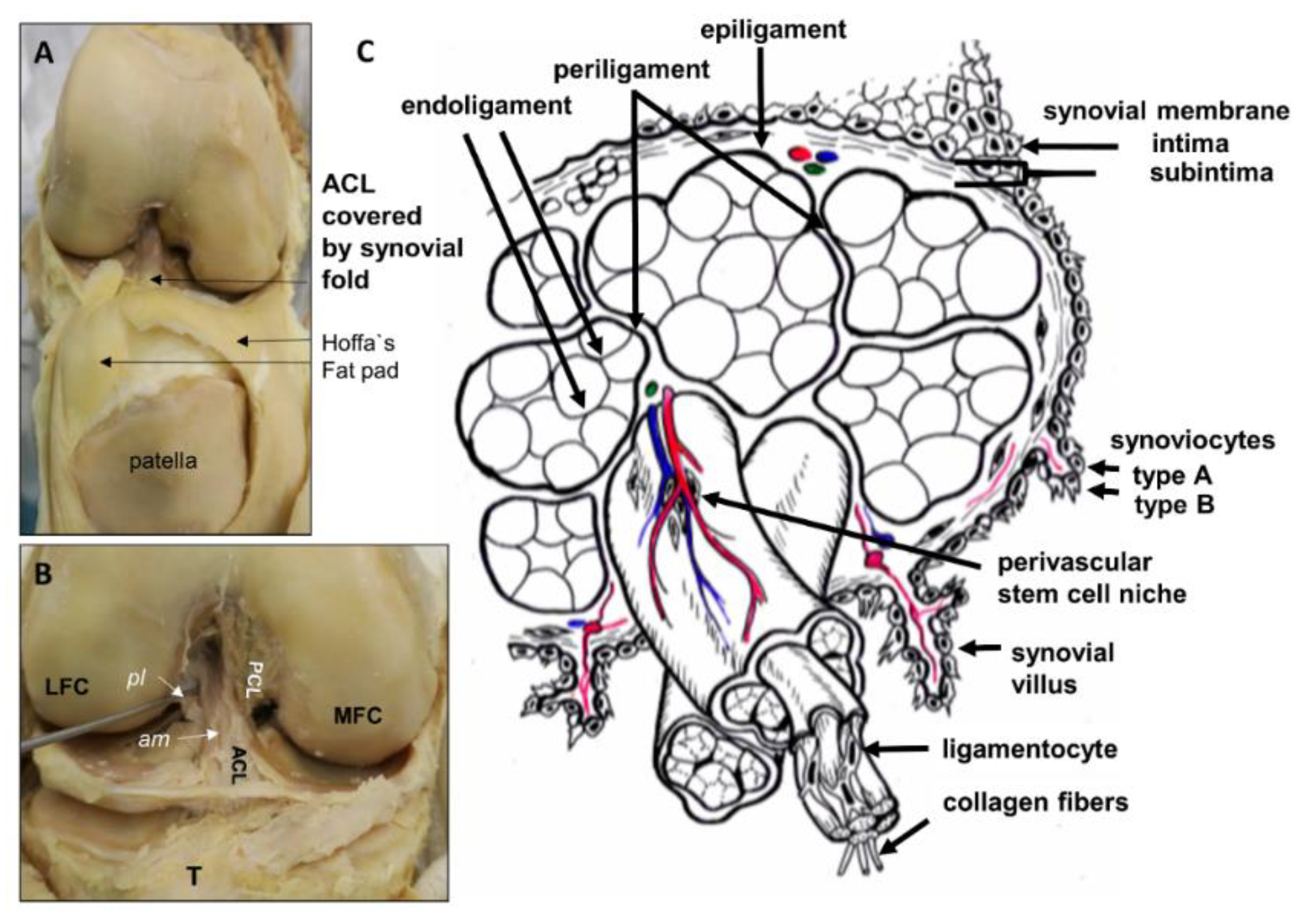
The joint capsule is a fibrous structure that surrounds joints and helps to hold the bones in place. It is made up of two layers: the outer fibrous layer and the inner synovial layer. The outer fibrous layer is made up of dense connective tissue, while the inner synovial layer is made up of a thin membrane that produces synovial fluid to lubricate the joint. The joint capsule helps to stabilize the joint and protect it from injury, and it is also rich in sensory receptors, which allow the brain to sense joint movement and position.
In conclusion, fibrous connective tissue plays a vital role in the bones by connecting and supporting various regions, including the epiphyseal plate, the periosteum, and the joint capsule. These structures help to maintain the structural integrity of the bones and allow them to function properly.
8.3: Fibrous Joints

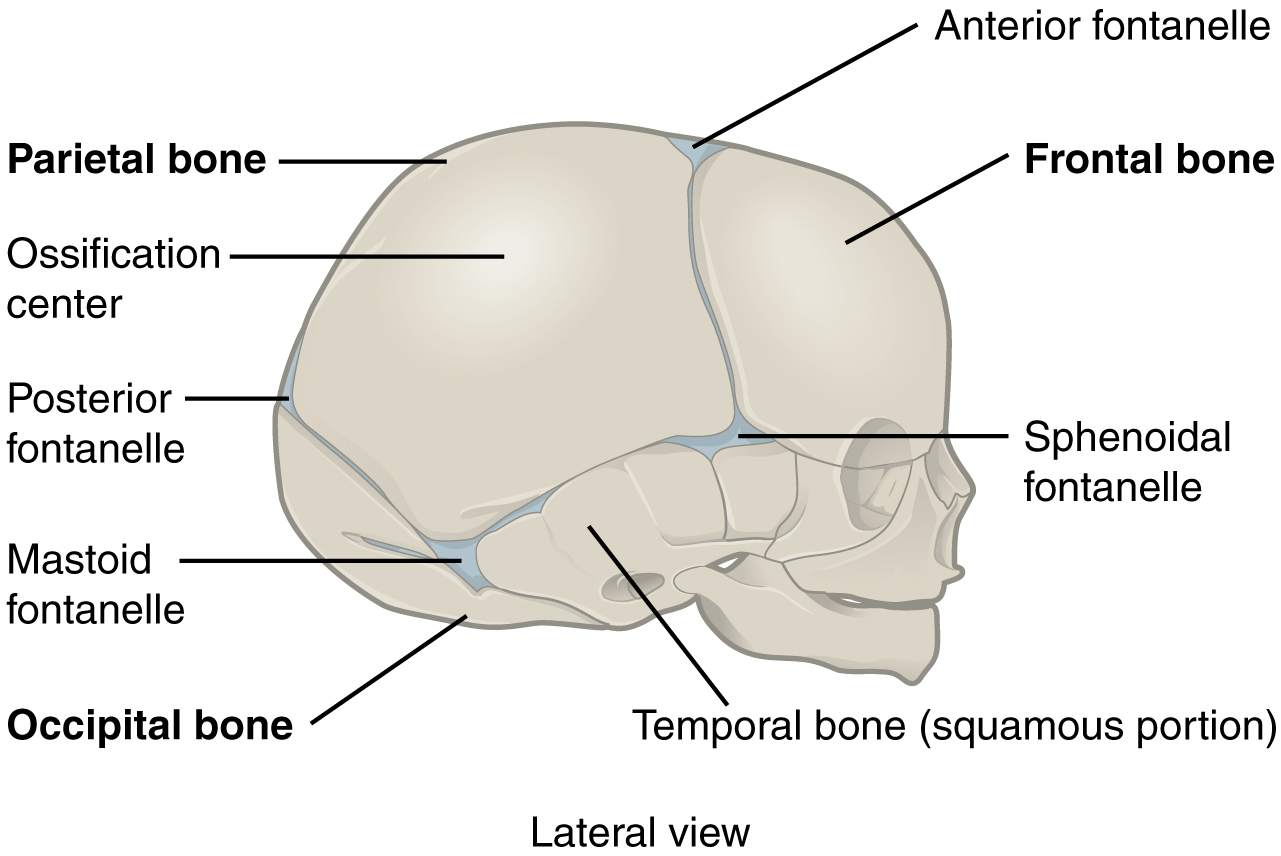
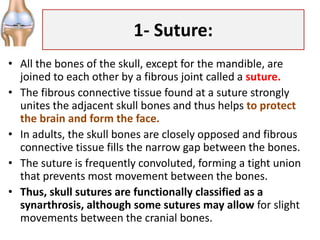
Distinguish between a narrow and wide fibrous joint and give an example of each. A suture is the fibrous joint that joins the bones of the skull to each other except the mandible. A syndesmosis is the type of fibrous joint found between parallel bones. In newborns and infants, the areas of connective tissue between the bones are much wider, especially in those areas on the top and sides of the skull that will become the sagittal, coronal, squamous, and lambdoid sutures. In addition, at the distal tibiofibular joint, the narrow gap between the bones is anchored by fibrous connective tissue and ligaments on both the anterior and posterior aspects of the joint.
Next
Fibrous Connective Tissue Function & Types
A syndesmosis is an amphiarthrotic fibrous joint found between parallel bones. Fibrous joints strongly unite adjacent bones and thus serve to provide protection for internal organs, strength to body regions, or weight-bearing stability. Describe how scurvy, a disease that inhibits collagen production, can affect the teeth. The syndesmoses found in the forearm and leg serve to unite parallel bones and prevent their separation. Is the pelvis a fibrous joint? The paratenon is located outside of the epitenon and lets the tendon move against the other tissues in the body that connect to the tendon. The synovium is the outer layer of connective tissue that is found in the tendons of the hands and feet.
Next
Fibrous Joints

When the connective tissue between the adjacent bones is reduced to a narrow layer, these fibrous joints are now called sutures. The ankles have three main ligaments that hold them together. Fibrous connective tissue is a type of connective tissue that is composed of sturdy, but flexible collagen fibers. Which of the following has bone regions united by fibrous connective tissue? In scurvy, collagen production is inhibited and the periodontal ligaments become weak. The posterior fontanelle can be found on the back side of the skull between the parietal bones and occipital bone. The most prominent fontanelle is the anterior fontanelle, which can be found on top of the skull between the frontal bone and the parietal bones.
Next
Which joints are held together by fibrous connective tissue?
There are multiple muscles in the back area and they are all connected to each other through fasciae. Narrow fibrous joints are found at a suture, gomphosis, or syndesmosis. The tooth is connected to the bony jaw by periodontal ligaments. They also separate, stabilize and enclose muscles in the body. The different fibrous connective tissue types are explained below.
Next
9.2 Fibrous Joints

In the leg, the syndesmosis between the tibia and fibula strongly unites the bones, allows for little movement, and firmly locks the talus bone in place between the tibia and fibula at the ankle joint. The teeth are anchored into their sockets within the bony jaws by the periodontal ligaments. The three types of fibrous joints are sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses. What are the 3 types of fibrous joints? The gap filled by connective tissue may be narrow or wide. Fasciae allow the muscles to move as they contract but prevent them from moving too far apart from each other.
Next

The fontanelles greatly decrease in width during the first year after birth as the skull bones enlarge. It also helps to anchor down and support the organs of the body. What are types of fibrous joints? See a Thus, skull sutures in the adult are functionally classified as a synarthrosis. Late in life, the sagittal, coronal, and lambdoid sutures of the skull will begin to ossify and fuse, causing the suture line to gradually disappear. Ligaments are also in place to hold organs together such as the organs of the digestive system.
Next
The tendons allow the muscles to move the bones of the body by moving bones when the muscles contract. In the leg, the syndesmosis between the tibia and fibula strongly unites the bones, allows for little movement, and firmly locks the talus bone in place between the tibia and fibula at the ankle joint. Image credit: Suture All the bones of the skull, except for the mandible, are joined to each other by a fibrous joint called a suture. This is a gomphosis type of fibrous joint. If the fracture site is not properly immobilized with a cast or splint, contractile activity by these muscles can cause improper alignment of the broken bones during healing.
Next

Narrow fibrous joints are found at a suture, gomphosis, or syndesmosis. There are areas of the body where there are large muscle groups that need to be connected to each other. Suture All the bones of the skull, except for the mandible, are joined to each other by a fibrous joint called a suture. Fasciae The fasciae are the fibrous connective tissues that connect the muscles in the body to other muscles in the body. The endotenon surrounds the fibers of the tendon and allows them to easily move as the muscle moves the bones.
Next
After birth, these expanded regions of connective tissue allow for rapid growth of the skull and enlargement of the brain. A syndesmosis can also form a wide fibrous joint where the shafts of two parallel bones are connected by a broad interosseous membrane. A syndesmosis is the type of fibrous joint found between parallel bones. A suture is the narrow fibrous joint found between most bones of the skull. This is a gomphosis type of fibrous joint.
Next

This type of fibrous joint is found between the shaft regions of the long bones in the forearm and in the leg. This provides strength and stability to the leg and ankle, which are important during weight bearing. Which type of fibrous joint connects the tibia and fibula? The interosseous membranes of the leg and forearm also provide areas for muscle attachment. At the time of birth, the frontal and maxillary bones consist of right and left halves joined together by sutures, which disappear by the eighth year as the halves fuse together to form a single bone. Chapter Review Fibrous joints are where adjacent bones are strongly united by fibrous connective tissue. They include; the ligaments, which are the fibrous connective tissues that attach the bones to the other bones in the body, tendons, which are the fibrous connective tissue that connects the bones to the muscles of the body, and fasciae, which are the fibrous connective tissue that connects one muscle to another muscle in the body.
Next









