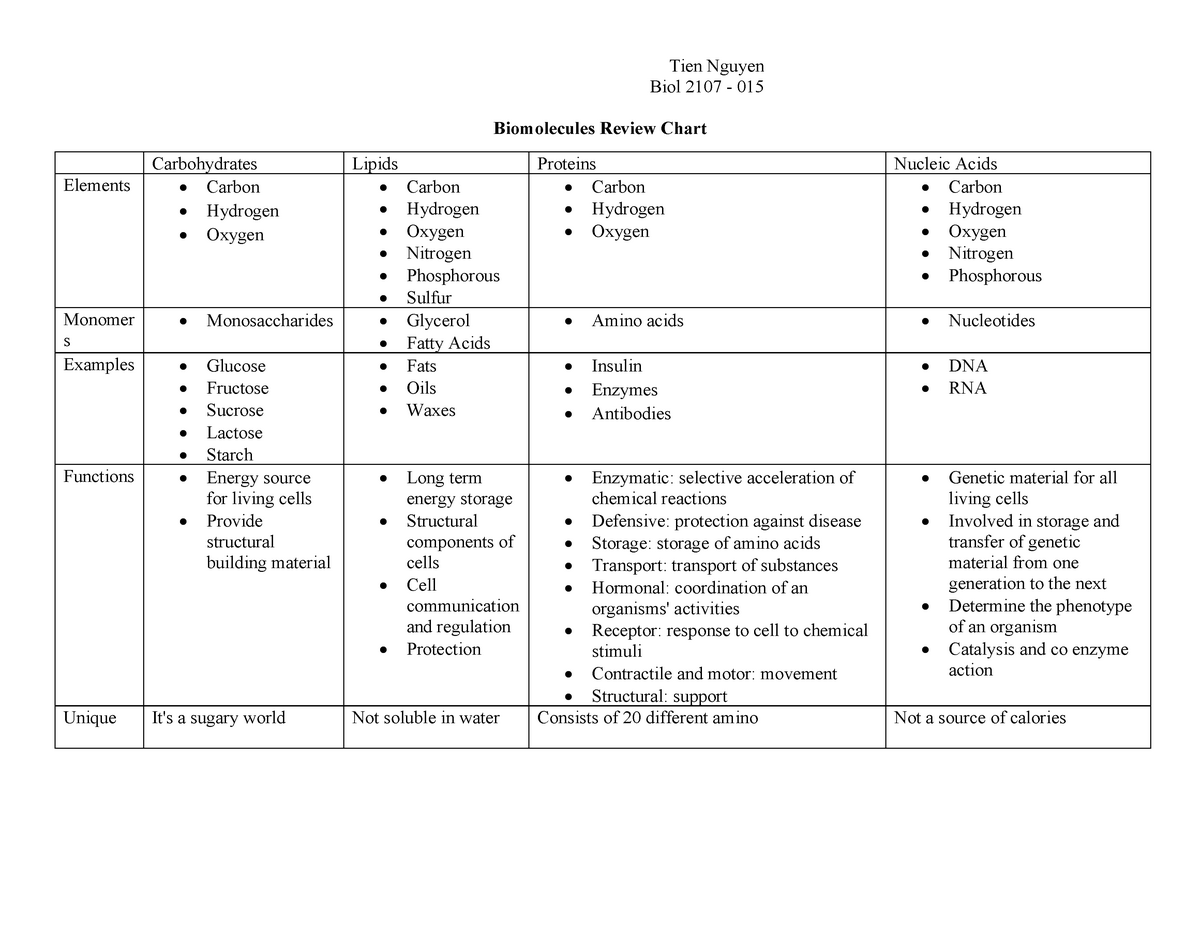
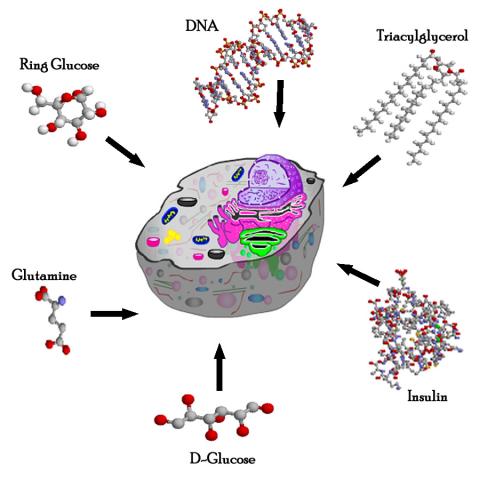
Biomolecules are organic molecules that are found in living organisms and perform various essential functions. These molecules are essential for the proper functioning of the body and play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of an individual. Biomolecules can be classified into four major categories: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Carbohydrates are biomolecules that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are a source of energy for the body and are found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, and grains. Carbohydrates can be classified into two categories: simple carbohydrates, which are found in foods such as sugar and honey, and complex carbohydrates, which are found in foods such as bread and pasta.
Lipids are biomolecules that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms and are characterized by their ability to dissolve in organic solvents such as alcohols. Lipids are an important source of energy for the body and are found in foods such as fats, oils, and waxes. There are several types of lipids, including triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesterol.
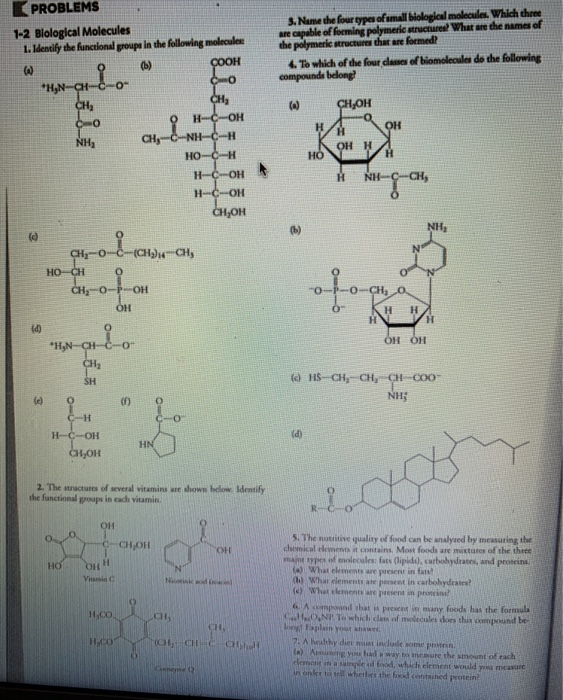
Proteins are biomolecules that are composed of long chains of amino acids. They perform a variety of functions in the body, including building and repairing tissues, regulating the body's metabolism, and supporting immune function. Proteins are found in foods such as meat, eggs, and dairy products.
Nucleic acids are biomolecules that are composed of long chains of nucleotides. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA is the genetic material that contains the instructions for the synthesis of proteins, while RNA is involved in the synthesis of proteins and the transmission of genetic information. Nucleic acids are found in all living cells and are essential for the proper functioning of the body.
In conclusion, biomolecules are essential for the proper functioning of the body and play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of an individual. They can be classified into four major categories: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, and each of these biomolecules performs specific functions in the body.