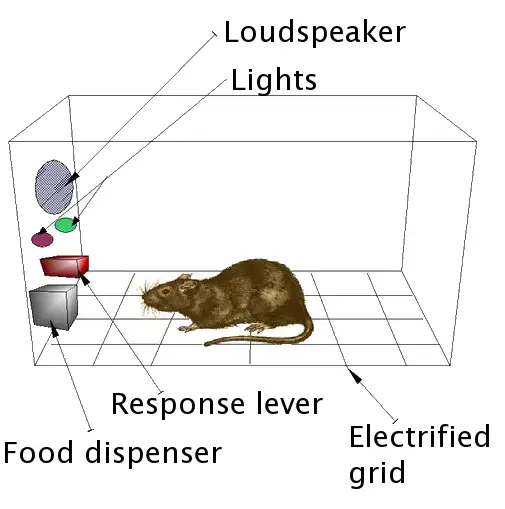
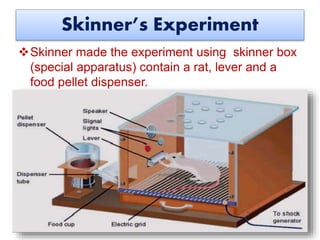
B.F. Skinner was a 20th century psychologist who is best known for his contributions to the field of behaviorism and his theory of operant conditioning.
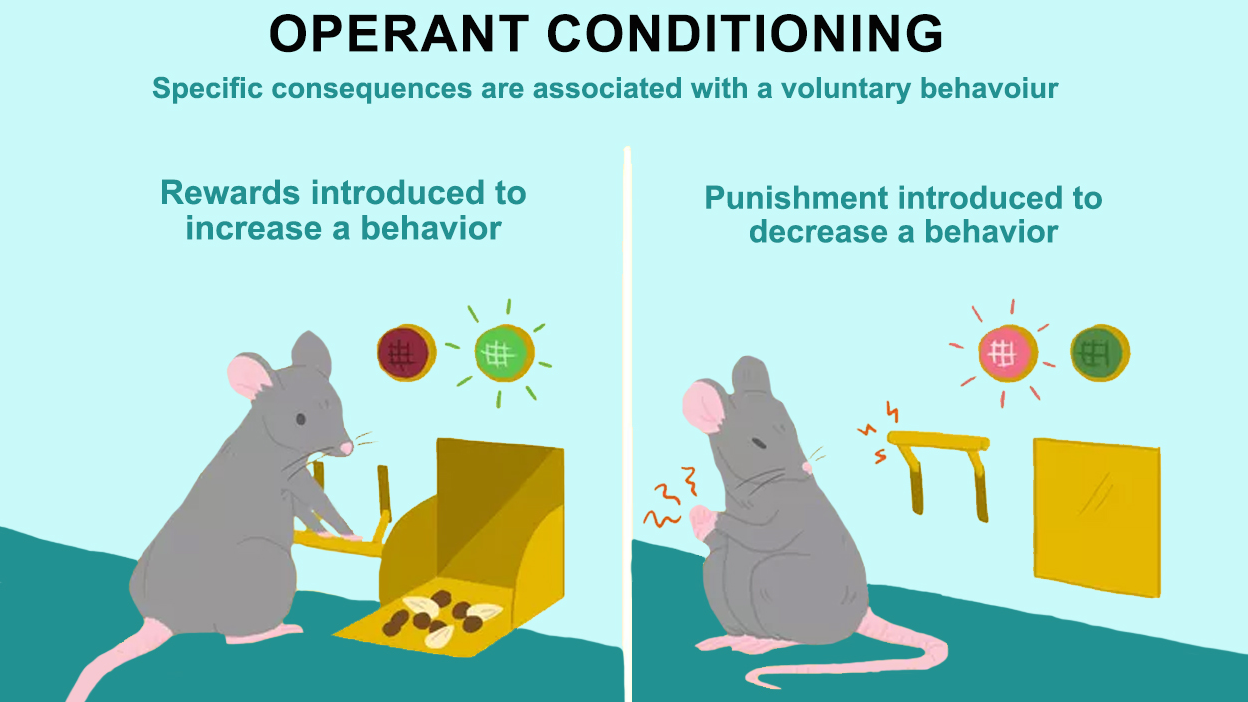
Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which an animal or human learns to associate a particular behavior with a particular consequence. This type of learning occurs through the use of reinforcement and punishment. Reinforcement is something that increases the likelihood that a behavior will be repeated, while punishment is something that decreases the likelihood that a behavior will be repeated.
Skinner believed that all behavior is determined by its consequences and that the best way to understand and modify behavior is through the use of reinforcement and punishment. He argued that we are all essentially "operating" on the environment in order to get what we want and that the consequences of our actions shape our future behavior.
One of the key concepts in operant conditioning is the idea of a "schedule of reinforcement." This refers to the timing and frequency with which reinforcement is provided. Skinner found that different schedules of reinforcement can produce different behaviors. For example, a continuous reinforcement schedule, in which a behavior is reinforced every time it is performed, can lead to a rapid acquisition of a new behavior. On the other hand, an intermittent reinforcement schedule, in which a behavior is reinforced only sometimes, can lead to a more persistent and resistant behavior.
Skinner's work on operant conditioning has had a significant impact on the field of psychology and has been applied in a variety of settings, including education, therapy, and the workplace. It has also been influential in the development of behavior modification techniques, which are used to help individuals change their behavior in order to improve their quality of life.
Despite the contributions of Skinner and operant conditioning, it is important to note that there are other theories of learning and behavior that have also contributed to our understanding of how we learn and behave. These include cognitive theories, which focus on the role of mental processes in learning and behavior, and social learning theories, which emphasize the importance of social and environmental factors in shaping behavior.
Overall, B.F. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning remains an important and influential part of psychology and has helped to shape our understanding of how we learn and behave.