The growth rate of bean plants varies depending on several factors, including the type of bean, the climate, and the soil conditions. Some bean plants, such as pole beans and runner beans, can grow up to several feet in a single growing season, while others, such as bush beans, tend to grow more slowly.
One key factor that affects the growth rate of bean plants is the type of bean. Some bean plants, such as pole beans and runner beans, are climbers that use long, slender stems to reach for support. These types of beans tend to grow more quickly than bush beans, which have shorter, sturdier stems and do not need to climb.
Another important factor that affects the growth rate of bean plants is the climate. In general, bean plants prefer warm, sunny conditions with plenty of moisture. In cooler or drier climates, bean plants may grow more slowly or produce fewer beans.
Soil conditions can also impact the growth rate of bean plants. Bean plants need well-draining soil that is rich in nutrients in order to thrive. If the soil is too dry or too compact, it may hinder the growth of the bean plants. On the other hand, if the soil is too wet or has poor drainage, the plants may be prone to root rot and other diseases that can slow their growth.
Overall, the growth rate of bean plants can vary widely depending on the type of bean, the climate, and the soil conditions. To encourage the fastest possible growth, it is important to choose the right type of bean for your climate, plant the beans in well-draining soil that is rich in nutrients, and provide the plants with plenty of sunshine and water.
Elements Affecting the Growth of Bean Plants
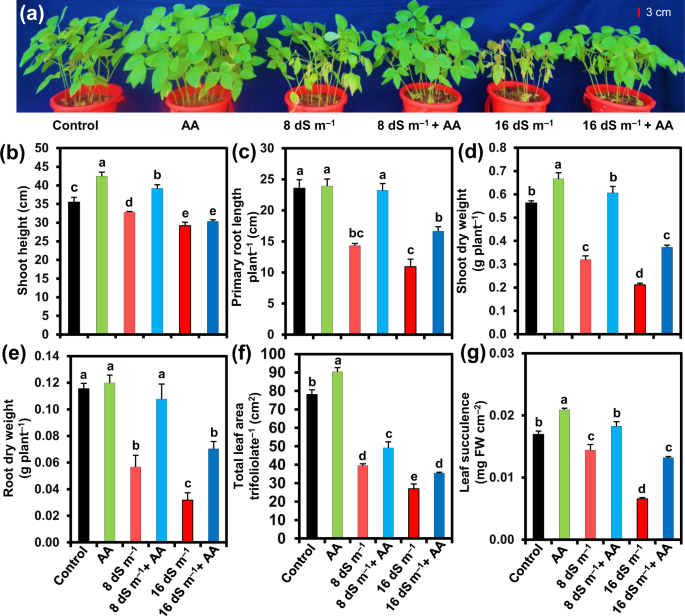
The fruit of this plant, referred to as a pod or bean, is harvested and turned into vanilla extract. Therefore, my hypothesis was proven Lab : Extended Experimental Investigation Aim: For the growth of all plants, specific levels of pH in the soil and in the plants themselves are important. I have another smaller plant to compare to and this one looks similar but longer. The auxins that stimulate growth gather on the shady side of the plant where the cells continue to elongate, causing the plant to bend at that spot toward the source of light. The root of the seed serves many purposes: it transports water and minerals to feed the plant itself and it also A Summary Of Phaseolus Abstract The sclerenchyma ring in the stem of Phaseolus lunatus, commonly known as lima bean, was measured in relation to the wavelength of light they were grown in 650, 475 nm.
bean plant research paper

A second cultivation at planting time removes the sprouted weeds. Some plants require several variables for successful seed germination. Never work around wet beans, and buy quality seed. Native to North America, green beans are members of the Leguminocae family and have been cultivated worldwide for more than 7,000 years. Incompatibles Basil, fennel, garlic, gladiolus, onion family.
Coffee Plant: Care & Growing Guide

R8 Full maturity: 95 percent of the pods have reached their mature pod color. Beans fall under three primary classifications -- snap or green beans, which may be either bush or pole varieties; dry beans, such as pinto or kidney beans; and shelled beans, such as lima beans, fava beans and black-eyed peas. If a fungal infection does occur, you may need to remove the infected plants to prevent the further spread of the disease. Make a hill at the base of each pole, enriched with compost or well-rotted manure, and plant 6-8 seeds in each. Bush, half runner and pole beans seem to race through the life cycle. The basic plant life cycle with alternation of generations is modified in angiosperms by the change of haploid n and diploid 2n generations, which take turns making each other.
Facts About Green Bean Plant Growth

Because these roots are growing close to the soil surface, cultivation to control weeds should be shallow. Some types of rot are successfully treated with commercial fungicides. V2 Stage second node At the V2 stage, the plants are 6 to 8 inches tall and three nodes have leaves with unfolded leaflets the unifoliolate node and the first two trifoliolate leaf nodes. At this stage, the plant has only accumulated about 25 percent of its total mature dry weight and nutrients, attained about 50 percent of its mature height, and has produced about 50 percent of its total mature node number. At R1, vertical root growth rates sharply increase and stay relatively high to the R4 to R5 stage.
Bean Growing and Harvest Information
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-grow-purple-hyacinth-bean-plants-412553205-debca3e07b304019817a959b406b3459.jpg)
The period of rapid, steady seed dry weight accumulation continues until shortly after R6. This node is unique in that the unifoliolate simple leaves are produced from it on opposite sides of the stem and are borne on short petioles. Called "cherries," the fruit should be picked when they're a bright crimson color. Fertilize your potted vanilla plants every two weeks throughout the spring and summer with a light dose of all-purpose or orchid fertilizer. Each branch develops trifoliolate leaves, nodes, axils, axillary buds, flowers, and pods similar in nature to the main stem.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-grow-purple-hyacinth-bean-plants-412553205-debca3e07b304019817a959b406b3459.jpg)