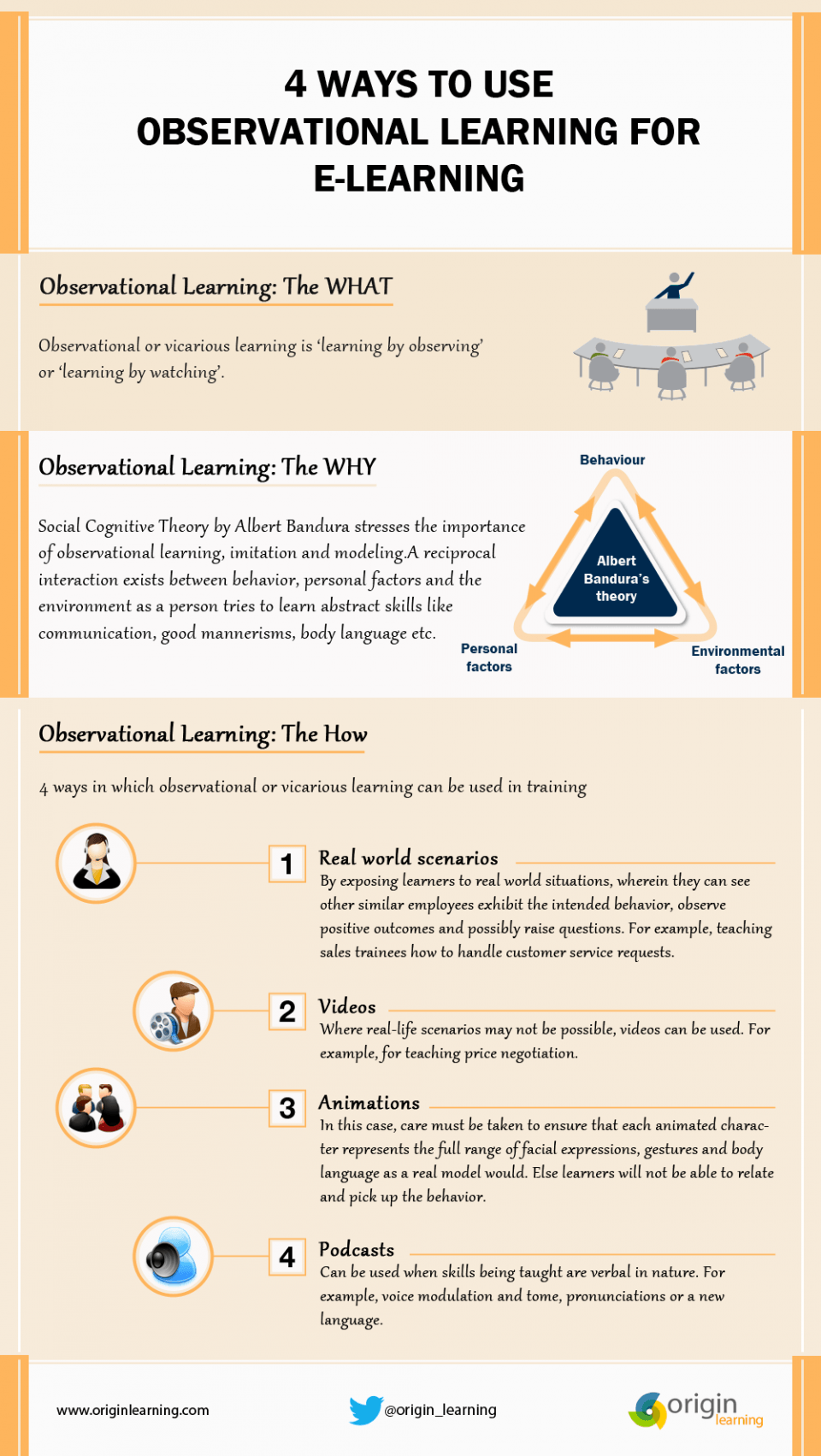
Observational learning, also known as social learning theory, was first proposed by psychologist Albert Bandura. It suggests that people can learn new behaviors, attitudes, and values by observing others. According to Bandura, this process occurs through four steps: attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation.
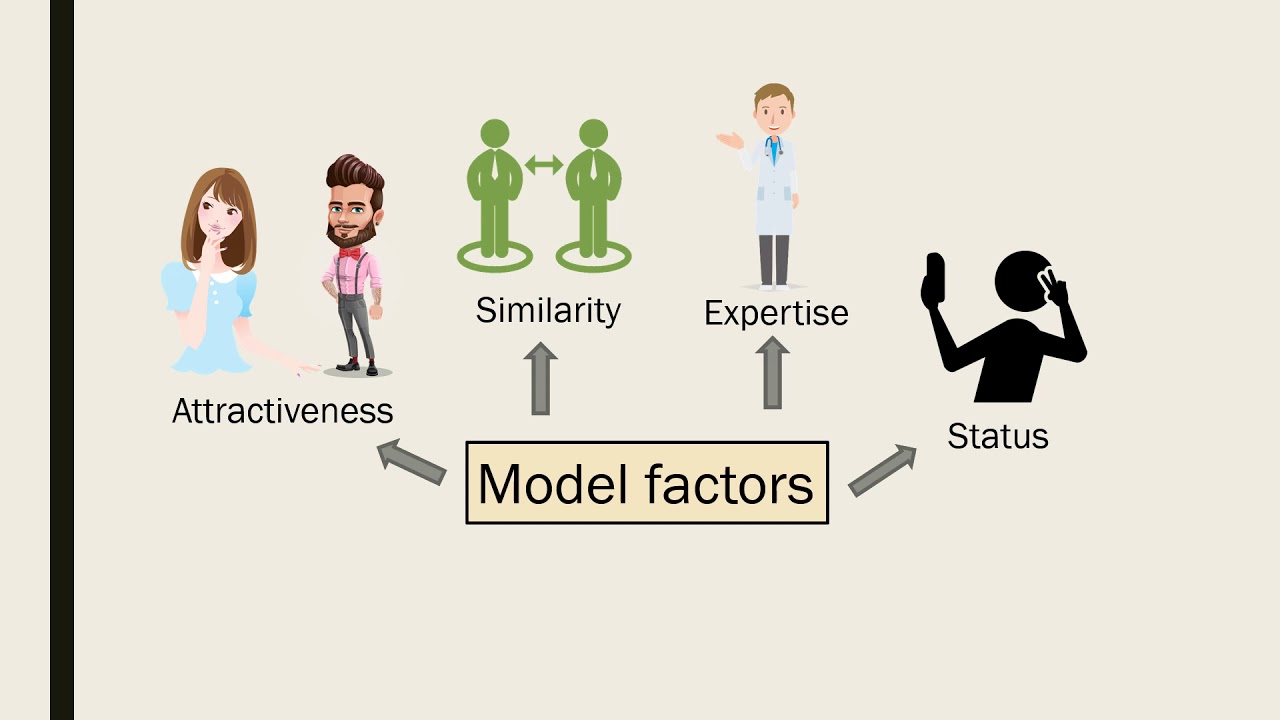
The first step in observational learning is attention. In order for learning to occur, the observer must pay attention to the behavior being demonstrated by the model. Factors that may influence attention include the perceived similarity of the model to the observer, the perceived consequences of the behavior, and the observer's level of personal interest in the behavior.
The second step is retention, or the ability to remember the observed behavior. This step involves the observer encoding and storing information about the observed behavior in their memory. The observer may also cognitively process this information in order to understand and make sense of it.
The third step is reproduction, or the ability to perform the behavior. In order for reproduction to occur, the observer must be able to physically perform the behavior. This may involve practicing and rehearsing the behavior in order to develop the necessary skills and muscle memory.
The final step is motivation, or the desire to perform the behavior. This step involves the observer deciding whether or not to perform the behavior based on their own personal values and beliefs.
Observational learning can have a powerful influence on an individual's behavior. For example, children who observe aggressive behavior in their parents or peers may be more likely to engage in aggressive behavior themselves. On the other hand, observing prosocial behavior (such as helping others) can lead an individual to engage in more prosocial behavior.
One important aspect of observational learning is the role of reinforcement. Reinforcement refers to any consequence that increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. If an observer sees a model being reinforced for a particular behavior, they may be more likely to perform that behavior in the future. This can be seen in the famous Bobo doll experiment conducted by Bandura, in which children who observed an adult being aggressive towards a Bobo doll were more likely to be aggressive towards the doll themselves when given the opportunity.
In conclusion, Bandura's theory of observational learning suggests that people can learn new behaviors, attitudes, and values by observing others. This process occurs through attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation, and can be influenced by reinforcement. This theory has important implications for understanding how social influences shape human behavior.
Albert Bandura: Observational Learning Theory

Now you are likely to engage the college community in productive discussions, and this may lead to personal satisfaction Bandura, 1997. Overall, continual exposure to violence on personal real-life accounts, or through the media, is related to increased aggression. Although competitions offer the potential for external reward, the individual might still set a personal standard for success, such as being satisfied only if they win at least one of the individual lifts. Economic and Social Research Council. Observers Must also retain, or remember, the behavior at a later time.
Bandura's Bobo Doll Experiment on Social Learning

For many children, unfortunately, the academic environment of school is a challenge. It was then that Claire knew she wanted to discipline her children in a different manner. When observers are unsure about a situation, they rely on cues to indicate what they perceive as evidence of past success by the model. If the student can solve the problem, no further action is needed; however, if the student struggles, a teacher may use one of four types of prompts — verbal, gestural, modeling, or physical — to assist the student. In cultures that admire youth, there may well be a tendency for the aged to lose their sense of self-efficacy and begin an inexorable decline toward death. Self-reinforcement works primarily through its motivational effects.
6.5 Observational Learning (Modeling)
Firing of these analogous neurons is prevalent in both primates and humans. Since many activities do not have absolute measures of success, the individual often sets their standards in relative ways. For example, Bandura notes that the labeling of psychological disorders, indeed the definition of what constitutes abnormal behavior, is made within a social context. Conclusively, frequent revelations of violent behavior may be imitated by certain individuals Swanson, 2015. Attention is therefore extremely important in whether a behavior influences others imitating it. First, the model laid the Bobo doll on its side, sat on it, and punched it in the nose.
Observational Learning: Albert Bandura's Social Learning...

Since all of these scenarios are based on beliefs and expectations, not on the unknown eventual outcome that will occur, it becomes clear that what we think about our ability to perform in various situations, as well as our actual expectations of the consequences of those actions, has both complex and profound effects on our motivation to engage in a particular behavior or course of action. Bandura 1973 mentions that these behaviors that continue into adulthood typically act as a coping response to stress or as a method of conflict resolution. These steps include attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation. Reinforcement can be external or internal and can be positive or negative. The aggressive models would punch Bobo, strike Bobo with a mallet, toss the doll in the air, and kick it around the room.