Bacillus cereus is a gram-positive, spore-forming bacterium that is widely found in the environment. It is commonly found in soil and has been isolated from a variety of sources, including plants, food, and water. One of the key characteristics of B. cereus is its ability to produce a variety of enzymes that allow it to break down complex molecules into simpler ones through the process of fermentation.
Fermentation is a metabolic process that occurs in the absence of oxygen, in which microorganisms such as B. cereus convert sugars and other organic compounds into acids, gases, or alcohols. In B. cereus, fermentation is a key mechanism for the production of various enzymes, including amylases, proteases, and lipases, which are essential for the breakdown of complex organic compounds.
B. cereus is capable of fermenting a wide range of sugars, including glucose, fructose, and maltose, as well as some non-sugar compounds, such as amino acids and certain fatty acids. The products of fermentation vary depending on the substrate being fermented and the conditions under which the fermentation takes place. For example, the fermentation of glucose by B. cereus produces lactic acid, while the fermentation of fructose produces acetic acid.
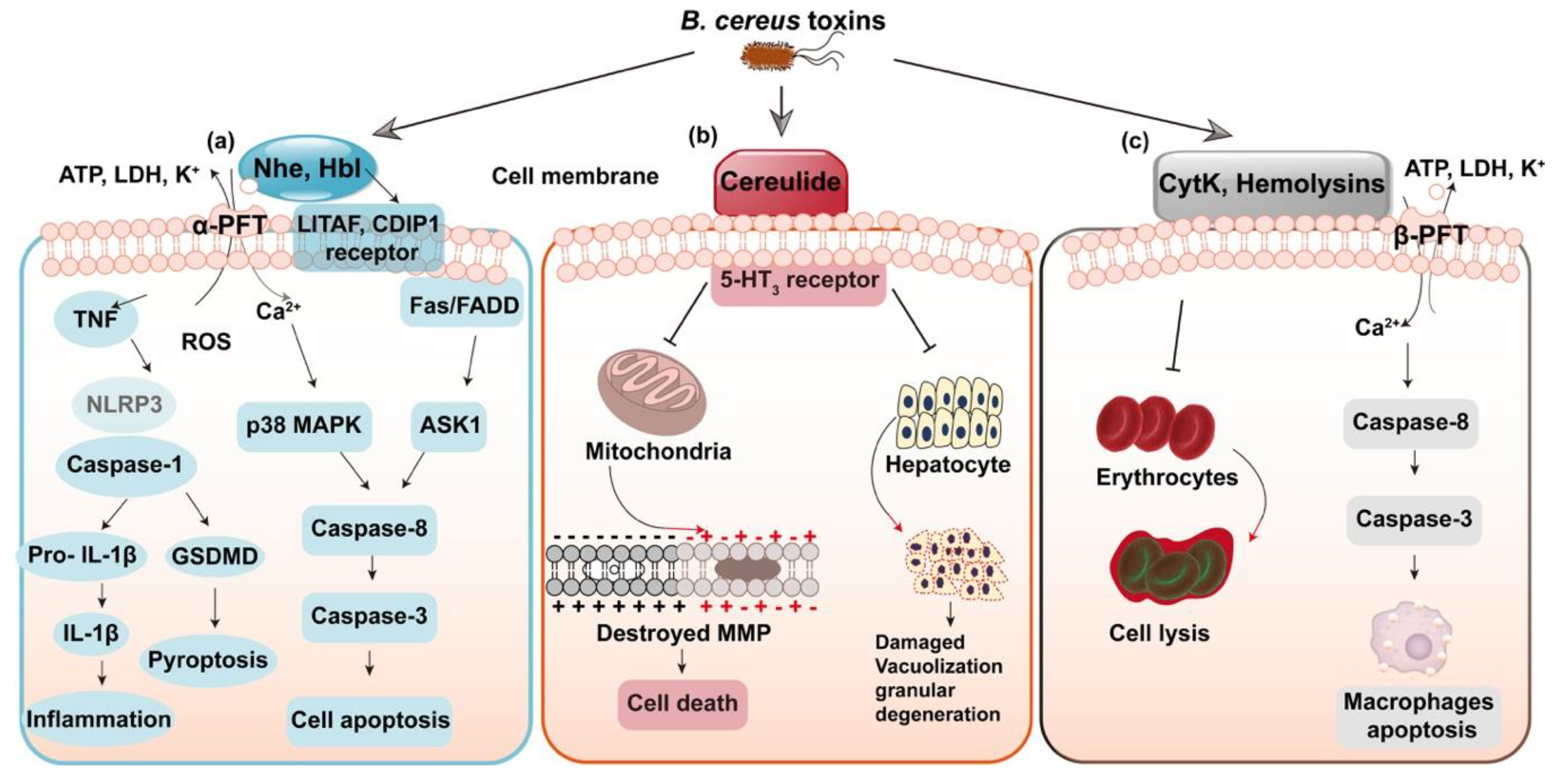
In addition to its ability to produce enzymes through fermentation, B. cereus is also capable of producing a number of toxins that can have harmful effects on humans. These toxins include cereulide, which is responsible for the emetic form of B. cereus food poisoning, and haemolysins, which can damage red blood cells and cause haemolytic anaemia.
Despite its potential to cause illness, B. cereus has also been used in a number of beneficial applications. For example, it has been used in the production of various fermented foods, such as soy sauce, miso, and tempeh, as well as in the production of antibiotics and enzymes for use in the food industry.
In conclusion, Bacillus cereus is a versatile bacterium that is capable of fermenting a wide range of sugars and other organic compounds through the production of various enzymes. While it is capable of producing toxins that can cause illness in humans, it has also been used in a number of beneficial applications, including the production of fermented foods and enzymes for use in the food industry.