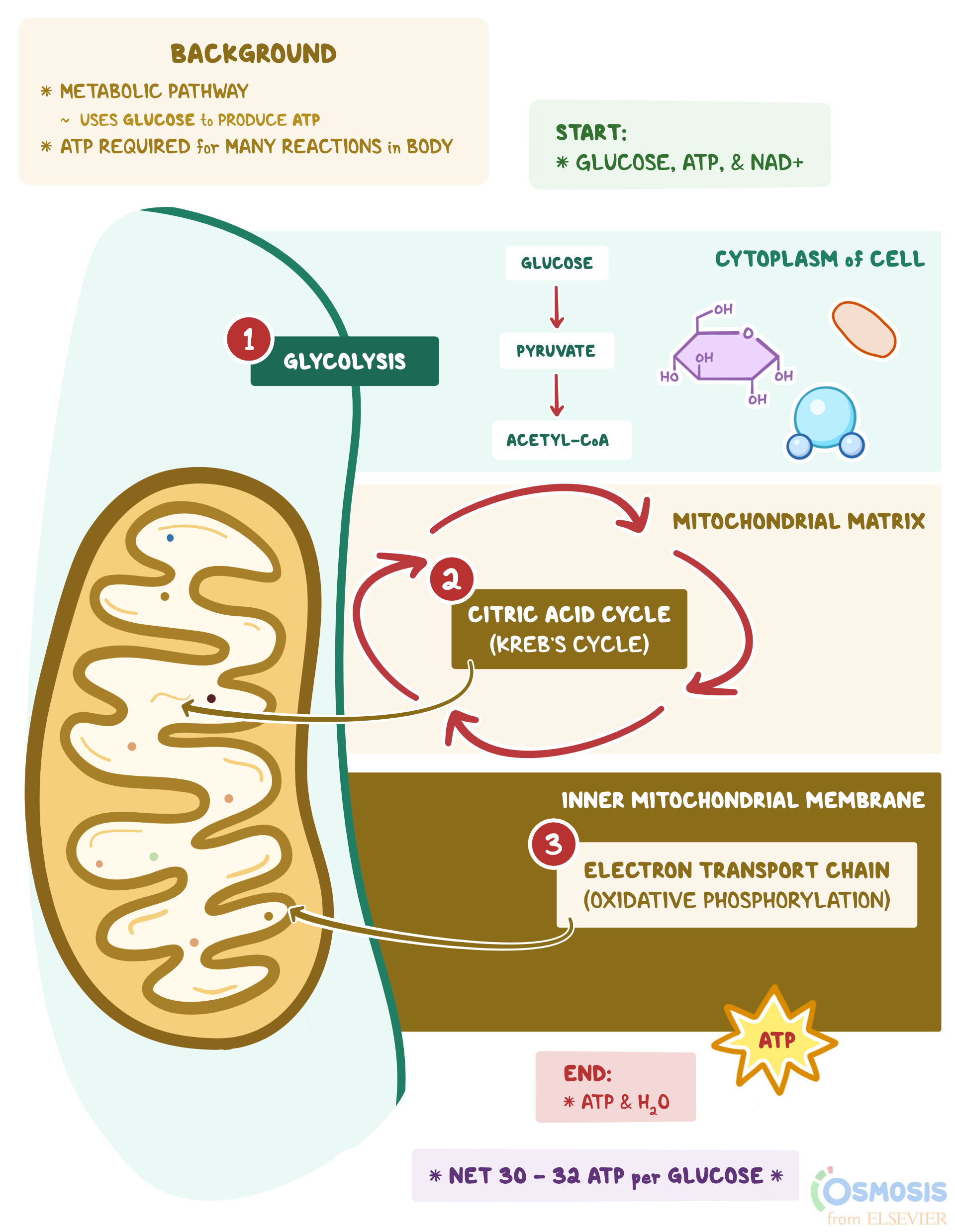
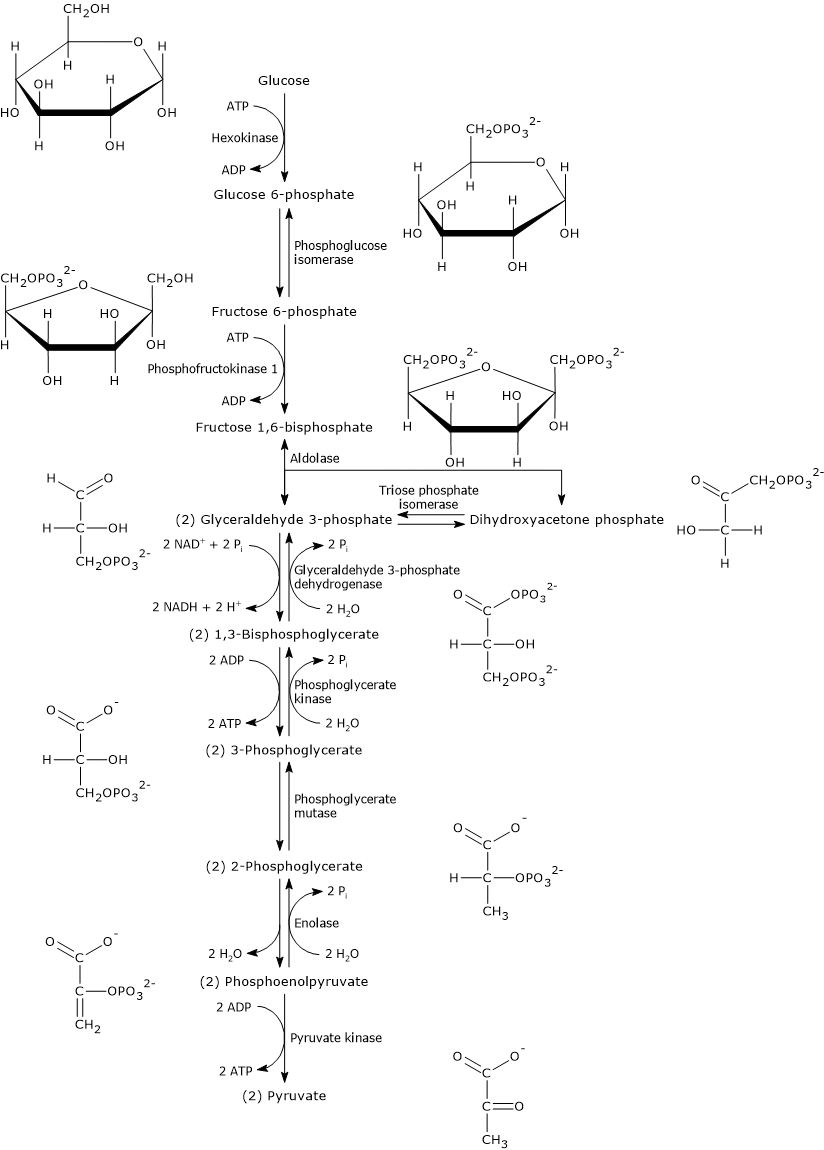
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytosol of cells and is responsible for the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. One of the primary functions of glycolysis is to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell. ATP is produced through a series of reactions that involve the transfer of electrons from glucose to oxygen, resulting in the release of energy that is used to synthesize ATP.
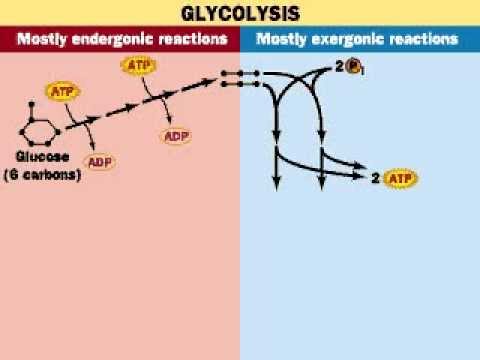
The first step of glycolysis is the conversion of glucose into glucose-6-phosphate through the action of the enzyme hexokinase. This reaction requires the input of ATP, but the end product, glucose-6-phosphate, is more reactive and can be further metabolized to generate ATP.
The next step in glycolysis involves the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate into fructose-6-phosphate through the action of the enzyme phosphoglucose isomerase. This reaction is reversible, meaning that it can occur in either direction depending on the needs of the cell.
The third step of glycolysis involves the cleavage of fructose-6-phosphate into two three-carbon molecules, dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, through the action of the enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. This reaction is also reversible and is regulated by the concentration of ATP in the cell.
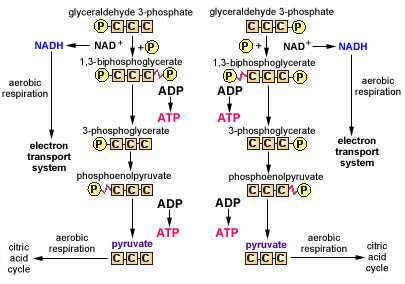
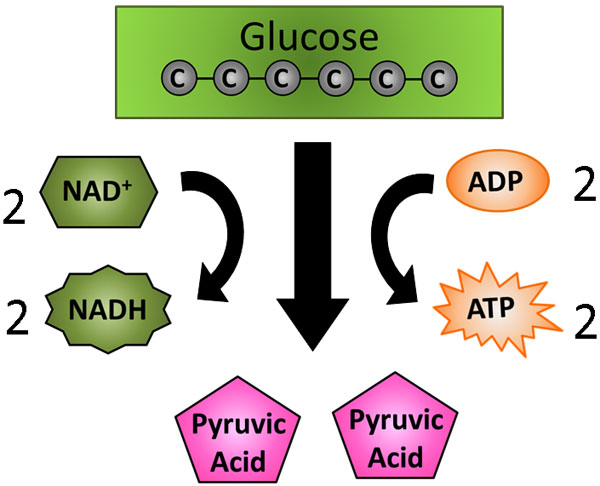
The fourth step of glycolysis involves the conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate into 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate through the action of the enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. This reaction releases NADH, a molecule that can be used to generate ATP through the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
The fifth step of glycolysis involves the conversion of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate into 3-phosphoglycerate through the action of the enzyme phosphoglycerate mutase. This reaction is not reversible and is not associated with the production of ATP.
The sixth step of glycolysis involves the conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate into 2-phosphoglycerate through the action of the enzyme enolase. This reaction is not reversible and is not associated with the production of ATP.
The seventh step of glycolysis involves the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate into phosphoenolpyruvate through the action of the enzyme pyruvate kinase. This reaction is not reversible and is the final step in the production of ATP during glycolysis. The end product of this reaction, phosphoenolpyruvate, can be further metabolized to produce additional ATP through the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
In summary, glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytosol of cells and is responsible for the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate. ATP is produced through a series of reactions that involve the transfer of electrons from glucose to oxygen, resulting in the release of energy that is used to synthesize ATP. The production of ATP during glycolysis is an important process that allows cells to generate the energy they need to function properly.