Asexual reproduction in euglena. How does Euglena reproduce sexually? 2022-10-16
Asexual reproduction in euglena
Rating:
6,9/10
1125
reviews
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction that occurs without the exchange of genetic material between two individuals. In the case of euglena, a unicellular organism belonging to the kingdom Protista, asexual reproduction is an important means of propagating the species.
Euglena undergoes a process called binary fission to reproduce asexually. During this process, the euglena cell undergoes cell division, resulting in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This process is initiated by the duplication of the euglena's DNA, followed by the separation of the cytoplasm and the cell organelles into the two daughter cells.
Binary fission is a relatively rapid process, allowing euglena to reproduce quickly and efficiently in environments that are favorable for growth. It also allows euglena to rapidly colonize new habitats, as a single cell can give rise to a large population in a short period of time.
While asexual reproduction is an effective means of reproduction for euglena, it does have its limitations. Because the offspring produced through asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent, there is little opportunity for genetic diversity within the population. This lack of diversity can make the population more susceptible to changes in the environment or to the emergence of diseases.
Despite these limitations, asexual reproduction plays an important role in the life cycle of euglena. It allows the organism to quickly and efficiently reproduce and colonize new habitats, ensuring the survival and continued existence of the species.
Reproduction

They grow and develop slowly and mostly by phototrophy. The cyst is secreted by the muciferous bodies lying below the pellicle. In this form, the Euglena rounds up into a ball and discards its flagellum. Meaning that we earn by showing ads and also through affiliate commissions on qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you. It is the process of becoming enclosed by a cyst.
Next
Anatomy and Reproduction of Euglena Cells
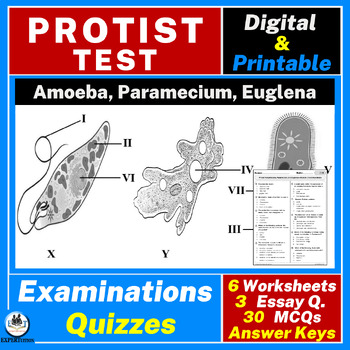
This is also called the Encystment of Euglena. The cyst is an extensive, thick, and mucilaginous coat covering the body of the Euglena. At this stage the euglena is non-motile and covered in mucilage. Since another individual of the species is not involved, binary fission is an asexual form of reproduction. In addition to photosynthetic euglenids, another major group of non-photosynthetic Euglena known as kinetoplastids are included in the Euglenozoa phylum. Why do Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes and Great Apes 24? Binary fission is a kind of asexual mode of reproduction. The main noticeable factor of the binary fission in Euglena is the production of two daughter cells from the parent cell in a perfectly symmetrical way.
Next
How does Euglena reproduce? (Reproduction in Euglena)

Euglena are single cellular which means they produce asexually. How is Euglena like a plant and animal? Some euglenoids also have an eyespot and a photoreceptor, which aid in the detection of light. Euglena have historically been classified by scientists in either the phylum Euglenozoa or the phylum Euglenophyta. We are also a verified publisher on various advertisement networks like Ezoic, and affiliate networks like Amazon Global Affiliate. Euglena live in a variety of aquatic habitats, both freshwater and marine.
Next
Reproduction/ Life Cycle

This can be due to the lack of food and oxygen, draught, and excessive heat, etc. Euglenids organized in the phylum Euglenophyta were grouped with Euglena do not have chloroplasts and the ones that do obtained them through endosymbiosis, some scientists contend that they should be placed taxonomically in the phylum Euglenozoa. For more information, it's suggested that you go through the. To reproduce sexually, it requires 2 parents. Euglena Reproduction In the free-swimming stage, Euglena reproduce rapidly by a type of asexual reproduction method known as binary fission. The flagellar process, the gullet and the stigma duplicate, followed by the forming of a cleavage. How do Euglena make their own food? Euglena viridis and Euglena gracilis are examples of Euglena that contain chloroplasts as do Euglena have no chloroplasts and must ingest food by phagocytosis.
Next
The mode of asexual reproduction of Euglena isA)\tTransverse binary fissionB)\tIrregular binary fissionC)\tMultiple fissionD)\tLongitudinal binary fission.

First the cell will go through the process of mitosis before it divides longitudinally starting at the front end of the cell. How many parents does Euglena need to reproduce? Metaphase Stage: In this stage, all the paired chromatids come to lie in a longitudinal plane. Under inactive conditions, Euglena stops its activities like movement from one place to another and protects itself by forming a coat around its body. Duplication of cell organelles: Organelles such as the reservoir, cytopharynx, cytosome, flagella, stigma, basal bodies, and contractile vacuole duplicates. Anaphase Stage: In this stage, the paired chromosomes separate and move towards their respective poles with mutual repulsion. While it has chloroplasts like a plant, the euglena lacks another characteristic of plants, a cellulose wall.
Next
How does Euglena reproduce sexually?
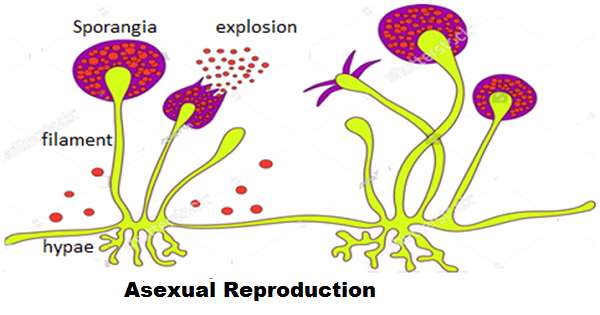
In the palmelloid stage, Euglena gather together discarding their flagella and become enveloped in a gelatinous, gummy substance. In reproductive, the walls become thinner to allow for cell division to occur. The process of fission to form two daughter cells The process of fission to form two form daughter cells in both binary and multiple fission processes include Mitosis Stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase and, later Karyokinesis and then Cytokinesis occurs. Prophase Stage: In this stage, all the nucleoli endosomes fuse together into a single nuclear body and each chromosome splits longitudinally into two daughter chromosomes or chromatids. This site does not constitute any kind of pet medical advice, so please consult a licensed veterinarian in your area for pet medical advice.
Next
The mode of asexual reproduction of Euglena is

Euglena chloroplasts have three-layered membranes, while plant chloroplasts only have two layers. The two halves then become equally separated Euglena, 2016 As Euglena live in mostly fresh, mineral latent water, they undergo asexual reproduction under many conditions. Karyokinesis: In this stage, the nuclear membrane fully deepens and finally separates the nucleus into two daughter nuclei. This can include when the fresh water lake gets too cold, or if there is a long period of time without sunlight. The Euglena reverts to this form when the conditions of their habitat are too harsh. These organisms engulf and feed on other unicellular organisms in their surroundings such as Euglenoid Protozoans. Several species produce resting cysts that can withstand drying.
Next
The mode of asexual reproduction in Euglena is
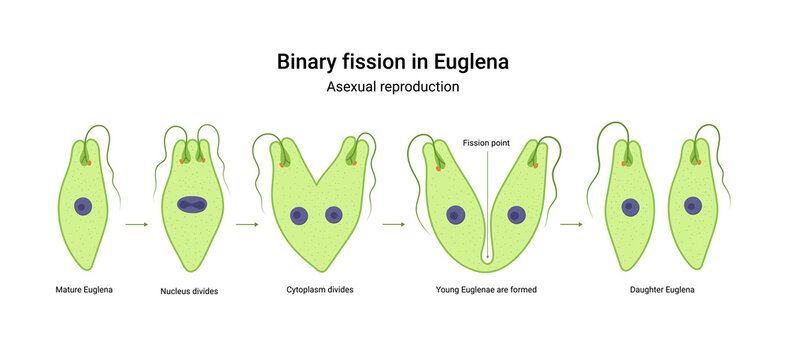
The following stages can be observed during binary fission. Euglinoids are part of the Euglinozoia phylum, which contains about 44 genera and more than 800 species. The encysted Euglena not only successfully withstands the adverse conditions of life, but also enjoys a far, and wide dispersal. Multiple Fission Multiple Fission Encystment in Euglena A- Encysted individual, B- Fission in encysted condition, C- Palmella stage Multiple Fission is usually performed under inactive conditions, that is when the favourable conditions of water, temperature, and food availability are not met. All content is therefore for informational purposes only for students, teachers, and curious learners out there.
Next
Euglena Reproduction

Daughter euglinoids As the daughter cells grow, the optimum number of various organelles is achieved. Individual euglenids form reproductive cysts in which binary fission occurs producing many 32 or more daughter cells. It is sometimes called a stigma. Due to these conflicting physical attributes, euglenoids necessitated the founding of the now-defunct Protista kingdom. Telophase Stage: In this stage, the nuclear membrane begins to constrict longitudinally and gets deepened. Then soon after encystment, the Euglena performs repeated longitudinal binary fission with mitosis and cytokinesis leading to the formation of several daughter individuals. Protective cyst formation is characteristic of the non-motile stage.
Next

Mitosis, or cell division, is the method used by plants and animals, and one most are familiar with. The euglenoid cell reproduces its organelles by mitosis and then splits longitudinally into two daughter cells. In the case of Euglena, the Longitudinal type of Binary Fission can be seen leading to the reproduction of symmetrical organisms. So it is the wrong option. This posed a problem for taxonomists at the time of its discovery, since the Protista kingdom had not been established at the time. Does the Euglena reproduce sexually or asexually? Euglena is a genus of protists, i.
Next








