Acidity and basicity are important properties of organic compounds that determine their behavior in chemical reactions and their reactivity with other compounds. Understanding the acidity and basicity of organic compounds can be useful in predicting and understanding the outcome of chemical reactions, as well as in the design of new materials and drugs.
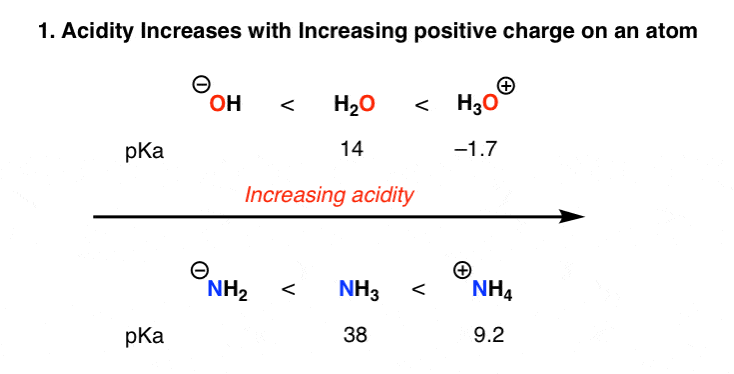
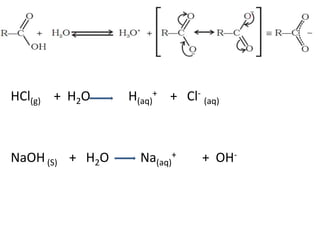
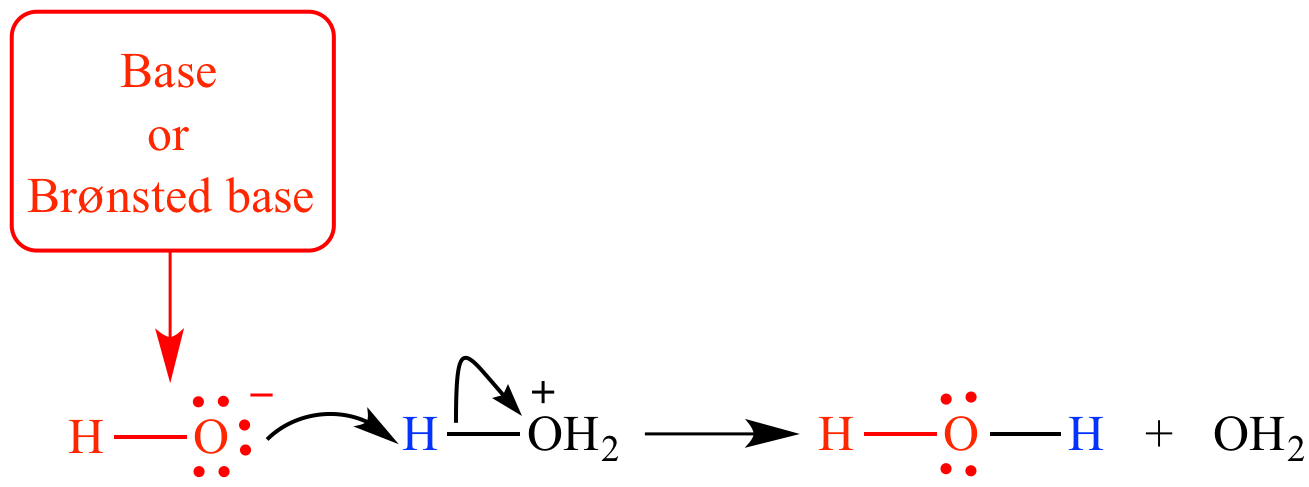
Acidity is a measure of the ability of a compound to donate protons, or hydrogen ions (H+), to a solution. Organic compounds that are acidic are called proton donors, or acids. The strength of an acid is determined by the ease with which it donates protons, and this is influenced by the stability of the resulting anion (the compound that is formed when the acid donates a proton).
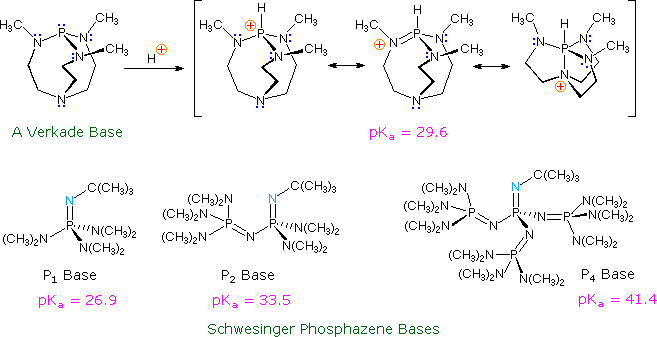
Basicity is a measure of the ability of a compound to accept protons, or hydrogen ions (H+), from a solution. Organic compounds that are basic are called proton acceptors, or bases. The strength of a base is determined by the ease with which it accepts protons, and this is influenced by the stability of the resulting cation (the compound that is formed when the base accepts a proton).
There are several different methods for measuring the acidity and basicity of organic compounds, including the pK a and pK b scales. The pK a scale is used to measure the acidity of an organic compound, while the pK b scale is used to measure its basicity. Both scales are logarithmic, with a lower pK a or pK b value indicating a stronger acid or base, respectively.
Organic compounds can be classified as either strong acids, weak acids, strong bases, or weak bases, depending on their acidity or basicity. Strong acids and bases are highly reactive and can completely dissociate into ions in aqueous solution, while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate.
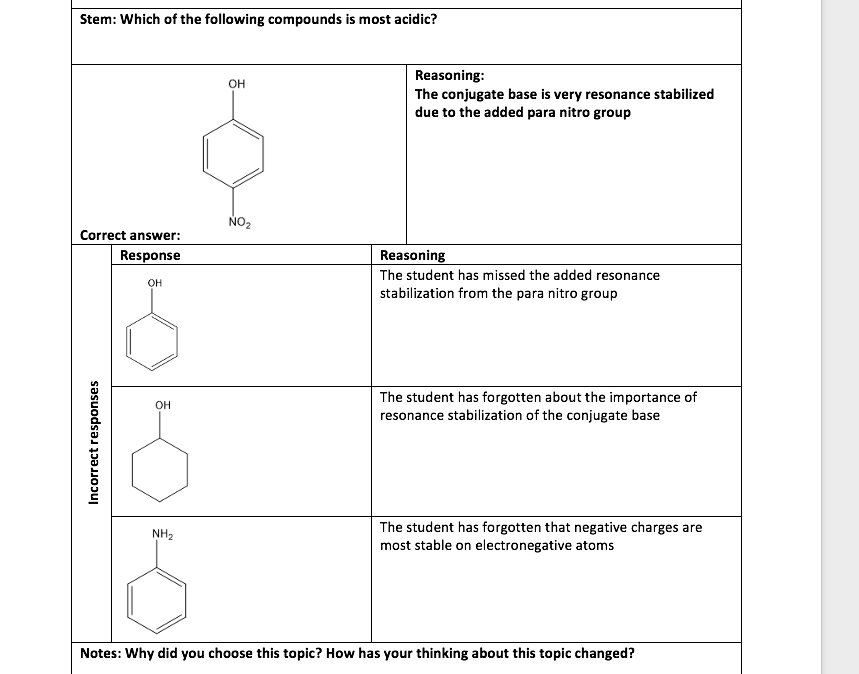
The acidity and basicity of organic compounds can be influenced by various factors, including the presence of functional groups, the size of the molecule, and the presence of conjugated systems. For example, compounds that contain functional groups such as carboxylic acids, amides, and amines tend to be acidic or basic, while compounds that do not contain these functional groups tend to be neutral. The size of the molecule can also influence acidity and basicity, with larger molecules tending to be less acidic or basic than smaller ones. The presence of conjugated systems, in which alternating double bonds and single bonds are present, can also influence acidity and basicity, as the electrons in these systems can be delocalized, resulting in an increase in reactivity.
In conclusion, acidity and basicity are important properties of organic compounds that determine their behavior in chemical reactions and their reactivity with other compounds. Understanding these properties can be useful in predicting and understanding the outcome of chemical reactions, as well as in the design of new materials and drugs.